Russian law provides commercial enterprises with the opportunity to work in the simplified tax system. What it is? This is a special taxation mechanism, involving a significant reduction in the financial burden of companies. This is due to the reduction of the base for calculating the corresponding fees to the treasury, as well as by reducing the basis for determining its individual components. At the same time, the company retains a number of obligations, the fulfillment of which will be required by the tax. STS is a regime that significantly facilitates the activities of Russian firms, but does not imply their complete exemption from payment of fees stipulated by law, as well as from the provision of necessary reports to competent structures. What is the specificity of "simplified"? What nuances of its use in practice deserve special attention?
General Information about STS
Consider the basic information about the simplified tax system. What it is? STS, or simplified tax system, is provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Most popular among novice entrepreneurs. The fact is that the simplified tax system for most of the features is much more profitable than the general taxation system - the common tax system, which is used in large enterprises.
Simplicity in the tax regime under consideration is expressed not only in terms of the amount of fees required to be paid, but also in relation to reporting procedures. There are very few of them in the simplified tax system.
USN Terms of Use
We study the essence of the simplified tax system (what it is) in more detail. Consider the "simplification" in the aspect of the rules of its application provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. As we noted above, counting on the use of this system of payment of fees can mainly start-up entrepreneurs - those who have a small business. But what are the criteria here? In order to apply the appropriate system under which the tax is paid by the simplified tax system, an enterprise must comply with the following main features:
- no more than 100 employees work in it;
- The annual revenue of the company does not exceed 60 million rubles. (in some interpretations - 45 million rubles for 9 months of the tax year);
- residual value of assets - not more than 100 million rubles.
There are additional criteria. So, the share in the ownership of the authorized capital of other enterprises in a company applying for work in the simplified tax system should not exceed 25%. Also, a company cannot take advantage of branches to take advantage of the simplified tax system.
What taxes can you not pay
In order to better understand the specifics of the simplified tax system, what it is, we will examine in more detail the advantages that an enterprise operating in the appropriate taxation regime receives. The main feature of the simplified tax system is that this system of calculating and paying fees to the budget replaces several taxes that are characteristic of the common tax system. Among them: income tax (excluding fees from dividends and certain types of obligations), property, VAT, personal income tax on an entrepreneur - if he is an individual entrepreneur. However, in some cases, the obligation to pay the appropriate types of fees is retained by the company - for example, if it acts as a tax agent. Or if it forms documents that reflect the need to pay certain taxes. We will consider similar scenarios a bit later.
Types of taxes on the simplified tax system
What does the business owner have to pay in return for these fees? The legislation provides for 2 schemes for its settlements with the state. In the first of these, the tax base is formed from the proceeds of the enterprise. Of this, 6% is payable to the treasury. Expenses under the simplified tax system are not taken into account. Another scheme is the calculation of fees based on the company's profit indicators. Of this, 15% is payable to the treasury. In the framework of this scheme, expenses under the simplified tax system are of great importance. So, if they are equal to incomes or exceed them, then the tax base is not formed.

Which of the two marked schemes is best for an entrepreneur? Obviously, this is determined by the industry specifics of the business. If he is engaged in the provision of services, then he will have little expenses. In this case, it is more profitable to pay taxes on revenue. If the person is the owner of the store, then in this case the costs will be tangible. In retail, the average profitability indicator is about 10-15%. In this case, it is more profitable to pay fees on profits. Consider an example that will clearly allow you to see in which cases one scheme is more profitable, and in which - another.
USN calculation example
Our task is to find a formula that allows us to determine the optimal basis for calculating the simplified tax system. Revenues, expenses of the company - factors that to a decisive degree influence the arrangement of relevant priorities. Consider an example that will clearly reflect the specifics of using the first or second scheme of calculating the simplified tax system.
Suppose a company provides services for printing and scanning documents. Estimated costs will be generated by buying paper and ink for the MFP (we agree that we have 2 of them and they got the company as a gift, and therefore are not included in the costs), electricity, as well as the transfer of labor compensation to employees.
Let's start by analyzing the company's potential costs. Suppose a company employs 2 people with a salary of 25 thousand rubles. The cost of paper and ink with an average intensity of commercial operation of one device of about 700 pages per day will be approximately 10 thousand rubles. per month. The necessary contributions to the PFR, FSS and MHIF for employees are about 30% of their salary. Thus, the costs based on the amounts that go towards the remuneration of the employees of the company and the fulfillment of social obligations will amount to 65 thousand rubles. (salary for two and 30% of contributions to funds). We add 10 thousand rubles to them, which will be used to buy paper and paint. It turns out that the total monthly expenses of the company are 75 thousand rubles.
What could be the company's expected earnings? The average cost of printing 1 sheet in large cities is 3 rubles. We multiply this indicator by 700, and then by 30 (we will agree that the company works every day). It turns out 63 thousand rubles. But we have 2 printers. In total, they will bring 126 thousand rubles. revenue. Let us also scan about 100 images per day. The average cost of processing each is 5 rubles. As a result, we earn on scanning about 15 thousand rubles. per month. The total revenue of the company for all services is 141 thousand. Profit including expenses - 66 thousand rubles.
What scheme to choose for the payment of STS? Revenues, expenses are known to us. If we pay the state a tax on revenue of 6% from 141 thousand rubles, then we will have 132 thousand 540 rubles. Net profit in this case will be 57 540 rubles. If we pay the state a tax on the difference between income and expenses - 15% of 66 thousand rubles, then we will have 56 100 rubles. net profit. Obviously, the payment of STS when calculating revenue tax in this case is more profitable.
Of course, these calculations are a very approximate example. STS may become unprofitable if, for some reason, for example, due to seasonal fluctuations in demand, there will be not so much revenue as in our example. It is clear that the main clients of printing and scanning companies: students, students of schools, lyceums - have a rest in the summer. But the law does not provide for a temporary change in the tax regime in the summer. Therefore, the owner of the company to provide the appropriate type of services should consider the corresponding changes in the dynamics of demand when determining the optimal scheme of work in the simplified tax system.
Taxes and fees at the simplified tax system
In both schemes, the enterprise must fulfill its obligations not only to transfer taxes to the Federal Tax Service, but also to pay the necessary contributions to state funds - PFR, FSS and MHIF. If the legal form of doing business is LLC, then the entrepreneur transfers the relevant fees to the treasury only for his hired employees. If a person runs a business as an individual entrepreneur, then he must also transfer contributions to the PFR, FSS and MHIF for himself. At the same time, he has the right to credit 100% of them against taxes - calculated both on revenue and on profit. Due to this opportunity, many entrepreneurs do not actually feel the additional financial burden due to the need to pay the corresponding fees for themselves.

As a rule, enterprises operating on the simplified tax system do not pay contributions and taxes of a different type. However, there are a number of statutory grounds for determining additional financial obligations of companies under “simplification”. Among these are excise taxes. Their formation can be associated with the import into the Russian Federation of goods that require appropriate documents, the purchase of petroleum products, the sale of alcoholic beverages and other excisable goods (including confiscated or ownerless ones), as well as the sale of products that were imported into the Russian Federation from the Republic of Belarus. Some enterprises that operate under the simplified tax system pay state and customs duties, land, transport and water taxes, as well as fees stipulated by law for the use of biological resources.
Payment of taxes at the simplified tax system and reporting procedures
We studied the basic information about the simplified taxation regime of Russian enterprises, the simplified tax system. What is it, what are its main advantages, we examined. Now we can explore some of the practical nuances of using the capabilities of the “simplified”. An interesting aspect regarding the procedure for paying the corresponding tax.
In relation to this obligation, the legislation sets specific deadlines. STS - a regime involving the quarterly transfer by enterprises of the necessary fees to the budget. The legislation requires entrepreneurs working on a “simplification” to transfer advance payments within 25 days from the end of the relevant tax period. It can be the first quarter, half a year, 9 months. The fee after the tax year can be transferred to the budget until March 31 - for the owners of the LLC, until April 30 - for the individual entrepreneur.

Another major aspect of the practical work of the enterprise in the STS mode is reporting. We noted above that the corresponding obligations of the business owner are simplified - that is, sending a large number of reporting forms to the Federal Tax Service is not required. In fact, the main document that needs to be periodically sent to the entrepreneur at the Federal Tax Service is the tax return. It must be submitted before March 31 of the year that follows the reporting year - to the owners of the LLC, and by April 30 - IP. A tax return is a standardized form, and the Federal Tax Service will always be able to issue a sample of it. STS - a mode that is associated with a minimum amount of reporting procedures. However, one must not forget about the need to submit a declaration to an entrepreneur. The pattern of filling its first page may look something like this.
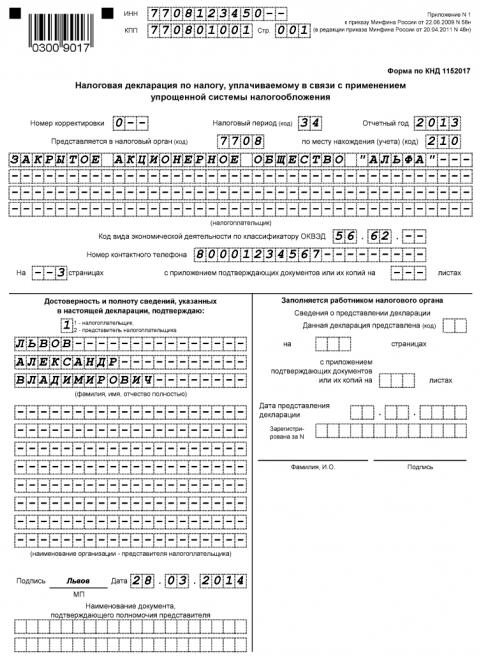
The structure of the document is very simple. The main thing is not to make a mistake in indicating personal data and figures reflecting the business momentum.
If the company is a tax agent
For firms with tax agent status , the law predetermines additional obligations regarding the payment of various fees to the treasury. Thus, companies hiring employees under employment contracts or ordering services under civil law contracts must pay the appropriate compensation to employees or personal income tax contractors.
Companies with tax agent status are also required to carry out a number of reporting procedures that may supplement the list noted above. So, for example, the appropriate type of enterprise must provide the Social Insurance Fund with a compiled statement of account in the established form - by the 15th day of the month that follows the tax period. Tax agents have reporting obligations to the FIU, they must be provided with the form RSV-1 to this institution - before the 15th day of the second month that follows the reporting period. At similar times, individual information is also submitted to the FIU. In some cases, the company has the status of a tax agent in terms of VAT. In this situation, the company needs to submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service by the 20th day of the month that follows the reporting period. If the company pays dividends, then it is also necessary to submit a declaration in which the figures for income tax will be reflected.
At the end of the year, enterprises in the status of a tax agent must submit: a payroll sheet to the FSS (until January 15), information on the average number of employees, a VAT return (until January 20), form RSV-1, as well as individual information in the FIU (up to 15 February) certificates in the form 2-NDFL (until April 1), declarations on land and transport taxes (until February 1).
How to switch to the simplified tax system
So, if you try to explain the essence of the simplified tax system (what it is) in simple words, then you can restrict yourself to this wording: the simplified tax system is a mode of paying fees to the treasury, which implies a minimum tax burden and also represents a strong incentive to start a business. But how can the owner of the enterprise take advantage of the simplified system? There are two main schemes for transferring a firm's activity to the appropriate regime.
As part of the first, it is planned to activate the simplified tax system at the time of registration of the company with the Federal Tax Service. In this case, the entrepreneur must, together with the package of documents necessary for issuing a certificate of registration of the company in state registers, transmit a notification to the Federal Tax Service. In relation to the relevant document, a special filling pattern has been established. STS - a regime in which an enterprise can go within 30 days after state registration by sending a corresponding document to the Federal Tax Service. It may look like this.
The second scheme assumes that the company will be transferred to the simplified tax system from other taxation regimes. The main thing is to keep in mind that certain deadlines are set by law. STS is activated only from the beginning of the next tax year. Under the second scheme, the entrepreneur must also submit a notification to the Federal Tax Service.
USN disadvantages
So, we have studied the essence of the simplified tax system, what it is and how it is calculated. The benefits of simplification are obvious. But there are some disadvantages of the simplified tax system. Thus, an enterprise whose turnover has increased sharply, for example, after concluding a major contract, may lose the right to work under a simplified taxation regime. In practice, this may mean the need for urgent surcharges of fees - for example, related to income tax. If the company will return from the simplified tax system to the common social network, this will be accompanied by the need to submit to the Federal Tax Service a large number of reporting documents. This may be accompanied by significant labor costs of specialists of the company to fill them. STS upon transition to this mode will require restoration of reporting, as well as VAT on capitalized assets.

Enterprises operating under OCH pay VAT. In turn, firms on the "simplified tax system" are not required to transfer this tax to the state. The simplified tax system in this sense significantly alleviates the financial burden of the company, but at the same time it can predetermine unwillingness to work with those contractors who pay VAT. This is due to the specifics of legislation in the field of calculation and payment of value added tax. The fact is that in some cases, firms can rely on its compensation - provided that the counterparty uses VAT. Since the company doesn’t transfer it to the budget in the simplified company, the number of potential partners may decrease, since some of them may not benefit from cooperation if the counterparty works without VAT.
Sometimes entrepreneurs try to adapt to this aspect of the law, trying to issue invoices, which contain a separate line with VAT. This is ineffective, lawyers say. The fact is that such a document predetermines the obligation of the enterprise to transfer the corresponding amount of VAT to the budget. Similarly, the relevant declaration must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service.
It can also be noted that the taxable base cannot be reduced by the amount of VAT in the case of “simplification” if the business owner pays fees on the profits of the company. Moreover, if an entrepreneur who works under the simplified tax system, in order to increase loyalty on the part of the counterparty, issues invoices in which VAT is fixed, then the corresponding sums of money that are transferred to his current account can be recorded as income in the interpretation of the tax authorities, and them in this case taxes must be paid.
If an entrepreneur working on “simplification” forms an invoice for a counterparty, in which VAT will be fixed, but does not transfer the corresponding amount to the budget, then the Federal Tax Service may, having discovered this violation, recover these funds from the company. Also, the Federal Tax Service may charge a fine on the basis that the tax stipulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation was not paid by the company. , , .
, , , . «», , , . , , — , .
, : " - ?" - , , . «», , , - .