Printed circuit boards are the construction base without which today no complex radio or electronic device in microprocessor technology can do. The manufacture of this framework involves the use of special raw materials, as well as technologies for the formation of the design of the carrier plate. One of the most effective methods of structural molding in relation to printed circuit boards is wave soldering, which allows automating assembly processes in the conditions of mixed mounting of solder.
Preparatory Activities
The initial stage, during which two tasks are solved - the choice of the component base and the list of necessary consumables for the operation, as well as equipment setup. As part of the first task, in particular, the basis for the board is prepared, its dimensions are fixed and the contours of soldered joints are outlined. Of the consumables, wave soldering requires the use of special agents to reduce the future formation of oxides. In addition, modifiers of the technical properties of the structure can be used if it is planned to be used in aggressive environments.
Equipment for this operation, as a rule, is a compact but multi-functional machine. The capabilities of a typical installation for wave soldering are designed to service single-layer or multi-layer boards with a working range of about 200 mm in width. As for the settings of this unit, first of all, the dynamic characteristics and waveform are set. The main part of these parameters is controlled through the nozzle of the wave feed, in particular, which allows the flow to be specified in Z- and T-shapes. Depending on the requirements for the printing unit, speed indicators with the direction of the wave are also assigned.
Work Fluxing
As in welding processes, when performing soldering, flux plays the role of a cleaner and a stimulator of the formation of high-quality compounds. Powder and liquid fluxes are used, but in both cases their main function is to prevent metal oxidation processes before the start of the brazing reaction, otherwise the solder will not bind the joint surface. The application of liquid flux is carried out using a spray or foaming agent. At the time of laying, the mixture should be diluted with the necessary activators, rosin and soft acids, which will improve the reaction. Foam solutions are applied using tubular filters, forming a fine bubble foam. In the process of wave soldering with metallization, such coatings improve wetting and stimulate the action of modifiers. Usually, both liquid and solid fluxes provide for separate washing or stripping operations of excess material. But there is also a category of indelible active substances that are fully included in the structure of the soldering material and do not require any further stripping.
Preheating
At this stage, the printed circuit board is preparing for direct contact with the solder. The tasks of heating are to reduce thermal shock and remove residual solvents and other unnecessary substances that remain after fluxing. The equipment for this operation is included in the infrastructure of the wave soldering installation and is a convection, infrared or quartz heater. The operator is only required to correctly set the temperature regime. So, if the work is carried out with a single-layer board, then the heating temperature can vary between 80 - 90 ° C, and if we are talking about multilayer (from four levels) workpieces, then the thermal effect can fit into the framework of 110-130 ° C. With a large number of through metallized holes, especially when working with multilayer boards, thorough intermittent heating should be provided at a temperature increase rate of up to 2 ° C / s.
Soldering
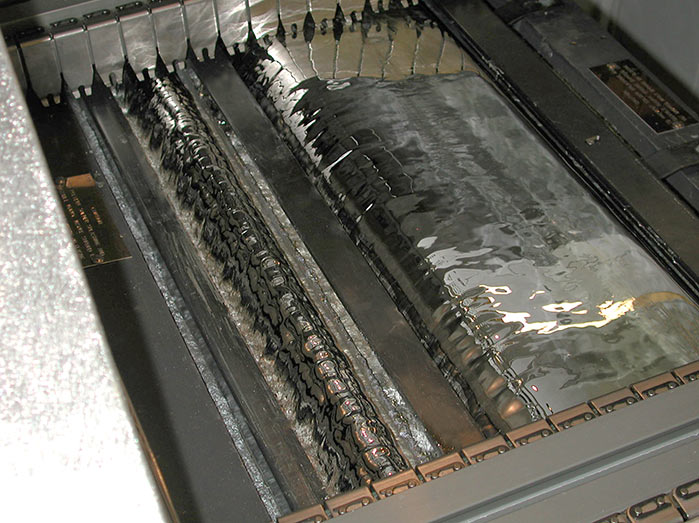
The temperature regime when performing solder is set in the range from 240 to 260 ° C on average. It is important to comply with the optimal level of thermal impact for a particular workpiece, since a decrease in the degree can lead to the formation of non-solders, and an excess to structural deformation of the functional coating of the board. The time of the contact operation itself lasts from 2 to 4 seconds, and the height of the solder during wave soldering is calculated individually, taking into account the thickness of the board. For example, for single-layer structures, the solder should cover approximately 1/3 of the thickness of the structure. In the case of multilayer workpieces, the immersion depth is 3/4 of the board thickness. The process is implemented as follows: with the help of the compressor of the soldering unit in the bath with molten solder, a wave flow is formed along which the board with the elements placed on it moves. At the moment of contact of the bottom of the board with solder, the formation of soldered joints occurs. Some modifications of the plants provide for the possibility of changing the inclination of the carrier conveyor within 5–9 °, which makes it possible to choose the optimal angle for the solder to drain.
Cooling conditions
It is not necessary to use special means for intensive cooling. Moreover, natural cooling is more beneficial from the point of view of acquiring a normal structural state of the workpiece. Another thing is that after wave soldering is completed, thermomechanical stress should be avoided, which may be caused by a difference in the linear expansion of the material of the processed heated components and the main components of the board.
Conclusion
The method of wave thermal soldering is characterized by many advantages from reducing the risk of deformation processes to the low cost of the operation. By the way, to complete the procedure in a full cycle requires minimal organizational labor compared to alternative methods. At the same time, progress does not stand still and today various modifications of the technology appear. In particular, soldering with a double wave of solder allows you to segment the functions of flows, improving the quality of the joints on the contact coating. The second wave is endowed with an exclusively cleansing function, within the framework of which excess flux and solder bridges are more effectively eliminated. Of course, in this case, it can not do without complicating the equipment. Installations are supplemented by pumps, nozzles and control units for each wave separately.