The ability to see clearly is a unique feature not only of humans, but also of animals. With the help of vision, orientation takes place in space and the environment, a large amount of information is obtained: it is known that with the help of the organ of vision a person receives up to 90% of all information about objects and the environment. The unique structure and cellular composition allowed the retina not only to perceive light stimulation sources, but also to distinguish their spectral characteristics. Let's look at how the retina works, the functions and features of its neuronal organization. But we will only talk about its structure not from the point of view of a person carrying a load of scientific knowledge, but from the point of view of an average citizen.
Retina Functions
Let's start with the highlights. The answer to the question what basic functions of the retina has is quite simple. First of all, this is the perception of light irritation.
By its nature, light is an electromagnetic wave with a certain oscillation frequency, which determines the perception of various colors by the retina. The ability to color vision is a unique feature of the evolution of mammals. With the help of scientific achievements, modern equipment, new luminescent chemical compounds, it was possible to look deeper into the structure of the organs of vision, to clarify biochemical processes and to better understand how the retina realizes its functions. And it turns out that there are a lot of them, and each is unique.
Retina : structure and function
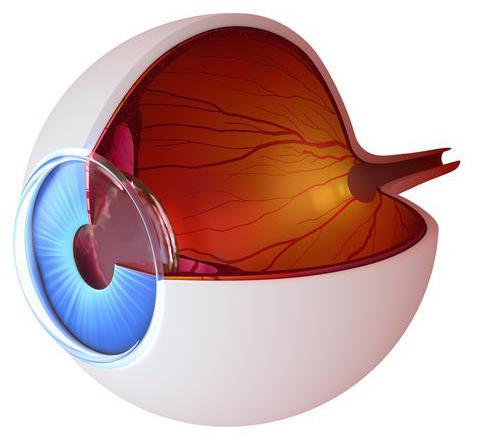
Many people know that the retina is located inside the eye and is its innermost shell. It is known that in its composition it contains the so-called photosensitive cells. Directly due to them, the retina performs the functions of photoreception.
Their names come from the shape of the cells. So, rod-shaped cells were called “rods”, and cells similar to a chemical vessel called “flask” were called “cones”.
The rods and cones differ among themselves not only by the features of the histological structure. The main difference between the two is how they perceive light and its spectral characteristics. The sticks are responsible for the perception of the light flux in twilight time - precisely when, as they say, "all cats are gray." But cones are responsible for the perception of color vision.
Functional features of cones
Three special classes are distinguished among cones: cones responsible for the perception of the green, red, and blue parts of the spectrum, respectively. Each cone contributes to the formation of color vision by processing the image projected by the lens. In painting, the formation of the final color depends on the proportions in which the paints were originally taken by the artist. Similarly, the retina transmits information about the spectral characteristic of light: depending on how the cones of each group are discharged by pulses, we have a vision of one color or another.
For example, if we see green, then the cones responsible for the green region of the spectrum are most strongly discharged. And if we see red, then, respectively, for red. Thus, the human retina functions not only in the perception of the light flux, but also in the initial assessment of its spectral characteristics.
Retinal layers and why they are needed
Perhaps someone thinks that immediately after the lens, light directly hits the rods and cones, and those in turn are connected to the fibers of the optic nerve and carry information to the brain. This is actually not the case. Before reaching the rods and cones, light needs to overcome all layers of the retina (and there are 10) and only then act on the photosensitive cells (rods and cones).
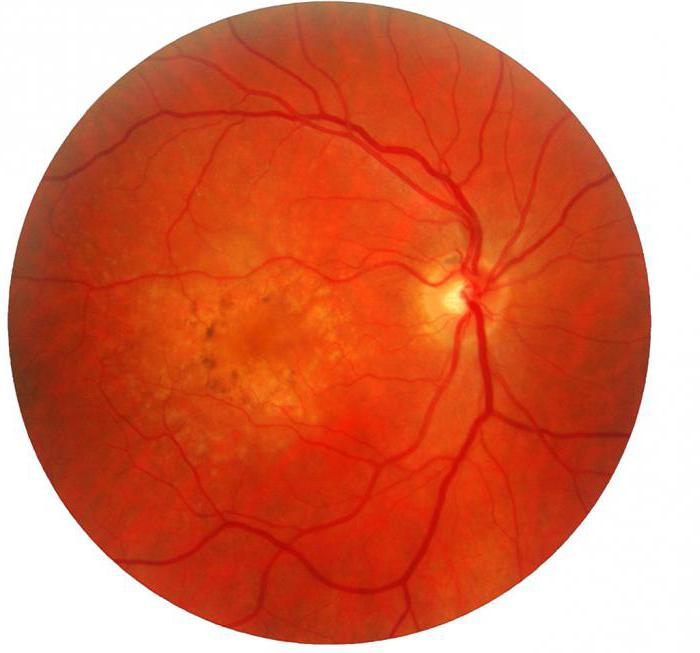
The outermost layer of the retina is the pigment layer. Its task is to prevent the reflection of light. This layer of pigment cells is a kind of black camera film camera (it is black that does not create glare, which means that the image becomes more clear, light reflections disappear). This layer provides a sharp image using optical media of the eye. In the very close proximity to the layer of pigment cells sticks and cones are adjacent, and this feature makes it possible to sharply see. It turns out that the layers of the retina are located, as it were, back to front. The innermost layer is a layer of specific cells that, through intermediate cells of the middle layer, process incoming information from rods and cones. Axons of these cells gather together from the entire surface of the retina and leave the eyeball through the so-called blind spot.
There are no photosensitive sticks and cones in this place, and the optic nerve leaves the eyeball. Moreover, it is here that the vessels that provide trophic retina enter. The condition of the body can affect the state of the vessels of the retina, which is a convenient and specific criterion for the diagnosis of various diseases.
Localization of rods and cones
Nature conceived so that the rods and cones are unevenly distributed over the entire surface of the retina. In the central fossa (the area of best vision), the highest concentration of cones is observed. This is due to the fact that this area is responsible for the clearest vision. As you move away from the central fossa, the number of cones decreases, and the number of rods increases. Thus, the periphery of the retina is represented only by sticks. This feature of the structure provides us with a clear vision at a high level of illumination and helps to distinguish the outlines of objects at low.
Retinal neural organization
Immediately behind the layer of rods and cones are two layers of nerve cells. These are layers of bipolar and ganglion cells. In addition, there is a third (middle) layer of horizontal cells. The main purpose of this group is the primary processing of afferent impulse, which comes from rods and cones.
Interesting facts about the structure of the retina
Now we know what the retina is. The structure and functions of it we have already considered. It is also necessary to mention the most interesting facts related to this topic.
In order to reach the pigment layer, light must pass through all layers of nerve cells, penetrate through the rods and cones and reach the pigment layer!
Another feature of the structure of the retina is the organization of providing clear vision in the daytime. The bottom line is that in the central fossa, each cone connects to its ganglion cell, and as it moves away to the periphery, one ganglion cell collects information from several rods and cones.
Retinal diseases and their diagnosis
So what function does the retina perform? Of course, this is the perception of the light flux that the refractive media of the eye form. Violation of this function leads to visual impairment. In ophthalmology, there are a large number of retinal diseases. These are diseases caused by degenerative processes, and diseases based on dystrophic and tumor processes, exfoliation, and hemorrhages.
The main and primary symptom that can speak of retinal diseases is visual disturbance. In the future, optical circles, loss of visual fields and many other symptoms may occur. It must be remembered that if visual acuity decreases, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist and undergo the necessary examination.
Conclusion
Vision is a huge gift of nature, and the retina, functions and its structure are a finely organized element of the eyeball, both structurally and functionally.
Timely consultation and preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist will help to identify diseases of the visual analyzer and start treatment on time. Fortunately, modern medicine has unique technologies that allow literally 20-30 minutes to get rid of visual disturbances and regain the ability to see clearly. And knowing which retina performs a function, you can restore it.