Suppose you have the following task: describe the function of bile in digestion. To do this, first you need to study its biochemical composition, properties and mechanisms of bile formation necessary for the normal breakdown of organic substances that make up food. Consideration of these issues will be devoted to this article.
Secretory function
The liver is the largest gland in the gastrointestinal tract inherent in vertebrates and humans. It consists of parenchymal cells called hepatocytes. A single hepatic cell has one or more nuclei and consists of two parts, called the biliary and vascular. The last side of the hepatocyte is in contact with a sinusoidal capillary receiving blood from the hepatic vein. This part synthesizes glucose, proteins, vitamins and lipocomplexes.
The other side of the hepatocyte is directed towards the bile capillary. It is called biliary. It produces bile. It flows into the capillary, and from it into the ducts. Thus, in a healthy liver, the bile produced by the hepatocyte side does not enter the blood, as the biliary capillary is separated from the sinusoidal body of the liver cell.
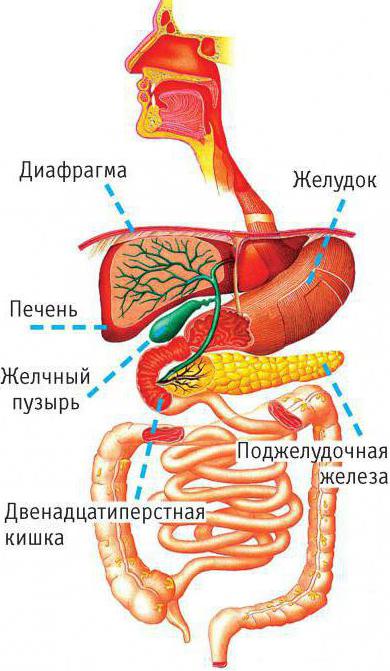
It should be noted that hepatocytes are grouped, forming lobules, from which the bile ducts exit. They merge and form two main directions - left and right. They exit the central lobes of the liver. And then, merging, form a common duct, which departs from its gate and flows into the gallbladder. Thus, the liver is an organ that secrets human bile. The anatomy of bile, the structure of the gallbladder and its functions will be considered by us further.
Why is bile secretion necessary?
Compounds that help break down complex macromolecules of organic food components include bile. It specifically acts on lipids, converting them from an insoluble state to the form of an emulsion. Cholic acids in bile - chenodeoxycholic and cholic - are surfactants. They emulsify the fats of food from the stomach to the duodenum, facilitating their cleavage by the pancreas enzyme - lipase.
Biochemical composition of bile
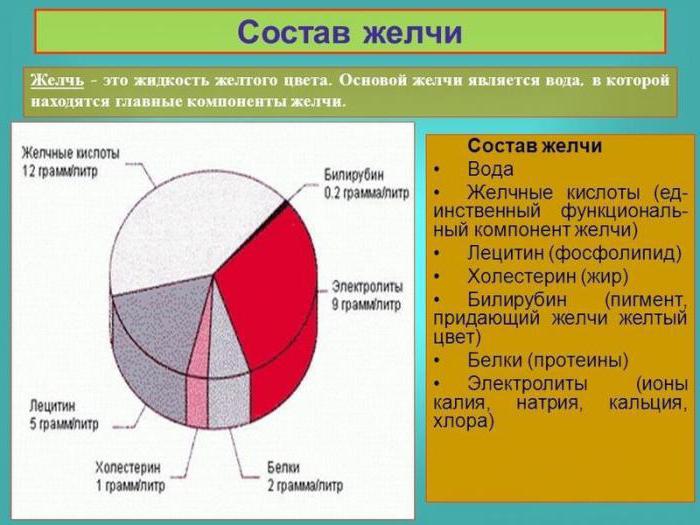
Knowing the structure of the structural elements of the hepatic lobules, the biliary parts of hepatocytes, as well as the biochemical composition, you correctly describe the functions of bile in digestion. Gastroenterologists have found that complex processes of plastic and energy metabolism occur in the liver. Bile itself is an olive or light brown liquid. It contains 98% water, as well as pigments, cholesterol, cholic acids, lecithin, vitamins and enzymes.
Consider the structure and circulation of bile acids. They are formed from steroid alcohol - cholesterol. It is also part of cell membranes. In hepatocytes, cholesterol is oxidized and primary bile acids form. They can change, turning into secondary: metacholic and deoxycholic. Those, in turn, form complexes with protein monomers - taurine and glycine.
These complexes are the most chemically active and are contained in the liquid in the form of sodium or potassium salts. Bile pigments are another biochemical component, the main of which is bilirubin. It is formed as a result of the destruction of hemoglobin, which occurs in macrophages of the liver - Kupffer cells, as well as in the spleen. Lecithin is a component of bile. It is also formed in the liver and plays an important role in the metabolism of fatty acids and cholesterol, reducing its level. He also takes part in the emulsification of fats.
What properties does bile have?
Having studied the chemical composition of the secretion of the liver, one can correctly imagine its role in the breakdown of organic substances and consider the main functions of bile in digestion, which are diverse. For example, it contains acids and is a detergent that helps break down large fat molecules into smaller ones. Bile affects both enzymes hydrolyzing carbohydrates and proteins: amylase and trypsin, enhancing their catalytic properties. On the enzyme of gastric juice - pepsin - it acts in the opposite way, that is, it inhibits its activity, which leads to a sharp increase in the pH of the gastric contents, since its acidity decreases.
Bile secretion enhances the absorption of solutions, mineral salts, vitamins A and D, as well as amino acids. The secretion of the liver regulates the motor and excretory functions of all parts of the small intestine. This is the role of bile in digestion.
Mechanisms of bile formation and bile secretion
Previously, we studied the properties of liver secretion produced by the biliary portions of hepatocytes. And also we found out that the composition, properties of bile and its importance in digestion are interconnected. These mechanisms are carried out both by the human nervous system and the humoral way. The formation of bile is enhanced as a reflex response to irritation of the interoreceptors of the walls of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, stomach, and small intestine.
Gall bladder: its structure and role in digestion
Being a muscle organ, it is located under the lower edge of the liver. It has a neck, body and bottom. After you anatomically justify the mechanism of its work, then you can easily describe the functions of bile in digestion. It, constantly forming in the liver, is secreted into the duodenum only at the moment of ingestion of food. Between meals, the secret is deposited in the gallbladder.
Diagnostic methods for the study of bile
For the normal course of metabolic reactions in the sections of the gastrointestinal tract, certain biochemical and physiological parameters of liver secretion are necessary. You are physiologically justified to describe the functions of bile in the digestion, if its clinical parameters are normal. They are determined by the method of multi-stage fractional duodenal sounding.
In the first phase of the study, a basal fraction is obtained. It should have a light yellow color and pH greater than 7. In the second phase, with the sphincter of Oddi closed, the secret should not be released from the probe. In the third stage of the study, the clinically normal indicators of bile are as follows: volume - from 3 to 5 ml, color - light brown. The fourth phase lasts about half an hour. The color of the secretion of the liver varies from olive (cystic bile) to amber yellow. Its pH is 6.5–7.5, and its density is approximately 1038. The last phase, the secretion of hepatic bile, lasts up to 20 minutes. The density decreases to 1011, pH = 7.5–8.2.
Deviations from the above parameters will indicate pathological disorders in the liver, gall bladder or ducts. The most common type of pathology is the formation of stones in the bladder due to increased viscosity of the fluid, as well as violations of its contractile function. As you can see, in this article we examined and studied the secret of the liver - bile, its significance and functions in the digestion process.