The CIS is the former international union formerly the Union of the SSR, the tasks of which were to regulate cooperation between the republics that made up the Soviet Union. This is not a supranational entity. The interaction of the subjects and the functioning of the association provided for a voluntary basis. What is the CIS and what is its role in international relations? How was the formation of the Commonwealth? What is the role of certain entities in its development? More on this later in the article. A map of the CIS will also be provided below.
Organization Formation
The Ukrainian SSR, RSFSR and BSSR took part in the creation of the organization. In 1991, on December 8, a corresponding agreement was signed in Belovezhskaya Pushcha. The document, which consisted of 14 articles and the Preamble, said that the USSR ceased to exist as a subject of geopolitical reality and international law. But on the basis of the historical community and relations of peoples, taking into account bilateral treaties, the desire to create a democratic rule of law, and if there are intentions to develop their relations with each other on the basis of mutual respect and recognition of sovereignty, the parties present agreed to form an international association.
Ratification of the agreement
On December 10, the Supreme Councils of Ukraine and Belarus gave the document legal force. On December 12, the agreement was ratified in the Russian Parliament. The overwhelming majority (188) of the votes were “for”, “abstained” - 7, “against” - 6. The next day, on the 13th day, the heads of the Central Asian republics that were part of the USSR met. These were representatives of Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan. As a result of this meeting, a Statement was drawn up. In it, the chapters expressed their consent to join the CIS (decoding of the abbreviation - Commonwealth of Independent States).
An indispensable condition for the formation of the association was the ensuring of equal rights for the entities that were formerly members of the Soviet Union and the recognition of all of them as founders. Later, Nazarbayev (head of Kazakhstan) put forward a proposal to organize a meeting in Alma-Ata, where the CIS countries, the list of which will be given below, will continue further discussion of issues and adoption of joint decisions.
Meeting in Alma-Ata
11 representatives of the republics that used to be part of the USSR arrived in the capital of Kazakhstan . They were the heads of Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Russia, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Moldova, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Belarus. There were no representatives of Georgia, Estonia, Lithuania and Latvia. As a result of the meeting, a declaration was signed. It laid out the principles and goals of the new Commonwealth.
In addition, the document enshrined the provision that all CIS countries will carry out their interaction on an equal footing through coordinating institutions. The latter, in turn, were formed on a parity basis. These coordinating institutions should have acted in accordance with the agreement between the CIS entities (the decoding is indicated above). At the same time, joint control over military-strategic facilities and nuclear weapons remained.
Speaking about what the CIS is, it should be said that this association did not imply a single border - each republic that was part of the USSR earlier retained its sovereignty, government, and legal system. At the same time, the creation of the Commonwealth was the embodiment of a commitment to the formation and development of a common economic zone.
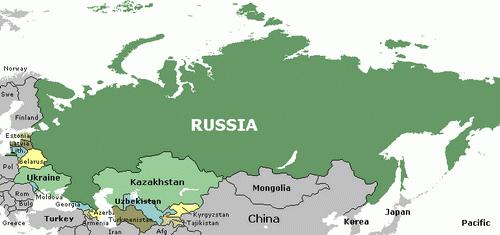
CIS map
Territorially, the Commonwealth has become smaller than the USSR. Some former republics did not express a desire to join the CIS. Nevertheless, the association as a whole occupied a rather large geopolitical space. Most entities sought mutually beneficial cooperation on an equal footing while maintaining their integrity.
It should be noted that the meeting on December 21 contributed to the completion of the transformation of the republics of the USSR into CIS countries. The list was replenished by Moldova and Azerbaijan, which became the last to ratify the document on the creation of the Commonwealth. Until that moment, they were only associate members of the association. This was an important milestone in the state building of the entire post-Soviet space. In 1993, Georgia was included in the CIS list. Among the largest cities of the Commonwealth are Minsk, St. Petersburg, Kiev, Tashkent, Alma-Ata, Moscow.
Organizational matters
At a meeting on December 30 in Minsk, the CIS member states signed the Interim Agreement. In accordance with it, the supreme body of the Commonwealth was established. The Council included the heads of the subjects of the organization.
Speaking about what the CIS is, it should be said about how decision-making was regulated. Each Commonwealth entity had one vote. Moreover, the general decision was made by consensus.
At the meeting in Minsk, an Agreement was also signed regulating control over the Armed Forces and the Border Forces. In accordance with it, each subject had the right to create his own army. In 1993, the organizational stage was completed.
On January 22 of the specified year, the Charter was adopted in Minsk. This document has become fundamental to the organization. In 1996, on March 15, at a meeting of the State Duma of the Russian Federation, Resolution 157-II of the State Duma was adopted. It determined the legal force of the results of the referendum held in 1991, March 17, regarding the preservation of the USSR. The third paragraph referred to the confirmation that the Agreement on the formation of the Commonwealth, which was not approved at the Congress of People's Deputies - the highest body of state power in the RSFSR - did not and does not have legal force in relation to the cessation of the further existence of the USSR.
The role of the Russian Federation in the Commonwealth
At a meeting of the Security Council of the Russian Federation, President Vladimir Putin spoke. Vladimir Vladimirovich admitted that Russia and the CIS have come to a certain milestone in their development. In this regard, as the president noted, it is necessary either to achieve a qualitative strengthening of the Commonwealth and the formation on its basis of a truly working regional structure with certain influence in the world, or otherwise the geopolitical space will be “blurred”, as a result of which interest in the Commonwealth among its subjects will be irretrievably lost.
After the Russian government suffered several significant failures in political relations between the republics that used to be the USSR (Moldova, Georgia and Ukraine) in March 2005, at the very height of the Kyrgyz crisis, Putin spoke out categorically. He noted that all the disappointments were the result of an excess of expectations. In short, the president of the Russian Federation admitted that only goals were programmed, but in reality the whole process went completely differently.
Commonwealth Sustainability Issues
Because of the growing centrifugal processes that took place inside the CIS, the question of the need to reform the association was repeatedly raised. However, there is no consensus on the likely directions of this movement. At the July informal summit in 2006, where the heads of the subjects of the Commonwealth gathered, Nazarbayev proposed several guidelines on which to focus the work.
First of all, the President of Kazakhstan believed that it was necessary to coordinate migration policy. What is necessary, in his opinion, is the development of common transport communications, cooperation in the fight against cross-border crime, as well as interaction in the cultural, humanitarian and scientific-educational spheres.
As noted in several media reports, skepticism about the effectiveness and vitality of the Commonwealth has been linked to a number of trade wars. In these crises, Russia was opposed by Moldova, Georgia and Ukraine. The CIS, according to some observers, was on the verge of survival. This was facilitated by recent events - trade conflicts between Georgia and the Russian Federation. According to some analysts, Russia's sanctions against the Commonwealth have been unprecedented. Moreover, as many observers noted, the policy of the Russian Federation towards the end of 2005 with regard to the post-Soviet states in general and the CIS countries in particular was formed by Gazprom (the gas monopoly of the Russian Federation). The cost of fuel supplied, according to several authors, was a means of punishing and encouraging the subjects of the Commonwealth, depending on their political interaction with the Russian Federation.
"Oil and gas relations"
Speaking of what the CIS is, one cannot fail to mention the factor uniting all subjects. It was the low cost of fuel supplied from the territory of the Russian Federation. However, in 2005, in July, a gradual increase in gas prices for the Baltic countries was announced . The cost was increased to a pan-European level of 120-125 $ / thousand m 3 . In September of the same year, an increase in the cost of fuel for Georgia from 2006 to $ 110 was announced, and from 2007 to $ 235.
In November 2005, the price of gas for Armenia was increased. The cost of deliveries was to be $ 110. However, the Armenian leadership expressed concern that the republic would not be able to purchase fuel at such prices. Russia offered an interest-free loan that could offset the increased cost. However, Armenia offered the Russian Federation another option - as an alternative to transfer to ownership one of the blocks of the Hrazdan TPP that it owned, as well as the entire gas transmission network in the republic. Nevertheless, despite warnings from the Armenian side about the likely negative consequences of further price increases, the republic was only able to postpone the increase in value.
For Moldova, price increases were announced in 2005. By 2007, a new supply value was agreed. The price of fuel was $ 170. By December, an agreement was reached on fuel supplies to Azerbaijan at market value. In 2006, the price was $ 110, and by 2007 deliveries were planned at $ 235.
By December 2005, a conflict broke out between the Russian Federation and Ukraine. Since January 1, 2006, prices have been announced to increase to $ 160. Since further negotiations were unsuccessful, Russia raised the price to $ 230. In some ways, Belarus had a privileged position in the gas issue. By March 2005, the Russian Federation announced an increase in supply prices. However, by April 4, Putin promised to leave the cost at the same level. But after the presidential election, Belarus again announced a price increase. After lengthy negotiations, the cost for 2007-2011 was set at $ 100.
The role of the subjects of the Commonwealth in oil and gas relations
It should be noted that, among other things, during 2006 the Russian government made efforts to form a union on the basis of the CIS. It was assumed that members of the Commonwealth should have become its members, one way or another connected by a system of gas and oil pipelines, recognizing, in addition, the leading role of the Russian Federation as a monopoly supplier of energy fuel to Europe from the former Soviet Union. In this case, neighboring countries should either fulfill the tasks of suppliers of their own gas to Russian pipelines, or become a transit territory. The collateral of this energy union was the exchange or sale of energy transport and energy assets.
Thus, for example, an agreement was reached with Turkmenistan on export deliveries of its gas via the Gazprom pipeline. On the territory of Uzbekistan, Russian companies are developing local deposits. In Armenia, Gazprom owns the main gas pipeline from Iran. An agreement was also reached with Moldova that the local gas company Moldovgaz, half of which is owned by Gazprom, would issue additional shares by paying gas distribution networks as payment.
Critical opinions
What is the CIS today? Analyzing the recent history of the subjects of the Commonwealth, one cannot but pay attention to the abundance of conflicts at various levels. Even military clashes are known - both inter- and domestic. To this day, the problem of manifestation of national intolerance, illegal immigration remains unresolved. In addition, there are still economic conflicts between the Russian Federation on the one hand and Ukraine and Belarus on the other.
The main problem to be resolved is the issue of commodity tariffs. Repeatedly, the Russian Federation as the largest subject of the Commonwealth (the map of Russia and the CIS, showing this, is presented below), which has the highest economic and military potential, was accused of violations of the fundamental agreement, in particular, agreements on conducting intelligence activities within the territory.
From a geopolitical point of view, the CIS today formally does not have a goal of returning in any way to the past, at a time when all currently existing sovereign states belonged first to the Russian Empire, and then to the USSR. Meanwhile, in reality, the official leadership of the Russian Federation, both in its speeches and through the media, often voices criticism of the authorities of other entities of the Commonwealth. Most often, members of the International Association are accused of disrespect for the past, which is common, in actions influenced by developed Western countries (mainly the USA), as well as revanchist moods (in particular, the presentation of the events of the 2nd World War in a light that contradicts as a universally recognized world , and Soviet-Russian historiography).