Solving problems in genetics for a blood group is not only an exciting pastime in biology classes, but also an important process that is used in practice in various laboratories and medical genetic consultations. This has its own characteristics that are directly related to the inheritance of genes in the human blood group.
Different options for recording a person’s blood type
Blood is a liquid medium of the body, and in it are formed elements - red blood cells, as well as liquid plasma. The presence or absence of any substances in human blood is programmed at the genetic level, which is displayed by the corresponding record when solving problems.
The most common are three types of recording of a person’s blood group:
- According to the system AB0.
- By the presence or absence of a Rhesus factor.
- According to the MN system.
AB0 system
This type of recording is based on gene interaction such as coding. It says that a gene can be represented by more than two different alleles, and each of them in the human genotype has its own manifestation.
To solve the blood group problem, one more rule of coding should be remembered: there are no recessive or dominant genes. This means that different combinations of alleles can produce a wide variety of offspring.
Gene A in this system is responsible for the appearance of antigen A on the surface of red blood cells, gene B for the formation of antigen B on the surface of these cells, and gene 0 for the absence of one or another antigen. For example, if a person’s genotype is written as IAIB (gene I is used to solve the problem of genetics per blood group), then both antigens are present on his red blood cells. If he does not have these antigens, but the antibodies “alpha” and “beta” are present in the plasma, then his genotype is written as I0I0.
Based on the blood group, a transfusion is carried out from the donor to the recipient. In modern medicine, they came to the conclusion that the best transfusion is the case when both the donor and the recipient have the same blood group. However, a situation may arise in practice when it is not possible to find a suitable person with the same blood group as the victim who needs a transfusion. In this case, phenotypic features of the first and fourth groups are used.
People with the first group on the surface of red blood cells do not have antigens, which makes it possible to transfuse such blood to any other person with the least consequences. This means that such people are universal donors. If we are talking about group 4, then such organisms belong to universal recipients, that is, they can receive blood transfusions from any donor.
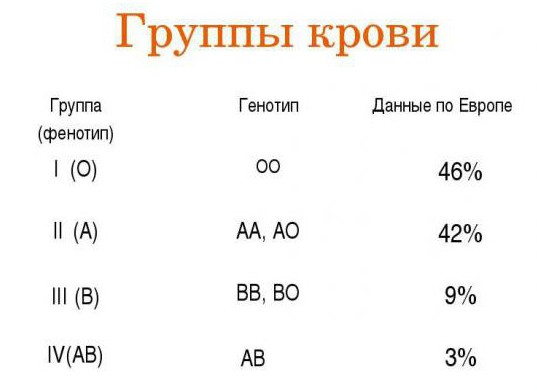
Tasks for a blood group require a certain record of genotypes. Here are 4 groups of people by the presence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells and their possible genotypes:
I (0) -group. Genotype I0I0.
II (A) group. Genotypes IAIA or IAI0.
III (B) -group. Genotypes IBIB or IBI0.
IV (AB) -group. Genotype IAIB.
Rhesus blood types
Another way to designate human blood groups, which is based on the presence or absence of a Rh factor. This factor is also a complex protein that forms in the blood. It is encoded by several pairs of genes, however, the genes, which are denoted by the letters D (positive Rhesus, or Rh +) and d (negative Rhesus, or Rh-), play a decisive role. Accordingly, the transmission of this trait is determined by monogenic inheritance, rather than coding.
Tasks for blood groups with a solution require the following record of genotypes:
- People with a Rh-positive blood group have the DD or Dd genotypes.
- In people with a negative Rh factor, the genotype is written as dd.
MN system
This recording method is more common in Western Europe, but can also be used to solve the problem of blood type. It is based on the manifestation of two allelic genes that are inherited by type of coding. Each of these alleles is responsible for the synthesis of protein in human blood. If the genotype of an organism is a combination of MM, then only the type of protein that is encoded by the corresponding gene is present in its blood. If such a genotype is changed to MN, then two different types of protein will already be in the plasma.
Tasks for a blood group according to the MN system require the following recording of genotypes:
- A group of people with the genotype MN.
- A group of people with the genotype MM.
- A group of people with the NN genotype.
Features of solving genetics problems
When making genetic tasks, the following rules must be observed:
- Write a table of the studied traits, as well as genes and genotypes that are responsible for the manifestation of this trait.
- Write the genotypes of the parents: first, the female is written, and then the male.
- Designate the gametes that each individual gives.
- Trace the genotypes and phenotypes of the descendants in F1, and, if the task requires it, write down the probability of their occurrence.
Also, solving genetics problems for blood groups requires an understanding of the type of interaction that you have been offered with the condition. The course of the decision depends on this, and you can also predict in advance the results of the crossing and the possible likelihood of zygotes. If two or more types of gene interaction are suitable for the same condition, the simplest one is always taken.
Tasks on the AB0 system
Tasks in biology per blood group in the AB0 system are solved as follows:
“A woman who has a first blood group married a man with a fourth blood group. Determine the genotype and phenotype of their children, as well as the likelihood of zygotes with different genotypes. ”
First we need to know which genes are responsible for which manifestation of the signs:
| Sign | Genes | Genotype |
| 1 blood type | I0 | I0I0 |
| 2 blood type | IA, I0 | IAIA, IAI0 |
| 3 blood type | IB, I0 | IBIB, IBI0 |
| 4 blood type | IA, IB | IAIB |
Then, we write the genotypes of the parents and their gametes:
- P: ♀ I0I0 x ♂ IAIB.
- G: I0 I0 IA IB.
Further, we alternately cross the gametes obtained among ourselves. To do this, you can use the Pennet lattice:
| gametes female / male | IA | IB |
| I0 | IAI0; 2 blood type | IBI0; 3 blood type |
| I0 | IAI0; 2 blood type | IBI0; 3 blood type |
Since the probability of gamete formation of both parents is 50%, then each of the 4 variants of the genotypes of children can appear with a 25% probability.
Problem solving: blood type, Rh factor
When solving problems for the Rh factor, we can use the rules of the usual monogenic inheritance of characters. For example, we a man and a woman got married and both were Rh positive heterozygotes. The first item we write a table of genes and corresponding phenotypic traits:
| Sign | Gene | Genotype |
| Rhesus positive; Rh + | D | DD, Dd |
| Rhesus negative; Rh- | d | dd |
Then we record the genotypes of the parents and their gametes:
- P: ♀ Dd x ♂ Dd.
- G: D d D d.
Mendel’s second law states that when two heterozygotes are crossed, splitting by phenotype will be 3: 1, and by genotype 1: 2: 1. This means that we can get children with a positive Rhesus factor in 75% of cases, and with a negative Rhesus factor with a probability of 25%. Genotypes can be as follows: DD, Dd and dd in a ratio of 1: 2: 1, respectively.
In general, tasks on blood groups and Rh factor are solved much easier than on the AB0 system. It is important to determine the Rhesus factor of parents and their unborn children when planning a family, because there are cases of Rhesus conflict when the mother has Rh + and the child has Rh-, or vice versa. In such cases, there is a threat of miscarriage, so pregnant women are observed in special institutions.
Tasks for blood groups according to the MN system
In genetic problems of this type, the rules of coding are observed, but the solution is simplified by the presence of only two types of allelic genes. Suppose a man with the MN genotype married a woman with the same genes. It is necessary to determine the genotype and phenotype of children, as well as the likelihood of their occurrence.
In this case, the recording of genes and traits is not necessary, since the notation is conditional and does not play a big role in solving the problem.
If we paint the Pennet lattice, we get a similar picture, as with monogenic inheritance. However, a 1: 2: 1 genotype cleavage will also coincide with a phenotype cleavage, since here each allele has its own manifestation, and recessive and dominant genes are absent. Children with the MN genotype will be born with a 50% probability, when a child with the MM or NN genotype will appear with a 25% probability each.