Powering electronic circuits for various purposes requires a constant voltage source. In a normal household network, the current is alternating, its frequency in most cases is 50 Hz. The shape of the graph of the voltage magnitude is a sinusoid with a period of 0.02 seconds, while one half period it is positive relative to the neutral, the second negative. To solve the problem of converting it to a constant value, AC rectifiers are used. They come in different designs, and their designs may vary.
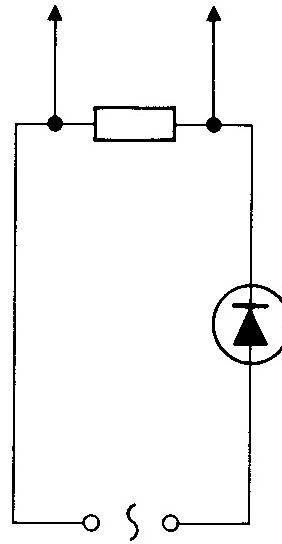
In order to understand how the simplest half-wave rectifier works, you first need to understand the nature of electrical conductivity. The current is the directed motion of charged particles, which can have opposite polarity, conditionally divide them into electrons and holes, otherwise - donors and acceptors having conductivities of "n" and "p" types, respectively. If a material with n-conductivity is connected to another, p-type, then a so-called pn junction is formed at their boundary, restricting the movement of charged particles in one direction. This discovery allowed the use of semiconductor technology, replacing it with most tube electronics.
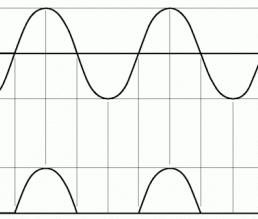
A half-wave rectifier basically contains a diode, a device with one pn junction. The alternating voltage supplied to the input of the circuit, the output contains only half of it, one that corresponds to the direction of inclusion of the rectifier diode. The second part of the period, which has the opposite direction, simply does not pass and is "cut off".
The diagram shows a single-phase rectifier, most often used in simple home devices and intended for domestic purposes. In industrial conditions, a three-phase network is often used , therefore, AC to DC conversion circuits can be more complicated. In addition, as a rule, fuses and filters are included in the circuit. At the input of the circuit, a step-down transformer or other AC voltage source can be turned on. Rectifier diodes differ in their parameters, the main of which is the amount of current for which the diode is designed.

A half-wave rectifier has a significant drawback compared to a half-wave rectifier. The voltage after rectification is not literally constant, it pulsates from the maximum value to zero in the semi-sinus shape of the graph and has a zero value in the interval between pulses. This irregularity of supply is usually compensated by the inclusion of a smoothing capacitor of a rather large value (sometimes measured in thousands of microfarads), designed for a voltage not less than that arises at the output of the circuit, usually with a margin. This measure also does not provide perfect evenness of the graph, but the deviations from the set value are significantly reduced, which makes it possible to use a half-wave rectifier to power simple circuits that do not require high voltage stability.
In more complex cases, two-half-wave rectification schemes with subsequent stabilization are used.