Siberian platform, or. as it is also called, the East Siberian platform, in order to distinguish it from the West Siberian, is one of the main objects of study of Russian geology. Significant mineral deposits are located on its territory, in addition, the study of its formation and current state is interesting from a purely scientific point of view. The bowels and landform of the Siberian platform excite the minds of more than one generation of scientists. Let us and we will analyze the main issues related to this continental stretch of the earth's crust.
Geographic location
First of all, we will find out where the foundation of the Siberian platform is geographically located. Its main massif is located in the eastern part of Russian Siberia in the territories of the Siberian and Far Eastern Federal Districts. In the south, the platform reaches the territory of Mongolia.
From the west, its natural boundary is the channel of the Yenisei River, in the north - the Byrranga Mountains in Taimyr, in the east - the Lena River, in the south - the Yablonovy, Stanovoi, Dzhugdur ridges, as well as the Baikal fault system.
In the geological section, the Siberian platform is a component of the Eurasian lithospheric plate and is located in its northeastern part. In the west, it adjoins the West Siberian platform, in the south - the Ural-Mongolian belt, in the east - the West Pacific belt, and in the north the waters of the Arctic Ocean, which are hidden under ice for most of the year, are splashing.
History of education
Now let's find out how the corresponding relief shape of the Siberian platform was formed over millions of years of geological processes.
This continental stretch of the earth's crust belongs to the type of ancient platforms, or cratons. Unlike other formations, it was formed back in the Precambrian period, which implies a minimum age of such formations in 541 million years. They served as the basis for the formation of continents, becoming their core.
The Siberian platform belongs to the Laurasian type. This means that in the Mesozoic era it was part of the mainland Laurasia. But much earlier than this period, the ancient Siberian platform began to form. The shape of the relief began to be outlined in the Archean era, that is, no later than 2.5 billion years ago. True, then it faintly resembled the modern one. The foundation was completed at the beginning of the Proterozoic era, at the end of which the platform was covered by a shallow sea, which significantly affected the formation of a sedimentary cover. In the late Ordovician, the platform of the platform was the continent of Angarida. Later it merged with other continents of the Earth into a single continent - Pangea. In the Mesozoic, as mentioned above, the Siberian platform, together with the West Siberian plate and the East European platform, after the division of Pangea, formed the continent of Laurasia. After its collapse, the Siberian platform became part of Eurasia.
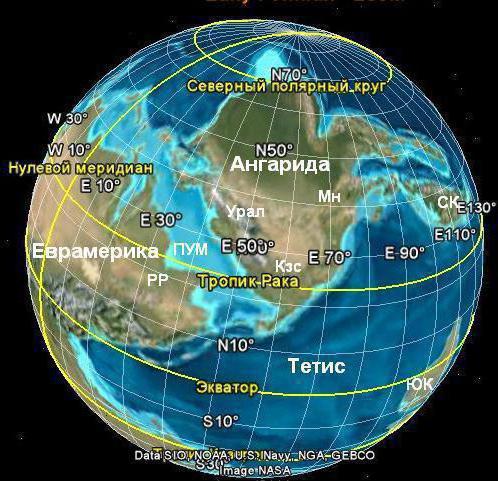
That's how the Siberian platform was formed approximately.
Structure
The structure of the Siberian platform is similar to the structure of all other ancient platforms. At its base is the foundation, formed back in the Archean and at the beginning of the Proterozoic era. A sedimentary cover made of rocks formed in later eras covers the foundation from above, mainly being a product of magmatic activity. This is due to the fact that in ancient times it was a region with high volcanic activity, and magma, emerging from the bowels of the earth, formed a cover of traps. But in two places the foundation of the platform still comes to the surface. The exit of Precambrian rocks to the surface is commonly called shields.
Shields consist of three rock complexes: greenstone, granular belts, as well as a complex of para- and orthogneisses.
Shields of the Siberian platform
On the territory of the Siberian platform, there are two shields - Anabar and Aldan.
Aldansky is located in the southeastern part of the platform. In geography, this place is called the Aldan Highlands.
The Anabar shield is much smaller and is localized in the northern part of the platform on the territory of the Central Siberian Plateau, in a place known as the Anabar Plateau. Its maximum height above sea level is 905 meters.
Central Siberian Plateau
Now let's see what the modern relief of the Siberian platform looks like.
The main part of the territory is occupied by the Central Siberian Plateau. There is an alternation of low ridges and plateaus. The highest point of the plateau is Mount Kamen. It is located in the middle mountains of Putorana and has a height of 1701 meters above sea level. But the average height of the Central Siberian Plateau is only 500-800 meters. In addition, the Anabar Plateau, which we mentioned a little higher, should be distinguished on this plateau. It is a protrusion of the Anabar shield to the surface. The highest point of this plateau is 905 meters above sea level.
In the west, the plateau is surrounded by the Yenisei Ridge, which at the same time serves as the border for him and the Siberian platform as a whole. Its average height is 900 meters above sea level, but it reaches its maximum on Mount Enashimsky Polkan and is 1104 m. The West Siberian Platform lies behind the Yenisei Ridge.
In the south and southeast, the border of the Central Siberian Plateau is the Angara Range. The average height is from 700 to 1000 meters above sea level, the maximum - 1022 m.
In the east and northeast, the Central Siberian Plateau, and hence the corresponding landform of the Siberian Platform, smoothly passes into the Central Yakut Plain. In another way, it is also called the Central Yakut, or Leno-Vilyui Lowland. In most of its territory, the maximum height above sea level does not exceed 100-200 m, but on the outskirts it can reach 400 meters.
The relief shape of the Siberian platform on the internal watersheds is quite smooth. Therefore, the height of these watersheds does not exceed 400-600 meters. In particular, this statement refers to the boundaries of the Angara, Lower Vilyui and Tunguska river basins.
Other relief elements of the Siberian platform
In the south-east of the Central Siberian Plateau lies the Aldan Highlands. Unlike the objects listed above, it is not part of the plateau, but, nevertheless, is part of the Siberian platform, representing an exit to the surface of its crystalline shield. It is on the territory of the Aldan Highlands that the highest point of the Siberian Platform is located, reaching a height of 2306 meters above sea level. But most of the highlands have a height not exceeding thousands of meters.

The relief shape of the Siberian platform in the extreme southeast is mountainous. Here, in the Khabarovsk Territory, the Dzhugdzhugur Mountains are located. Although the average height of this complex is higher than the Aldan Highlands, the highest peak of Topko is inferior in size to the highest point of the highlands. Topko Mountain has a height of only 1906 meters above sea level. The length of the Dzhugdzhugur Mountains from northeast to southwest along the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk is 700 kilometers.
So, in general terms, we learned what the relief shape of the Siberian platform is.
Hydrography
Now let us dwell on the main water bodies of the Siberian platform. As a rule, their initial location depended directly on the relief, and only then, after their emergence, the rivers and lakes, which are quite large in the region, themselves begin to influence the formation of the terrain.
The largest water artery, the Yenisei, is the natural western border of the Siberian platform. This is one of the largest rivers in the world, the length of which is 3487 meters.
To a large extent, the border of the Siberian platform, only already in the east, is another large river - the Lena. Although partially it carries its waters directly through the platform. Its length is 4400 km.
In the south, the Siberian platform in a small area is in contact with the deepest lake in the world - Baikal.
Among other large water arteries flowing along the Siberian platform, the Angara, Lower Vilyui and Tunguska rivers should be distinguished.
Minerals of the southern part of the Siberian platform
Now we should study the minerals of the Siberian platform. It should be noted that mother nature gave them a considerable amount of the region. What is stored the bowels of the East Siberian platform?
Aldan shield is a real repository of iron ore. In addition, copper, coal, mica, and even gold are also mined in the Aldan Highlands.
But the largest reserves of gold and diamonds are located on the territory of Yakutia, which is the real treasury of Russia. In the same republic, “combustible stone” is mined on the territory of the Lensky coal basin.
In addition, coal mining occurs in the bowels of the Tunguska and Irkutsk basins, which are located in the territories of Yakutia, the Krasnoyarsk Territory and the Irkutsk Region.
Minerals of the north of the Siberian platform
The mineral resources of the Siberian platform in its northern part are mainly concentrated on the territory of the Anabar shield. There are deposits of apatites, anorthosites, and titanomagnetites. Copper and nickel are mined near Norilsk.
But on oil and gas, in comparison with the regions of Western Siberia, the territory of the East Siberian platform is poor. Although there are also oil fields in the south and north, but in much smaller volumes.
The soil
The topmost layer covering the area of the Siberian platform is the soil. Consider what species they are represented in the study region.
Given that most of the Siberian platform is covered by taiga, the soils formed here correspond to this natural zone. In the north, it is permafrost-taiga, to the south, sod-forest. In the south, soddy-podzolic soils occupy significant areas , sometimes gray forest and even chernozems are found. Only the last type of soil from all of these is highly fertile.
General characteristics of the Siberian platform
As you can see, the Siberian platform is one of the oldest geological formations on Earth. The relief in most of the territory is represented by plateaus, and only at the borders of the platform is framed by relatively low mountains or elevations.
The region is very rich in various minerals. Among them are iron ores, coal, apatites, gold and diamonds. There is oil, although this is not the main indicator of the region’s wealth. But the soils on the platform do not differ in high fertility.