As we know from the school course of geometry, symmetry can be one of three types: central, axial, and symmetry relative to any plane. Central is the symmetry of an object relative to a point (the simplest example is any circle), axial is symmetry about a straight line, and the last form of proportionality (relative to a plane) is also known to us as mirror symmetry.
Geometry with mathematics give us clear criteria by which we can unambiguously determine which object can be considered symmetrical and which not. However, in addition to boring formulations, there is another parameter that a person selects almost unmistakably - this is beauty.
Even the ancient Greeks noticed that harmony and beauty are inherent in symmetrical objects. The German mathematician G. Weil once wrote the work "Studies on Symmetry", in which he argues that symmetry and beauty are closely interconnected. According to him, what is considered symmetrical has a good proportion of proportions, and symmetry itself is a special type of coordination of parts of the whole.
Mirror symmetry in geometry is often associated with
regular polygons, but if you look closely, these figures are quite common in nature. Some of them can be seen in the form of crystals, others in the form of simple microorganisms or viruses.
Mirror symmetry is very common in architecture. It is present in all the constructions of Ancient Egypt and the temples of ancient Greece, amphitheaters, basilicas and triumphal arches of the Romans, churches and palaces of the Renaissance, as well as in many works of modern architecture.
In nature, mirror symmetry is characteristic of animals and plants that move or grow parallel to the earth's surface, and is also often found as a reflection of the terrain in the water surface of a river, lake, etc. A striking example of this is the colorful butterfly wings, the pattern on which coincides surprisingly precisely.
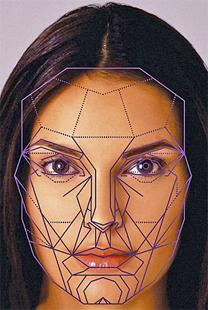
Now let us turn our attention to man. Why are some people reputed to be handsome writers, while others are completely devoid of human attractiveness? British scientists, led by evolutionary biologist William Brown, set out to get an accurate answer to this question and conducted a study in which 37 girls and 40 young people took part (a detailed report was published in the PNAS publication). Initially, scientists using a scanner created a three-dimensional three-dimensional model of the body of each of the participants in this test. Then, the researchers determined by 24 parameters how accurate the mirror symmetry of each model is. After this, each volunteer was asked to rate the attractiveness of participants of the opposite sex.
The result dispelled all doubts. The experiment confirmed that the mirror symmetry of the body has a direct effect on human beauty. And this is true both for men and for women.
Which of these can be concluded? The ideals of beauty are changing, but at the same time remain the same - the reason for the attractiveness lies in the symmetry. And this is true for everything that surrounds us in this wonderful world.