The history of Europe begins with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. On the ruins of this largest state, barbarian kingdoms formed, which became the basis of modern Western European states. The history of Western Europe is conditionally divided into four stages: the Middle Ages, the New and Modern times and the modern era.
Western European Middle Ages
In the 4th – 5th centuries A.D. Germanic tribes settled on the borders of the Roman Empire. The emperors attracted new settlers to the service, not suspecting what fateful role they would play in the fate of their state. Gradually, the Roman army was filled with immigrants from strangers, who during the period of unrest that shook the empire, often determined the policies of sovereigns, and sometimes even took part in coups, raising their own proteges to the throne.
A similar alignment of events led to the fact that in 476 the military commander Odoacer overthrew the last Roman emperor Romulus Augustus, and new states of Western Europe were formed on the site of the former Western Roman Empire. The largest and most powerful of them was the kingdom of the Franks, who achieved power under the monarch Clovis. The peak of the heyday of the new state reached under the King of Francs, Charlemagne, who in 800 took the title of emperor. His possessions included Italian territories, part of Spain, Saxon lands. The collapse of the empire after the death of Charlemagne determined the further development of the mainland.
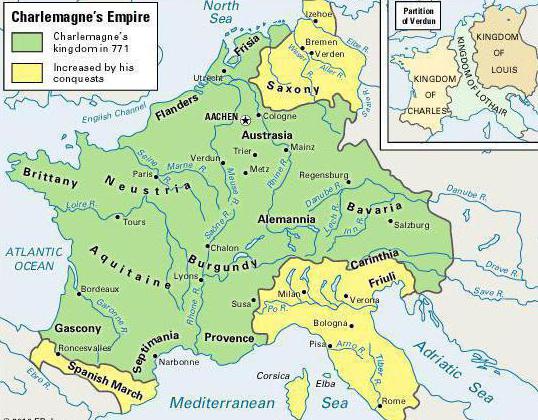
The history of Europe in the Middle Ages is characterized by the establishment in most countries of the feudal mode of production. The power of the monarch in the early stages of development was strong, but due to the strengthening of centrifugal tendencies, the states broke up into a number of independent possessions. In the 11th – 12th centuries, the rapid development of cities began, which became the basis of capitalist production.
New time
Europe, whose history is characterized by a rapid pace of development, in the XV-XVII centuries experienced a real turning point in socio-economic and political relations, primarily because of the beginning of the era of great geographical discoveries. Portugal, Spain, and after them the Netherlands, France embarked on a real race for the discovery and conquest of new territories.
In the economic sphere, the period of the so-called initial accumulation of capital begins when the preconditions for an industrial revolution developed. England became a pioneer in machine production: it was in this country that already in the 17th century the rapid development of large-scale industry began. Europe, whose history so far did not know anything like it, experienced the intensive development of industrial production, largely thanks to the English experience.
The era of bourgeois revolutions
The new history of Europe at the next stage was largely determined by the replacement of feudalism with the capitalist mode of production. The consequence of this struggle was a series of bourgeois revolutions, which Europe experienced in the 17th – 18th centuries. The history of these coups is closely connected with the crisis of absolutist regimes in the leading states of the mainland - England and France. The establishment of unlimited power of the monarch met stiff resistance from the third estate - the urban bourgeoisie, which demanded economic and political freedoms.
These ideas and aspirations of the new class were reflected in a new cultural trend - enlightenment, whose representatives put forward revolutionary ideas about the monarch’s responsibility to the people, natural human rights, etc. These theories and concepts have become the ideological basis for bourgeois revolutions. The first such revolution took place in the Netherlands in the 16th century, then in England in the 17th century. The great French revolution of the eighteenth century marked a new stage in the socio-economic and political development of Western Europe, since in its course the feudal order was legally abolished and a republic established.
West European countries in the 19th century
Understanding the significance of the Napoleonic wars reveals the general patterns by which history developed in the century under consideration. The countries of Europe completely changed their appearance after the Vienna Congress of 1815, which determined new borders and the territory of Western European states.
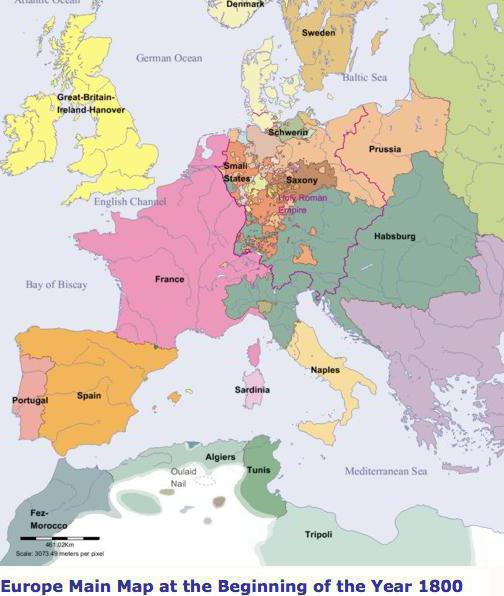
The principle of legitimism was proclaimed on the mainland, suggesting the need for rule of legal dynasties. At the same time, the conquests of revolutions and Napoleonic wars did not pass without a trace for the states of Europe. Capitalist production, the creation of large-scale industry, heavy industry brought into the arena a new class - the bourgeoisie, which from now on began to determine not only the economic, but also the political development of countries. Europe, whose history was determined by the change in socio-economic formations, has embarked on a new path of development, which was consolidated by the revolutions in France, the reforms of Bismarck in Germany, and the unification of Italy.
XX century in the history of Western Europe
The new century was marked by two terrible world wars, which again led to a change in the map of the mainland. After the end of the first war in 1918, the largest empires broke up, and new states formed in their place. Military-political blocs began to take shape, which subsequently played a decisive role in World War II, the main events of which unfolded on the Soviet-German front.
After its completion, Western Europe became a springboard for the capitalist camp that opposed the Soviet Union. Large political entities such as NATO and the Western European Union were created here, as opposed to the Warsaw Treaty Organization.
Western European countries nowadays
The countries of Western Europe include 11 states: Belgium, Austria, Great Britain, Germany, Ireland, Luxembourg, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Netherlands, Switzerland, France. However, for political reasons, it is also customary to include Finland, Denmark, Italy, Spain, Portugal, and Greece on this list.
In the 21st century, the continent tends to political and economic integration. The European Union, the Schengen area contribute to the unification of states in various fields. At the same time, today there are centrifugal aspirations of a number of states that want to pursue an independent policy, regardless of the decision of the European Union. The latter circumstance indicates the growth of a number of serious contradictions in the European zone, which are exacerbated by migration processes, which have especially intensified recently.