The twentieth century is a century of unremitting wars, civil and world, a time of rapid processes and changes, a century of grandiose achievements, but at the same time terrifying events. This century brought a lot of bloody and cruel battles, including sea ones. The battle of Skagerrak, the battle of La Plata, the battle of Tsushima and the defense of Port Arthur, the battle in Leyte Bay, the battle of Midway - it seems that this list can be continued endlessly, like the list of warships created at that time.
How it all started
At the beginning of the 20th century, the number of military clashes between world powers increased exponentially, and this, in turn, led to the fact that the quality of their weapons and the number of their military equipment also grew inexorably, in particular, there was an active improvement in the construction of warships. The turning point in the development of military proceedings was the creation of battleships.
What is a battleship?
The battleship (short for the phrase “battleship”) is a class of military armored ships equipped with heavy artillery pieces. The length of these vessels varied from 150 to 280 meters, and their displacement reached 70 tons. Created to destroy and destroy enemy ships, battleships were direct evolutionary followers of armadillos. The progenitor of the class of battleships was the English ship Dreadnought, which was born in 1906. The Dreadnought had a steam turbine power plant, which provided him at that time with a tremendous speed of 21 knots (translating nodes into kilometers, we can say that its speed then reached 39 km / h). The construction of the Dreadnought and the use of its advantages in the open sea have significantly changed the situation in the race of naval arms and in the field of shipbuilding in general. So after the British, one after another, countries began to create battleships with single-caliber guns and upgrade them, wanting to overtake their rivals. Ships of this type received the name of their ancestor - "dreadnoughts", and more advanced versions - "superdreadnoughts" and "superdreadnought".
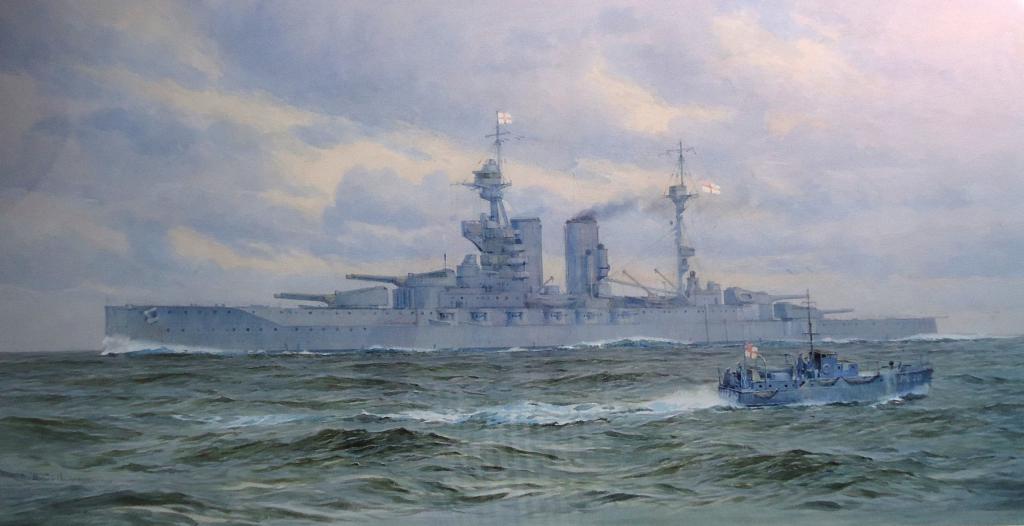

History of the Queen Elizabeth Series
The next step in the development of world and military shipbuilding was the creation by the British of linear ships of the Queen Elizabeth class. Five superdreadnoughts were designed and presented in this series: Malaya, Veliant, Barham, Warspite and the lead ship Queen Elizabeth, named, like the series itself, in honor of the Queen of England, Queen of the Seas, Elizabeth I. These vessels owe their appearance to Winston Churchill, who, being the first Lord of the Admiralty, with his characteristic fervor and ideas, insisted on a different design for these battleships and on their significant modifications, ordering to supply these ships with super-heavy combat guns. According to rumors, the United States, Germany and Japan have already actively improved their ships, ahead of the Royal Navy of the UK a few steps forward. There was no time for thorough weapons tests, so Sir Winston Churchill had no choice but to take the risk and, taking responsibility, lay down a series of ships without waiting for the verification and testing of the guns. Fortunately, the risk was justified. On average, the construction of such battleships took 1,960,000 pounds.
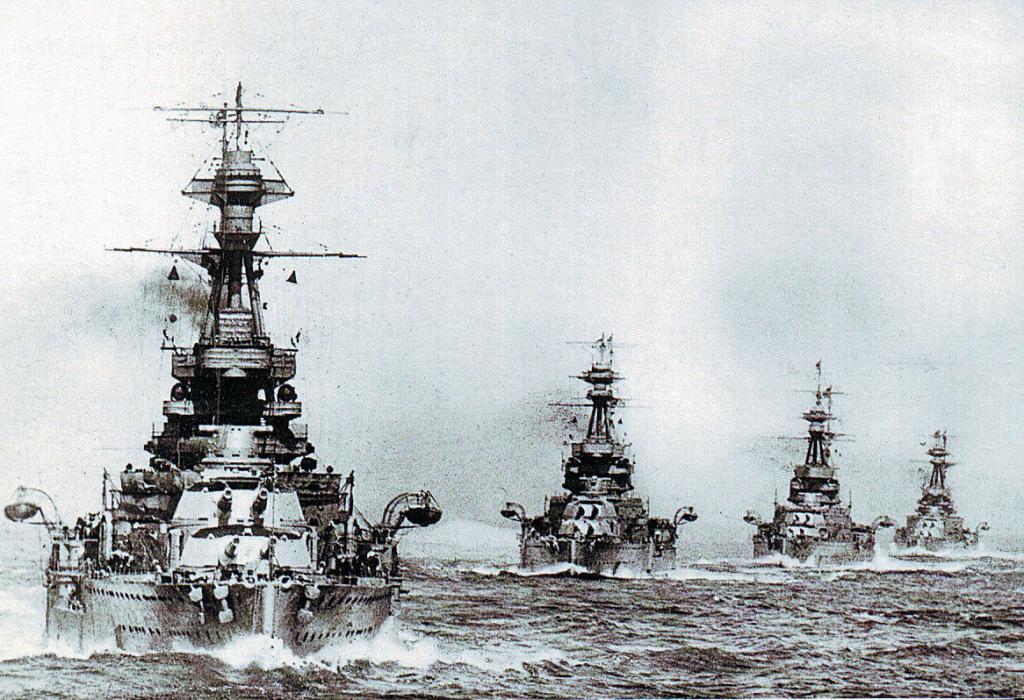
Series Features
The battleship “Queen Elizabeth” and similar ships, as mentioned earlier, differed from their predecessors and had a number of features. First of all, these battleships had guns with a 15-inch caliber - tremendous power at the time. Secondly, the superdreadnoughts of this series were the first large oil-powered ships, previously battleships of this size worked only for a couple. Thirdly, the speed of the Queen Elizabeth class battleships reached 24 knots (if you translate the knots into kilometers per hour, it will be clear that the speed of such ships reached 45 km / h). In addition, these ships had the highest metacentric height in the entire British fleet, this perfectly ensured their stability, helped withstand shock waves and strong gusts of winds.
Battleship "Queen Elizabeth": characteristics and description
The lead ship of the series was laid down at the Portsmouth military shipyard on October 12, 1912. Built in the shortest possible time, it was launched in October of the thirteenth year and later was completed afloat. The outbreak of World War I also contributed to the accelerated completion of the ship, so it is not surprising that at the beginning of 1915 the battleship was already included in the British Navy.
The length of the Queen Elizabeth battleship is 183.41 m, the width is 27.6 m, and the standard displacement is 29,200 tons. Booking this ship is almost the same as its predecessor, Iron Duke, with the exception of some elements, for example, the layer of metal armor along the waterline was increased, and along the main deck, on the contrary, weakened. Armament of a super dreadnought: 8 sea guns (381 mm), 16 anti-mine installations (152 mm), 2 anti-aircraft guns (76 mm), 4 underwater single-tube torpedo tubes (533 mm). For Queen Elizabeth, Parsons turbines and 24 Babcock and Wilcox boilers were used. Thus, the power of this battleship reached 75,000 horsepower.
The fate of the battleship
In 1915, the Queen Elizabeth battleship was sent to the Dardanelles to support the landing during the Gallipoli battle, during this mission the British battleship sank the Turkish transport in the shallow Bay of Nagara from the third salvo. Despite the high speed and super-heavy guns, the lead ship could not participate in the largest battle of the First World War - the Battle of Jutland, but in 1917 it became the flagship of Admiral David Beatty, commander of the Grand Fleet.
The Second World War caught the battleship Queen Elizabeth at the time of modernization. Until 1941, the ship Queen Elizabeth served in the British Home Fleet. But in December of the forty-first year, at the anchorage in Alexandria, the battleship was heavily damaged by Italian military swimmers with the help of magnetic mines, which led to the formation of a large hole and the flooding of many compartments. After repair, the battleship was sent to the Indian Ocean and from the beginning of 1944 became the flagship of the Eastern Fleet, having made several raids on the islands of Indonesia and Malaysia. In July, the forty-fifth battleship Queen Elizabeth made his last military campaign, went into reserve in August of that year and was sold for scrap a couple of years after that.