Of great importance for understanding this or that phenomenon of public life are its signs. Capitalism is a system of economic relations based on the dominance of private private, free enterprise and focused on profit. It should be noted right away that this concept is the name of only an ideal model, since in no country in the world does such a structure exist in its purest form.
The emergence of the concept
To analyze the features of the economic development of countries in a historical perspective, its features help. Capitalism is a term that has been actively used since the second half of the 19th century. It was first used in France, then German and English authors introduced it into scientific circulation.
An interesting fact is that at first it had a negative meaning. Scientists, writers put in this word a negative attitude to the dominance of finance, which was observed in developed European countries in the middle of this century. Representatives of socialism (Marx, Lenin and others) used this concept especially actively.
Market Theory and Class Conflict
Characterize the features of the development of the economy and trade help their signs. Capitalism is a system based on the free functioning of the market, which serves as an arena of confrontation between the working class and the owners. The former strive to sell their strength more expensively, while the latter seeks to buy it cheaper. In addition, it is the market that is the main condition for trade, without which it is impossible to imagine the existence of a capitalist structure. The second important feature of the system is the concentration of the means of production in the hands of the upper classes and the preservation of the labor force by the proletariat.
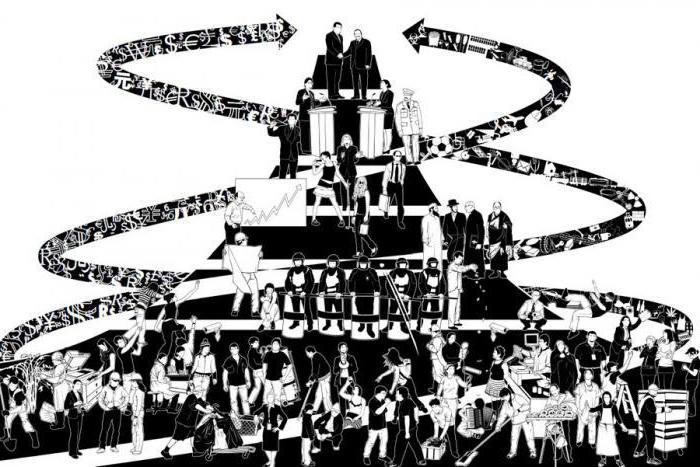
Between these groups there is a constant struggle for labor and wages. This leads to the class struggle, which in a number of states led to revolutions. However, practice shows that the capitalist way of life is most acceptable for the normal functioning of states, and therefore from the very beginning it quickly spread throughout the world, capturing almost all spheres of society, including politics and culture. The above features of the system were highlighted by the famous scientist Marx, who devoted one of his most fundamental monographs to this issue.
Protestant Ethics Concept
To understand the reasons for the emergence of this new for Western European history, its features help. Capitalism is not only a special form of organization of production, but also a specific way of organizing society. This is how the famous German scientist and sociologist Weber considered this stage of economic history.
Unlike Marx, he believed that this system is inherent only in Western European countries. In his opinion, it arose in those states where Protestantism was established, which developed a cult of labor discipline in society, a high degree of social organization, as well as the desire for profit and income. He highlighted the following signs of the development of capitalism: the competition of producers, the presence of a dynamic market, the active use of capital in entrepreneurial activity, the desire to maximize profits. And if Marx believed that this structure not only influences, but also determines the policies of countries, Weber opposed these two social spheres, although he recognized that they are closely in contact.
About innovation
The main signs of capitalism have been the subject of research by the famous political scientist and sociologist Schumpeter. He identified the following features of this system: a dynamic market, entrepreneurship and the dominance of private property. However, unlike the indicated authors, the economist singled out such an important component of capitalist production as the introduction of innovations. In his opinion, it is the introduction of innovations that stimulates the rapid development of the economies of countries.
At the same time, Schumpeter assigned great importance to lending, which provides entrepreneurs with the opportunity to introduce modern technology and thereby increase production efficiency. The scientist believed that this way of life ensured the material well-being of society and the personal freedom of citizens, but he saw the future of the system in a pessimistic light, believing that over time it would exhaust itself.
The emergence of manufactories
One of the main prerequisites for the transition from the feudal mode of production to the capitalist one was the departure from the old guild system and the transition to the division of labor. It is in this important change that one should look for the answer to the question of why the emergence of manufactories is considered a sign of the birth of capitalism.
Indeed, the main condition for the existence and normal functioning of the market is the widespread use of wage labor. In the 14th century, in many European cities, manufacturers abandoned the traditional set of apprentices and began to attract people specializing in a particular craft to their workshops. Thus arose the labor market, which, according to Marx, is the main sign of the capitalist structure.
Types of enterprises
In Western European countries there were various types of manufactories, which indicates the rapid development and introduction of a new method of production. An analysis of the problem under consideration (why the emergence of manufactories is considered a sign of the birth of capitalism) allows us to understand the development of the economy. The owners of the scattered enterprises handed out the raw materials to the workers at home, then, already processed, they went to a professional craftsman who, having made yarn, gave the material to the next manufactory. So the work was carried out by a number of workers who transferred the manufactured goods along the chain. In a centralized manufactory, people worked in the same room, using technology. These different types of enterprises prove the high rates of development of capitalist production on the mainland.
Scientific revolutions
Signs of the emergence of capitalism are associated with the peculiarities of the European economy, where the transition to trade began very early due to the development of cities and the formation of markets. The new impetus for the development of the capitalist mode of production was the introduction of new technologies. This brought the economy to a whole new level. The use of machines in factories has allowed entrepreneurs to increase sales. Advances in science have led to the fact that the creation of the gross product has become cheaper, because instead of workers, machines are now used in enterprises.
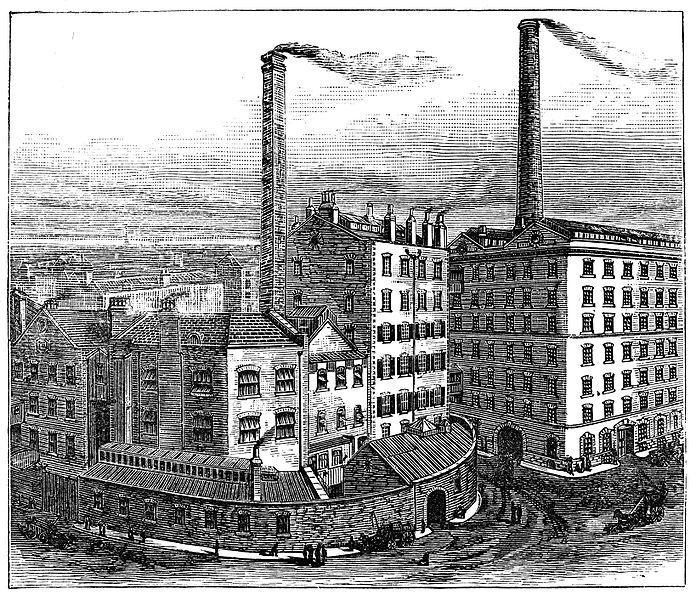
Of great importance was the invention of the steam engine, electricity, as well as the construction of railways. The discovery and development of new mineral deposits led to the rapid development of heavy industry and metallurgy. These changes completely changed the urban appearance of Western European countries, as well as Russia, where, after the abolition of serfdom, the rapid development of industry began. So, the signs of capitalism in the 19th century were determined by the introduction of the achievements of science into production.
The emergence of monopolies
During the first stage of the development of capitalism, production organizations were single and medium in size. The scale of their production was not wide, and therefore entrepreneurs could single-handedly run their own business. In the 19th century, the system entered a new phase of development. The volume of production increased sharply, the factories expanded, which led to the need to combine the efforts of entrepreneurs. Based on the foregoing, we can distinguish the signs of monopoly capitalism: concentration of production, reduction in the number of factories, the emergence of large, capital-intensive enterprises.

At the turn of the century, the main role was played by heavy industry: machine building, metalworking, oil production and others. As a rule, enlargement took place within the framework of one industry in which such associations as cartels and syndicates arose. The first concept should be understood as an agreement of several independent enterprises that coordinate among themselves the price of goods, markets and quotas. The second term means a higher degree of monopolization, in which firms, while maintaining legal and economic independence, organize a single office for the sale of their products.
Large forms of enterprises
The signs of monopoly capitalism allow us to understand what were the features of the new stage of development of this system. The highest form of association of factories, factories and firms are trusts and concerns. The first organizations jointly carry out not only sales, but also production, and are also subject to unified management, but at the same time they maintain financial independence. Trusts are created in any one industry and immediately occupy a leading position. Concerns are considered the most developed form of association. They are formed in related industries and have unified finances.
Capital mergers provide faster and more efficient integration, unlike the above forms. The signs of capitalism in the 20th century testify to the development of this system due to its entry into a new, higher phase of its development, which gave scientists the opportunity to talk about the onset of the phase of imperialism, which is characterized by the merger of banks and production.