A living organism is very complicated. Even the small cell of our body has its own complex structure, consisting of organelles and inclusions, which, like human organs, perform their functions. In this article, we describe one of the structural units of a cell. This is centriole.
What is centriole
In our cell there are specialized organelles and general purpose. The second type is the cell center, consisting of two centrioles and one centrosphere. Why is all this necessary to the cage? For the assembly of microtubules, which, having strength, provide support to the cytoskeleton and support active intracellular transport.
Thus, centriole is the organelle of a eukaryotic cell, which has a cylindrical shape and is responsible for the assembly of microtubules. It is a self-regulating structure that doubles in the cell center.
Centriole structure
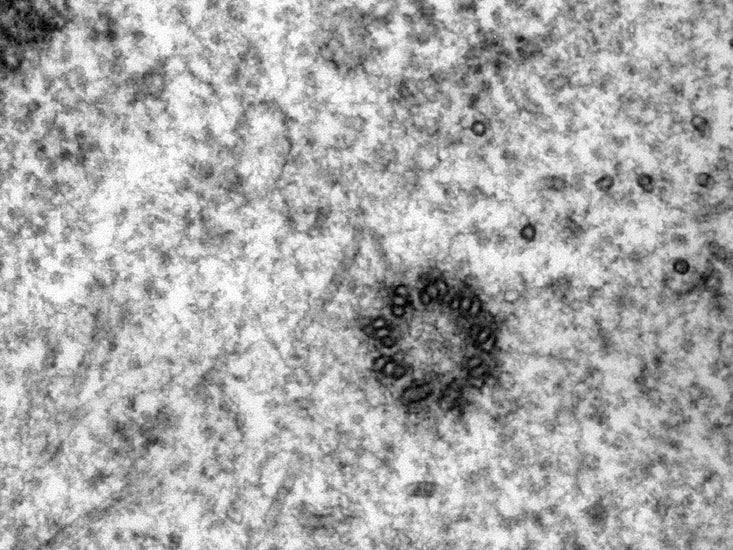
Each centriole is a cylinder, the wall of which consists of nine triplets, or complexes of three microtubules of the same length and diameter.
See the green tubes in the picture? This is a centriole, depicted in a simpler form, without internal components, with triplets.
Triplets are located at an angle of 50 ° to each other, the upper end is connected to an adjacent triplet, and the other to the center of the cylinder. So in the inner part a star shape and the likeness of a wheel with spokes are formed.
As we already know, the cell center has two centrioles. Relative to each other, they are located perpendicularly, that is, one of them (daughter) rests with its end against the side surface of the other (mother). The first arises by doubling the mother.
The latter can also be distinguished by the specific balls surrounding it. This is an electron-dense bezel consisting of satellites and tightly connected to the outside of each triplet. What are they for? And it is here that the microtubules are assembled. When this process is completed, they are sent to different parts of the cell to integrate into its cytoskeleton.
Centrioli Functions
So what do we already know? Centriol is an organoid of the cell center. From here you can guess about its functions:
- It is the assembly of microtubules. This is very important for a cell, which, like humans, needs support, and if this is provided by our skeleton with muscles, then the cell is a cytoskeleton, which consists of these very microtubules.
- She takes part in the formation of basal bodies of flagella and cilia. And this is the basis of the movement of the cell in air and the aquatic environment. Without it, even fertilizing an egg with a motile sperm would be impossible. This would deprive us of such a rich variety of species forms, and to some extent - the evolution of organisms. Cilia, in turn, help in removing dust.
- It plays an important role in the formation of the mitotic spindle of division, which, shortening, breaks doubled chromosomes for their subsequent despiralization and the formation of nuclear material of a new cell.
It is amazing how everything in the living world is interconnected: cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, and we are all made up of them. It turns out that even such a small organoid as centriole performs vital functions and plays a large role in the formation of the cell and its subsequent correct vital activity.