In the process of studying statics, which is one of the components of mechanics, the main role is given to axioms and basic concepts. Moreover, there are only five main axioms. Some of them are known from school physics lessons, as they are Newton's laws.
Mechanics definition
First you need to mention that statics is a subsection of mechanics. The latter should be described in more detail, since it is directly related to statics. At the same time, mechanics is a more general term that combines dynamics, kinematics and statics. All these subjects were studied in a school course in physics and are known to everyone. Even the statics included in the study of statics are based on Newton’s laws known from school . However, there were three of them, while the basic axioms of statics were five. Most of them relate to the rules of maintaining equilibrium and rectilinear uniform movement of a certain body or material point.
Mechanics is the science of the simplest way of moving matter - mechanical. The simplest movements are considered actions that are reduced to the movement in space and time of a physical object from one position to another.
What mechanics study
In theoretical mechanics, the general laws of motion are studied without taking into account the individual properties of the body, in addition to the properties of extension and gravity (this implies the properties of particles of matter to be mutually attracted or to have a certain weight).
Basic definitions include mechanical force. This term is called movement, in mechanical form transmitted from one body to another during interaction. According to numerous observations, it was determined that the force is considered a vector value, which is characterized by the direction and point of application.
By the method of construction, theoretical mechanics is similar to geometry: it is also based on definitions, axioms, and theorems. Moreover, the connection does not end with simple definitions. Most of the drawings related to mechanics in general and statics in particular contain geometric rules and laws.
Theoretical mechanics in this case includes three subsections: statics, kinematics and dynamics. In the first, methods of converting forces applied to an object and an absolutely solid body are studied, as well as the conditions for the emergence of equilibrium. In kinematics, a simple mechanical motion is considered that does not take into account the acting forces. In dynamics, the movements of a point, of a system or of a solid are studied, taking into account the acting forces.
Axioms of Statics
First you need to consider the basic concepts, axioms of statics, types of relationships and their reactions. Static refers to a state of equilibrium with forces that are applied to an absolutely solid body. Its tasks include two main points: 1 - the basic concepts and axioms of statics include the replacement of an additional system of forces that were applied to the body by another system equivalent to it. 2 - the conclusion of the general rules under which the body, under the influence of the applied forces, remains in a resting state or in the process of uniform forward rectilinear movement.
Objects in such systems are usually called the material point - the body, the size of which under the given conditions can be omitted. A set of points or bodies that are interconnected in any way is called a system. The forces of mutual influence between these bodies are called internal, and the forces that influence this system are called external.
The resultant force in a particular system is the force equivalent to the reduced system of forces. The components of this system are called component forces. The balancing force is equal in magnitude to the resultant, but is directed in the opposite direction.
In statics, when solving the problem of changing the system of forces affecting a solid body, or about the balance of forces, the geometric properties of the force vectors are used. From this, the definition of geometric statics becomes clear. Analytical statics based on the principle of permissible displacements will be described in dynamics.
Basic concepts and axioms of statics
The conditions for finding the body in equilibrium are derived from several basic laws that are used without additional evidence, but having confirmation in the form of experiments, are called the axioms of statics.
- Axiom I is called Newton's first law (axiom of inertia). Each body remains in a state of rest or uniform rectilinear movement until the moment when external forces act on this body, removing it from this state. This ability of the body is called inertia. This is one of the basic properties of matter.
- Axiom II - Newton's third law (axiom of interaction). When one body acts on another with a certain force, the second body together with the first will act on it with a certain force, which is equal in magnitude, opposite in direction.
- Axiom III - a condition for the balance of two forces. To obtain the equilibrium of a free body, which is under the influence of two forces, it is enough that these forces are identical in their modulus and opposite in direction. It is also connected with the next paragraph and is included in the basic concepts and axioms of statics, the equilibrium of the system of convergent forces.
- Axiom IV. The balance will not be disturbed if a balanced system of forces is applied or removed to a solid body.
- Axiom V - axiom of parallelogram of forces. The resultant of two intersecting forces is applied at the point of their intersection and is depicted by the diagonal of a parallelogram built on these forces.
Relations and their reactions
In theoretical mechanics, a material point, a system, and a solid can be given two definitions: free and not free. The differences between these words are that if the specified restrictions are not imposed on the movement of a point, body or system, then these objects will, by definition, be free. In the opposite situation, objects are usually called nonfree.
Physical circumstances leading to the restriction of freedom of these material objects are called bonds. In statics, there may be the simplest connections made by different rigid or flexible bodies. The strength of a link to a point, system, or body is called a link reaction.
Types of bonds and their reactions
In ordinary life, a bond can be represented by threads, laces, chains or ropes. In mechanics, weightless, flexible and inextensible connections are taken for this definition. Reactions, respectively, can be directed along a thread, a rope. In this case, there are connections whose lines of action cannot be determined immediately. As an example of basic concepts and axioms of statics You can bring a fixed cylindrical hinge.
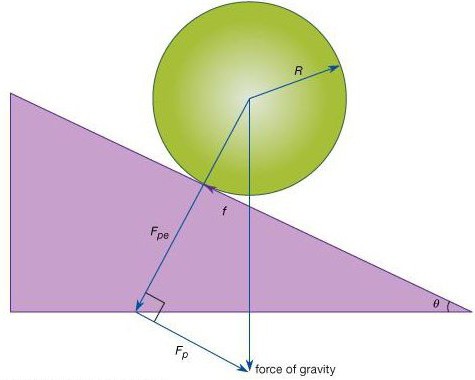
It includes a fixed cylindrical bolt, on which a sleeve with a cylindrical hole is put on, the diameter of which does not exceed the size of the bolt. When fastening the body to the sleeve, the first can only rotate along the axis of the hinge. In an ideal hinge (subject to neglecting the friction of the surface of the sleeve and bolt), a barrier appears to displace the sleeve in the direction perpendicular to the surface of the bolt and sleeve. In this regard, the reaction in an ideal hinge has a direction along the normal — the radius of the bolt. Under the influence of the acting forces, the sleeve is able to press against the bolt at an arbitrary point. In this regard, the direction of the reaction for a fixed cylindrical hinge cannot be determined in advance. From this reaction, only its location in a plane perpendicular to the hinge axis can be known.
During the solution of problems, the hinge reaction will be established by the analytical method by decomposing the vector. The basic concepts and axioms of statics include this method. The projection values of the reaction are calculated from the equilibrium equations. They also do this in other situations, including the inability to determine the direction of the communication reaction.
Converging Force System
Among the main definitions can include a system of forces that converge. The so-called system of converging forces will be called the system, the lines of action in which intersect at a single point. This system leads to a resultant or is in a state of equilibrium. This system is also taken into account in the axioms indicated above, since it is connected with maintaining the balance of the body, as indicated in several positions at once. The latter indicate both the reasons necessary for creating equilibrium and the factors that will not cause changes in this state. The resultant of this system, the converging force is equal to the vector sum of the named forces.
System balance
The system of convergent forces is also included in the basic concepts and axioms of statics in the study. To find the system in equilibrium, the mechanical value becomes the zero value of the resultant force. Since the vector sum of forces is zero, the polygon is considered closed.
In an analytical form, the equilibrium condition of the system will be as follows: a spatial system of convergent forces that is in equilibrium will have an algebraic sum of the projections of the force on each coordinate axis equal to zero. Since in this equilibrium situation the resultant will be zero, the projections on the coordinate axis will also be zero.
Moment of power
By this definition we mean the vector product of the vector of the point of application of forces. The vector of the moment of force is directed perpendicular to the plane in which the force and the point lie, in the direction from which the rotation from the action of the force is seen to occur counterclockwise.
Power pair
This definition refers to a system consisting of a pair of parallel forces of equal magnitude, directed in opposite directions and applied to the body.
The moment of a pair of forces can be considered positive if the forces of the pair are directed counterclockwise in the right-handed coordinate system, and negative - directed clockwise in the left coordinate system. When moving from the right coordinate system to the left, the orientation of the forces changes to the opposite. The minimum value of the distance among the lines of action of forces is called the shoulder. It follows from this that the moment of a pair of forces is a free vector modulo equal to M = Fh and having a direction perpendicular to the plane of action that from the top of this vector of forces were positively oriented.
Equilibrium in arbitrary systems of forces
The required equilibrium condition for an arbitrary spatial system of forces applied to a solid is considered to be the vanishing of the main vector and moment with respect to any point in space.
From this it follows that in order to achieve equilibrium of parallel forces located in one plane, it is necessary and sufficient that the sum of the projections of the forces on the parallel axis and the algebraic sum of all the component moments of the forces provided with respect to a random point is zero.
Body center of gravity
According to the law of universal gravitation, each particle located near the surface of the Earth is affected by gravitational forces called gravity. With small body sizes, in all technical applications, one can consider the gravity of individual body particles as a system of almost parallel forces. If we assume that all the forces of gravity of the particles are parallel, then their resultant will be numerically equal to the sum of the weights of all the particles, i.e., the weight of the body.
Kinematics subject
Kinematics is a section of theoretical mechanics that studies the mechanical motion of a point, a system of points, and a solid, regardless of the forces that affect them. Newton, based on a materialistic position, considered the nature of space and time to be objective. Newton used the definition of absolute space and time, but separated them from moving matter, so it can be called a metaphysician. Dialectical materialism considers space and time to be objective forms of the stay of matter. Space and time without matter cannot exist. Theoretical mechanics says that space, including moving bodies, is called three-dimensional Euclidean space.
Compared to theoretical mechanics, the theory of relativity is based on different ideas about space and time. This emergence of the new geometry created by Lobachevsky helped. Unlike Newton, Lobachevsky did not separate space and time from vision, considering the latter to be a change in the position of some bodies relative to others. In his own work, he indicated that in nature man only knows movement, without which sensory representation becomes impossible. From this it follows that all other concepts, for example, geometric, are created by the mind artificially.
It can be seen from this that space is considered as a manifestation of the connection between moving bodies. Almost a century before the advent of the theory of relativity, Lobachevsky indicated that Euclidean geometry is related to abstract geometrical systems, while in the physical world spatial relationships are determined by physical geometry, which differs from Euclidean in which the properties of time and space are combined with the properties of matter moving in space and time.
It does not hurt to notice that the leading scientists from Russia in the field of mechanics consciously adhered to the correct materialistic positions in the interpretation of all the main definitions of theoretical mechanics, in particular time and space. Moreover, the opinion of space and time in the theory of relativity is similar to the ideas of space and time of the supporters of Marxism, which were created before the emergence of works on the theory of relativity.
When working with theoretical mechanics during space measurement, the meter is taken as the main unit, and the second is taken as time. The time is the same in each reference system and is independent of the alternation of these systems with respect to each other. Time is indicated by a symbol and is considered as a continuous variable used as an argument. During the time measurement, the definitions of the period of time, time instant, initial time are applied, which is included in the basic concepts and axioms of statics.
Technical mechanics
In practical application, the basic concepts and axioms of statics and technical mechanics are interconnected. In technical mechanics, both the mechanical process of motion itself and the possibility of its use for practical purposes are studied. For example, when creating technical and building structures and checking their strength, which requires a brief knowledge of the basic concepts and axioms of statics. At the same time, such a brief study is suitable only for lovers. In specialized educational institutions, this topic is of considerable importance, for example, in the case of a system of forces, basic concepts and axioms of statics.
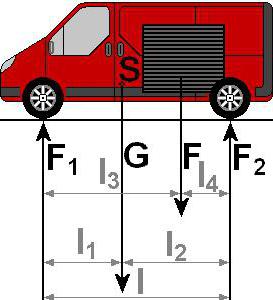
In technical mechanics, the above axioms are also used. For example, axiom 1, the basic concepts and axioms of statics are associated with this section. Despite the fact that the very first axiom explains the principle of maintaining equilibrium. In technical mechanics, an important role is assigned not only to the creation of devices, but also to stable structures, in the construction of which stability and strength are the main criteria. However, creating something like this without knowledge of the basic axioms will be impossible.
General remarks
The most simple forms of movement of solids include translational and rotational motion of the body. In the kinematics of solids with different types of movements, the kinematic characteristics of the movement of its different points are taken into account. The rotational motion of a body around a fixed point refers to such a movement in which a straight line passing through a pair of arbitrary points during the motion of the body is maintained at rest. This straight line is called the axis of rotation of the bodies.
The text above briefly summarized the basic concepts and axioms of statics. At the same time, there is a large amount of third-party information with which you can better know the statics. , , , .
. , , . , , . , . . , , , . .