The formation of a eukaryotic cell became the second most important (after the appearance of life itself) evolutionary event. The main and fundamental difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotic organisms is the presence of a more advanced genome system. Due to the appearance and development of the cell nucleus, the degree of adaptability of unicellular organisms to regularly changing conditions of existence and the ability to quickly adapt without making significant hereditary changes in the gene system has increased dramatically.
The eukaryotic cell, the cytoplasm of which is the region of active metabolic processes, safely separated from the storage area, reading and reduction of genetic information, was able to further biological evolution. This epoch-making and fateful evolutionary event, according to scientists, occurred no later than 2.6 billion years ago at the junction of two geological milestones - Archean and Proterozoic.

The growth of adaptability and stability of biological structures is an indispensable condition for full-fledged biological evolution. Due to its high ability to adapt, the eukaryotic cell was able to evolve to multicellular organisms with complex structural organization. Indeed, in multicellular biological systems, cells with the same genome, adapting to changing conditions, form completely different tissues, both in their morphological properties and in functionality. This is the great evolutionary victory of eukaryotes, which caused the emergence of such a grandiose variety of life forms on the planet and entry into the evolutionary arena of man himself.
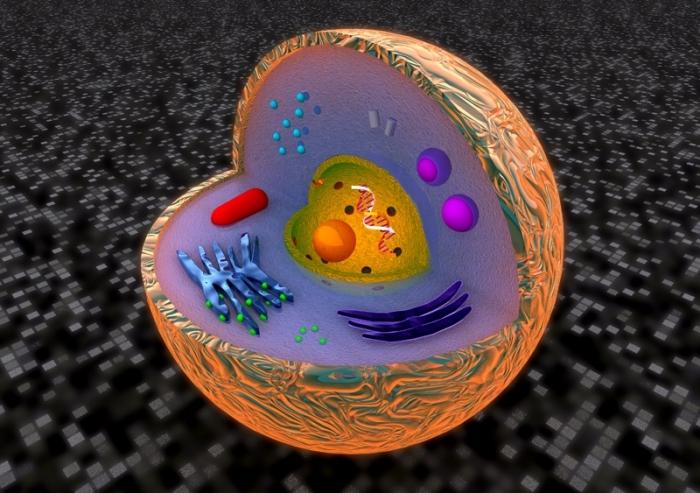
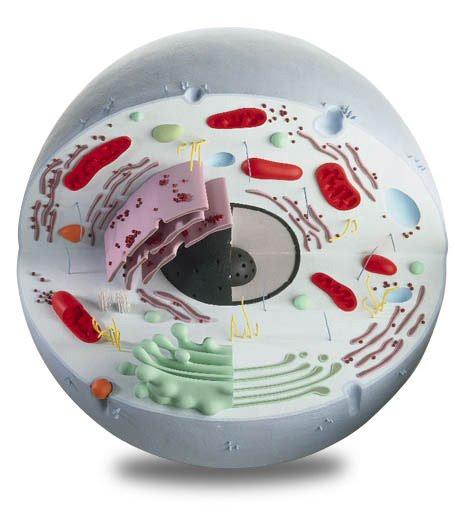
The structure of eukaryotic cells has several characteristic features not characteristic of prokaryotes. A eukaryotic cell contains a large amount of genetic material (90%), which is concentrated in chromosomal structures, which ensures their differentiation and specialization. Any eukaryotic cell is characterized by the presence of a separate nucleus. This is the main distinguishing feature of this type of cell. Another important difference from prokaryotes is the eukaryotic cell organoids - constant and diverse intracellular structures.
A eukaryotic cell, in comparison with a prokaryotic cell, has a more complex multistage system for perceiving a variety of substances. In nature, there is no typical universal eukaryotic cell type. All of them are characterized by incredible diversity, which is due precisely to the need for evolutionary adaptation. A very important feature of eukaryotes is their inherent compartmentalization - the localization of all biochemical processes in individual cell compartments separated by an intracellular membrane. Eukaryotes have a number of complex structural components. Such as a membrane system; cytoplasmic matrix, which is the main intracellular substance; cellular organelles are the main functional components of eukaryotes.