As early as the beginning of the 20th century, the theory of relativity was formulated. Today, every schoolchild knows what it is and who its creator is. It is so fascinating that even people far from science are interested in it. This article describes the theory of relativity in an accessible language: what it is, what its postulates and application are.
They say that to Albert Einstein, its creator, insight came in an instant. The scientist seemed to be riding a tram along the Swiss Bern. He looked at the street clock and suddenly realized that this clock would stop if the tram accelerates to the speed of light. In this case, there would be no time. Time in the theory of relativity plays a very important role. One of the postulates formulated by Einstein is that different observers perceive reality in different ways. This applies in particular to time and distance.
Observer position
On that day, Albert realized that, in the language of science, the description of any physical phenomenon or event depends on what reference frame the observer is in. For example, if a passenger of a tram drops his glasses, they will fall vertically down in relation to it. If you look from the position of a pedestrian standing on the street, then the path of their fall will correspond to a parabola, as the tram moves and points fall at the same time. Thus, each has its own reference system. We propose to consider in more detail the main postulates of the theory of relativity.
The law of distributed motion and the principle of relativity
Despite the fact that when the reference systems change, the descriptions of events change, there are universal things that remain unchanged. In order to understand this, one must ask not the fall of the glasses, but the law of nature that causes this fall. For any observer, regardless of whether he is in a moving or stationary coordinate system, the answer to it remains unchanged. This law is called the law of distributed motion. It acts equally both in the tram and on the street. In other words, if the description of events always depends on who observes them, then this does not apply to the laws of nature. They are, as is commonly expressed in a scientific language, invariant. This is the principle of relativity.
Two Einstein Theories
This principle, like any other hypothesis, had to be checked first, correlating it with the natural phenomena acting in our reality. Einstein deduced 2 theories from the principle of relativity. Although they are related, they are considered separate.
The particular, or special, theory of relativity (SRT) is based on the proposition that for all kinds of reference systems whose speed is constant, the laws of nature remain the same. General Relativity Theory (GTR) extends this principle to any reference frame, including those moving with acceleration. In 1905, A. Einstein published the first theory. The second, more complex in terms of mathematical apparatus, completed by 1916. The creation of the theory of relativity, both STR and GR, became an important stage in the development of physics. Let us dwell on each of them.
Special theory of relativity
What is it, what is its essence? Let's answer this question. It is this theory that predicts many paradoxical effects that contradict our intuitive ideas about how the world works. We are talking about those effects that are observed when the speed of movement approaches the speed of light. The most famous among them is the effect of time dilation (clock progress). A watch that moves relative to the observer is slower for him than the one in his hands.

In the coordinate system, when moving at a speed close to the speed of light, time stretches relative to the observer, and the length of the objects (spatial extent), on the contrary, is compressed along the axis of this movement. Scientists call this effect the reduction of Lorentz-Fitzgerald. As early as 1889, he was described by George Fitzgerald, an Italian physicist. And in 1892, Hendrik Lorenz, a Dutchman, supplemented it. This effect explains the negative result that the Michelson-Morley experiment gives, in which the speed of our planet in outer space is determined by measuring the "ether wind". These are the main postulates of the theory of relativity (special). Einstein supplemented these equations with a mass transformation formula made by analogy. According to her, as the speed of the body approaches the speed of light, the mass of the body increases. For example, if the speed is 260 thousand km / s, that is, 87% of the speed of light, from the point of view of an observer who is in a resting frame of reference, the mass of the object will double.
STO Confirmations
All these provisions, no matter how contrary to common sense, have been directly and fully confirmed in many experiments since Einstein. One of them was conducted by scientists at the University of Michigan. This curious experiment confirms the theory of relativity in physics. Researchers put on board an airliner, which regularly made transatlantic flights, ultra-precise atomic clocks. Each time after his return to the airport, the readings of these watches were checked with the control. It turned out that the clock on the plane each time more and more lagged behind the control. Of course, we were talking only about insignificant figures, fractions of a second, but the fact itself is very indicative.

For the past half century, researchers have been studying elementary particles at accelerators - huge hardware complexes. In them, beams of electrons or protons, that is, charged subatomic particles, are accelerated until their speeds approach the speed of light. After that, they target nuclear targets. In these experiments, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the mass of particles increases, otherwise the experimental results cannot be interpreted. In this regard, SRT has long been not just a hypothetical theory. It has become one of the tools used in applied engineering, along with Newtonian laws of mechanics. The principles of the theory of relativity have found great practical application today.
SRT and Newton's laws
By the way, speaking of Newton’s laws (the portrait of this scientist is presented above), it should be said that the special theory of relativity, which, it would seem, contradicts them, actually reproduces the equations of Newton’s laws almost exactly if it is used to describe bodies whose speed of motion much less than the speed of light. In other words, if the special theory of relativity is applied, Newton’s physics is not canceled at all. This theory, by contrast, complements and expands it.
The speed of light is a universal constant
Using the principle of relativity, we can understand why in this model of the structure of the world, it is the speed of light that plays a very important role, and not something else. This question is asked by those who are just starting to get acquainted with physics. The speed of light is a universal constant due to the fact that it is defined as such by the natural science law (you can learn more about this by studying the Maxwell equations). The speed of light in a vacuum, by virtue of the principle of relativity, is the same in any reference frame. You might think that this is contrary to common sense. It turns out that the light simultaneously reaches the observer both from a fixed source and from a moving one (regardless of what speed it moves with). However, it is not. The speed of light, due to its special role, is given a central place not only in special, but also in general relativity. We will tell about her too.
General theory of relativity
It is used, as we have already said, for all reference systems, not necessarily those whose speed of movement relative to each other is constant. Mathematically, this theory looks much more complicated than a special one. This explains the fact that 11 years have passed between their publications. GR includes special as a special case. Consequently, Newton’s laws also enter into it. However, GRT goes much further than its predecessors. For example, it explains gravity in a new way.
Fourth dimension
Thanks to GR, the world becomes four-dimensional: time is added to three spatial dimensions. All of them are inextricable, therefore, we need not talk about the spatial distance existing in the three-dimensional world between two objects. We are now talking about space-time intervals between different events, combining both spatial and temporal remoteness of them from each other. In other words, time and space in the theory of relativity are considered as a four-dimensional continuum. It can be defined as space-time. In this continuum, those observers who are moving relative to each other will have different opinions, even about whether two events happened simultaneously, or whether one of them preceded the other. However, cause-effect relationships are not violated. In other words, the existence of such a coordinate system, where two events occur in a different sequence and not simultaneously, does not allow even general relativity.
GR and the law of gravity
According to the law of universal gravitation, discovered by Newton, the force of mutual attraction exists in the Universe between any two bodies. The Earth from this position revolves around the Sun, since there are forces of mutual attraction between them. Nevertheless, GR makes us look at this phenomenon from the other side. Gravity, according to this theory, is a consequence of the “curvature” (deformation) of space-time, which is observed under the influence of mass. The heavier the body (in our example, the Sun), the more space-time "bends" under it. Accordingly, its gravitational field is the stronger.
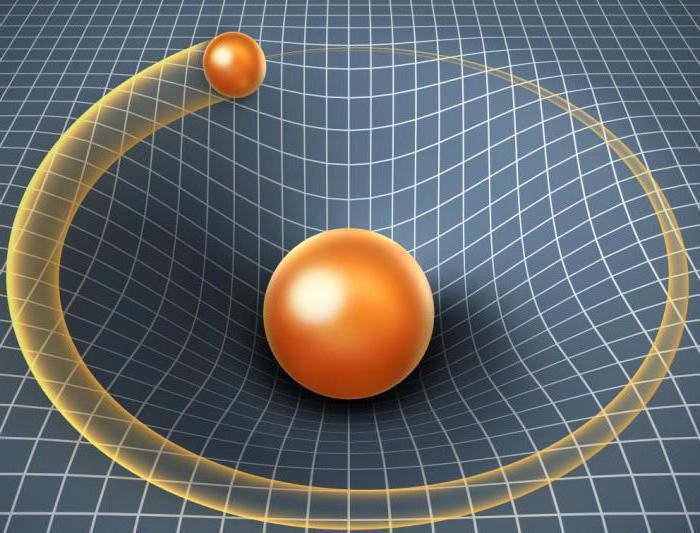
In order to better understand the essence of the theory of relativity, let us turn to comparison. The Earth, according to GTR, revolves around the Sun, like a small ball that rolls around a cone of a funnel created as a result of space-time “pushing” by the Sun. And what we used to consider gravity is actually an external manifestation of this curvature, and not a force, in Newton’s understanding. To date, no better explanation for the phenomenon of gravity than that proposed in GRT has been found.
Methods of checking GR
Note that GR is not easy to verify, since its results in laboratory conditions are almost consistent with the law of universal gravitation. However, scientists still conducted a number of important experiments. Their results allow us to conclude that Einstein's theory is confirmed. GR, in addition, helps to explain the various phenomena observed in space. These, for example, are small deviations of Mercury from its stationary orbit. From the point of view of Newtonian classical mechanics, they cannot be explained. This is also why electromagnetic radiation emanating from distant stars bends when it passes near the Sun.

The results predicted by general relativity actually differ significantly from those that give Newton's laws (his portrait is presented above), only when superstrong gravitational fields are present. Consequently, for a full verification of general relativity, either very accurate measurements of objects of enormous mass or black holes are necessary, since our usual ideas are not applicable to them. Therefore, the development of experimental methods for testing this theory is one of the main tasks of modern experimental physics.
The minds of many scientists, and even people far from science, are occupied by the theory of relativity created by Einstein. What is this, we briefly told. This theory turns our usual ideas about the world, so the interest in it still does not fade.