Over the past few decades, a lot of new information has been obtained about bile and its acids. In this regard, it became necessary to revise and expand ideas about their significance for the life of the human body.
The role of bile acids. General information
The rapid development and improvement of research methods made it possible to study bile acids in more detail. For example, now there is a clearer idea of metabolism, of their interaction with proteins, lipids, pigments and their content in tissues and fluids. Information has been confirmed that bile acids are of great importance not only for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. These compounds are involved in many processes in the body. It is also important that thanks to the use of the latest research methods, it was possible to most accurately determine how bile acids behave in the blood, and also how they affect the respiratory system. Among other things, compounds affect some parts of the central nervous system. Their importance in intracellular and external membrane processes has been proven. This is due to the fact that bile acids act as surfactants in the internal environment of the body.
Historical facts
This type of chemical compounds was discovered by the scientist Strecker in the middle of the 19th century. He managed to find out that bile of cattle has two organic acids. The first of them contains sulfur. The second also contains this substance, but has a completely different formula. During the breakdown of these chemical compounds, cholic acid is formed. As a result of the conversion of the first compound mentioned above, glycerol is formed. At the same time, another bile acid forms a completely different substance. It is called taurine. As a result, the original two compounds were given names of the same name as the produced substances. So appeared tauro-and glycocholic acid, respectively. This discovery of the scientist gave a new impetus to the study of this class of chemical compounds.
Sequestrants of bile acids
These substances are a group of drugs that have a lipid-lowering effect on the human body. In recent years, they have been actively used to lower blood cholesterol. This has significantly reduced the risk of various cardiovascular pathologies and coronary disease. At the moment, in modern medicine, another group of more effective drugs is widely used. These hypolipidemic agents are statins. They are used much more often due to fewer side effects. Currently, sequestrants of bile acids are used less and less. Sometimes they are used exclusively as part of a comprehensive and supportive treatment.
Detailed information
The steroid class includes monocarbainic hydroxy acids. They are active solids that are poorly soluble in water. These acids result from the processing of cholesterol by the liver. In mammals, they are composed of 24 carbon atoms. The composition of the dominant bile compounds in different animal species is different. These types form taucholic and glycolic acids in the body. Chenodeoxycholic and cholic compounds belong to the class of primary. How are they formed? In this process, the biochemistry of the liver is important. Primary compounds result from cholesterol synthesis. Next, the conjugation process occurs along with taurine or glycine. Then these types of acids are secreted in bile. Litocholic and deoxycholic substances are part of the secondary compounds. They are formed in the colon from primary acids under the influence of local bacteria. The absorption rate of deoxycholic compounds is significantly higher than that of lithocholic compounds. Other secondary bile acids occur in very small volumes. For example, they include ursodeoxycholic. If chronic cholestasis occurs, then these compounds are present in large numbers. The normal ratio of these substances is 3: 1. While with cholestasis, the content of bile acids is pretty much exceeded. Micelles are aggregates of their molecules. They are formed only when the concentration of these compounds in aqueous solution exceeds the limit mark. This is due to the fact that bile acids are surfactants.
Cholesterol
This substance is poorly soluble in water. The rate of cholesterol solubility in bile depends on the ratio of lipid concentration, as well as the molar concentration of lecithin and acids. Mixed micelles occur only while maintaining a normal proportion of all these elements. They contain cholesterol. The precipitation of its crystals is subject to a violation of this ratio. The functions of bile acids are not limited to removing cholesterol from the body. They contribute to the absorption of fats in the intestines. Micelles also form during this process.
Connection movement
One of the main conditions for the formation of bile is the active movement of acids. These compounds play an important role in the transport of electrolytes, water in the small and large intestines. They are solid powdery substances. Their melting point is quite high. They have a bitter taste. Bile acids are poorly soluble in water, while in alkaline and alcoholic solutions it is good. These compounds are derivatives of cholanic acid. All such acids occur exclusively in cholesterol hepatocytes.
Influence
Among the acidic compounds, salts are of primary importance. This is due to a number of properties of these products. So, for example, they are more polar than salts of free bile acids, have a small size of the limiting concentration of micelle formation and are secreted faster. The liver is the only organ capable of converting cholesterol into special cholanic acids. This is due to the fact that the enzymes that take part in conjugation are contained in hepatocytes. The change in their activity is directly dependent on the composition and vibration rate of bile acids of the liver. The synthesis process is regulated by a negative feedback mechanism . This means that the intensity of this phenomenon is in proportion to the flow of secondary bile acids in the liver. The rate of their synthesis in the human body is quite low - from two hundred to three hundred milligrams per day.
Main goals
Bile acids have a wide range of uses. In the human body, they mainly carry out the synthesis of cholesterol and affect the absorption of fats from the intestines. In addition, the compounds are involved in the regulation of bile secretion and bile formation. These substances also have a strong influence on the process of digestion and absorption of lipids. Their compounds gather in the small intestine. The process occurs under the influence of monoglycerides and free fatty acids, which are located on the surface of fat deposits. In this case, a thin film is formed, which prevents the small droplets of fat from joining into larger ones. Due to this, a strong decrease in surface tension occurs . This leads to the formation of micellar solutions. They, in turn, facilitate the action of pancreatic lipase. With the help of a fatty reaction, she breaks them down to glycerin, which is subsequently absorbed by the intestinal wall. Bile acids combine with fatty acids that are not soluble in water and form choleic acids. These compounds are easily broken down and rapidly absorbed using the villi of the upper small intestine. Choleic acids are converted to micelles. Then they are absorbed into the cells, while easily overcoming their membranes.
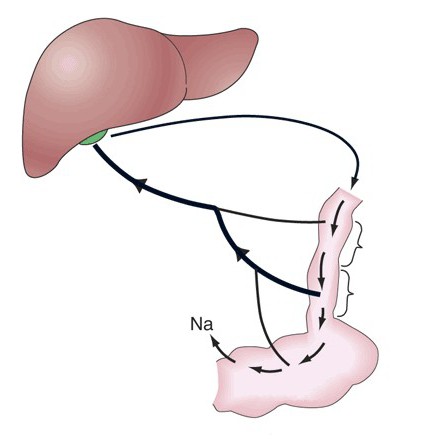
Information was received from the most recent research in this area. They prove that the relationship of fatty and bile acids in the cell breaks down. The former are the final result of lipid absorption. The latter - through the portal vein penetrate the liver and blood.