Taxes in modern society have two functions. On the one hand, they fill the budget (the main economic instrument of the state), and on the other, they regulate the economy, make it possible to align social standards and prioritize the development of the sectors needed by society. A harmonious system of these payments in a codified form is legally enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Functionally, it consists of two parts: the general, which establishes the integrating principles of the tax system, and the special, which reveals the mechanism of each individual tax or fee. Separate chapters in the second part of the Tax Code present value added tax (VAT) and excise duty (or simply excise tax). This article will be devoted to their consideration.
State tax policy
The peculiarity of tax regulation is that the state changes the macroeconomic environment by varying tax rates. This is the tax policy. It is characteristic that they must correspond to the reproductive principle, that is, contribute to the growth of social production, to an increase in labor productivity. However, tax regulation is a delicate matter, therefore, changing the tax rate, you should carefully keep your finger on the pulse of the economic situation.
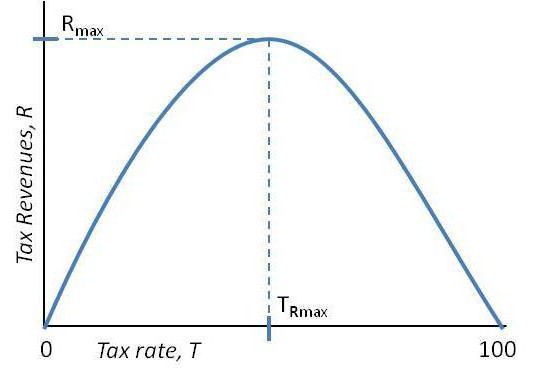
Its regularities are demonstrated by the Laffer curve, named after an economist from the University of Los Angeles, who discovered the principle of dependence of budget revenues on tax rates. He displayed the functional dependence classically: along the abscissa axis - the percentage charged by the state to the treasury, along the ordinate axis - the amount of tax received. At first, this curve increases. The economic meaning of this is as follows: production in this segment increases faster than the tax rate, respectively, and the economy is progressing, and tax revenues are increasing. However, at the level of 40-50% of the tax rate (for countries of the I world) and 35-40% (for countries of the III world), the curve reaches a maximum and begins to decrease. In this case, they say that the tax policy is discriminatory. With relatively high incomes of the working population, the tax burden is 40–45% of its income.
Therefore, a consistent decrease in the share of the tax burden in relation to population incomes is considered to be an indicator of the progressiveness of social policy.
Direct and indirect taxes
Taxes by the nature of tax exemptions are divided into direct and indirect. The tax base for direct taxes is income (salary, profit, rent, interest) or property (land, home, securities) owned by the taxpayer. Examples of direct taxes include land tax, income tax, property tax , transport tax, and income tax . Indirect tax, in contrast to direct, has a fundamentally different character - premiums to price or tariff.

However, for the benefit of the case, we comment on the circumstances of the formation of the tax base for income tax. The term “indirect” is also used there, but in this aspect it has nothing to do with indirect taxes (income tax, as we have already mentioned, is direct). In this interpretation, the similarity of the name is not associated with the characteristic of the tax itself, but with the process of determining its value. When determining the tax base, direct costs associated with the main production are deducted from it and indirect costs are not deducted. Income tax in such a purely economic way contributes to greater specialization of the company, minimizing its non-production costs.
As for indirect taxes, the outstanding German economist Karl Marx commented on their essence in the hidden, hidden in every purchase, state seizure of funds from citizens. It seems that consumers just buy the product, so they can not control the appetite of the budget. In fact, the payer is the consumer, the seller of goods and services acts as a collector of indirect taxes and an intermediary in transferring them to the state.
The following net indirect taxes are valid in Russia: value added tax (VAT), excise taxes and customs duties.
Indirect taxes. VAT
VAT was first introduced in France, in 1958 it was pilot tested and then introduced. In the 70s, it was borrowed by other European countries. In Russia, the Law “On VAT” was adopted in 1992 by the Government of Yegor Gaidar. First, its rate was 28%, which created a significant tax burden, and then it was reduced twice: to 20% and 18%, respectively.
Indirect VAT is successfully distributed in global tax systems. What is the reason for its popularity? Most likely, it is insensitive to crisis phenomena in the economy and acyclicity, because it is not production that is taxed, but consumption.
The main directions of the Russian budget policy for 2012 and for the period until 2014 emphasize the leading importance of VAT in the federal tax system. This tax accounts for 32–35% of federal tax revenues.
VAT as an example of an indirect tax assumes the basis of taxation (according to Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) the sale of goods and services in Russia, the transfer of goods and the performance of services for which no deduction is expected, installation and construction work carried out for own needs, import of goods into the territory RF
Preferential treatment in the VAT tax base
The Tax Code excludes certain operations from the extremely wide scope of VAT taxation: the circulation of rubles and foreign currency, the transfer of property by a company to its assignee, the transfer of property for the statutory activities of non-profit organizations, transfer of property as an investment, return of the down payment to a participant in a business partnership and society, privatization by physical persons of state and municipal apartments, confiscation, inheritance of property.
Indirect VAT is also subject to a number of preferential tax rates. Firstly, a zero rate. It is used for goods exported, determined by the regime of STZ (customs free zone). It is also used in relation to services for loading, transporting, escorting exported goods related to the international transit of goods through the territory of Russia and for the transport of baggage and passengers if they are not sent from the territory of the Russian Federation.
However, if we talk further about such a complex tax as VAT, then it also applies a reduced rate (10%) with respect to food, children's goods, the media and books. Thus, the federal tax legislation offers a facilitated tax regime for these categories of goods by lowering their prices and, accordingly, increasing demand for them. As you can see, indirect taxes in the Russian Federation operate in a certain area that is not related to production cycles, and their inflow to the budget is more uniform.
What else is included in the tax base of VAT
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs, when filling out a VAT tax return, also include in the tax base:
- Advances received. The exception is similar payments for goods subject to a rate of 0% (see above) and for products having a production cycle exceeding 6 months.
- Funds with the status of “financial assistance”, but received in exchange for the sold services and goods.
- Interest on a commodity loan, bills, bonds regarding the excess of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- The listed compensation under insurance contracts in case of default by the counterparty.
But there is an exception to the rule: a legal entity or individual entrepreneur whose income for the previous 3 months amounted to no more than 2 million rubles, writes the corresponding application to the tax authority and is exempted from VAT for 12 months.
On the complexity of determining the VAT base
We examined the example of indirect VAT tax according to Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation only in terms of the formation of a tax base. Why one example? For readers to appreciate the complexity of its calculation according to primary documents. For a large manufacturing enterprise, the competent preparation of a VAT tax return, entailing the non-application of penalties on the part of the tax, is relevant and important. This is a truly qualified work requiring specific knowledge of the auditor. This area of activity is defined by Law N 943-1 “On Russian Tax Authorities” dated 03/21/1991. Value added tax, as well as corporate income tax, are the most difficult to calculate, therefore, even inside the tax authorities there is an unspoken specialization: some people check VAT, others - income tax. Much less common are generalists who can do both.
About the method of tax audits of VAT
Let's look at the “inner kitchen” of the tax, related to checking, for example, indirect VAT. Generally speaking, checks are cameral, visiting and including both of the previous types. According to the degree of coverage of the tax base, they are divided into thematic and complex, continuous and selective.
How does a desk audit of VAT take place? Tax inspectors carry it out directly in their office. At their service are tax declarations previously submitted by the audited legal entity or individual entrepreneur and the accounting registers and primary documents required during the audit itself. Field inspection is carried out directly at the accounts department of a legal entity (entrepreneur).
As a rule, on the eve of a planned exit complex documentary audit of VAT, an off-site check of the VAT reporting provided by the taxpayer and the calculations submitted to them is carried out to subsequently determine its discrepancies with the tax auditors actually determined by the primary tax documents.
VAT, as an example of an indirect tax, demonstrates two areas of audit by auditors of an enterprise’s statements: the completeness of the VAT tax base presented therein and the correct application of tax deductions by accountants.
Analysis of the purchase of goods during the audit of VAT
With a comprehensive check, at first the availability of primary documents by suppliers is carefully checked. Regarding suppliers, the figures for the goods and services they provide both in the tax base and in the deduction (determined in accordance with article No. 171-173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) can be taken into account only if certain conditions are met. There must be an initial document - an invoice from the supplier, which according to accounting is capitalized on the account allocated to it, the transaction on it is included in the corresponding tax reporting period (meaning the corresponding tax return).
An example of such a reimbursement is the return of the excess of the actually paid VAT over a certain Tax Code of the Russian Federation in the following situation: a publishing company buys paper and paints, paying 18% tax, but finished goods (books) are taxed 10%. Based on the above, the amount of excess tax on the purchase of paper and paints over tax on the sale of books is included in the tax deduction.
Analysis of the sale of goods during the audit of VAT
The sale of goods is monitored on the basis of invoices issued by the audited legal entity and its sales journal (a specific consolidated tax register, and in fact a handwritten database for the tax return).
This check relates to the compliance of accounting registers in terms of settlements with suppliers and contractors and settlements with accountable persons. In this case, the second copies of invoices must be attached to the journal.
Indirect VAT is determined by the principle of non-operation of operations (for the delivery of each product there must be a corresponding calculation by bank transfer - from the current account of the enterprise, or from the cash desk - in cash). In this way, possible attempts to return VAT to the enterprise for virtually nonexistent transactions are determined.
The tax authorities verify transactions on the account number 201 01 610 and the account number 201 04 610. If there is no invoice for the sale of goods (services), a counter tax audit is carried out on it in the accounting department of the legal entity’s counterparty. If there is none there, the transaction is fictitious, and this is an economic crime. At the same time, attention is drawn to the chronological order of preparation and registration of invoices. Selective-counter checks are also assigned for large deliveries for which invoices are available.
An example of a tax error when selling a product
The supplier should have competent legal support for the execution of contracts. The point is that the sale of services and goods should always be subject to an increase in their price by the amount of VAT. The parties to the contract are obliged to clearly define the mandatory requisite of the indicated price - with or without tax. The price without VAT is indicated in the contract, it is it that acts as the basis of taxation. Therefore, it is highly desirable to allocate the VAT amount in a separate line in the contract itself.
The latter is due to the fact that according to Art. 424 of the Civil Code of Russia, the parties pay the price of the goods at the details specified in the contract.
Concluding our review of VAT, we note that due to its universal nature, it is one of the most complex taxes among the taxes existing in the Russian Federation.
Excise duty. Tax base
Indirect taxes in the Russian Federation (except for the largest of them - value added tax) include the federal tax - excise duty (often called abbreviated as excise tax) and customs duties. It is levied on certain groups of goods both when selling them on the territory of Russia, and when moving them across the Russian border. They transfer it to the budget of the legal entity and the individual entrepreneur, and the actual payers are consumers, because it is included in the price of the goods they buy. Since the amount of tax is included in the price of the goods, it is obvious that the excise tax is an indirect tax.
As a rule, automobiles, alcoholic products, diesel fuel, motor oils, beer, straight-run and motor gasoline, alcohol and alcohol-containing products, and tobacco products are excisable.
According to Article 182 of the Tax Code, the object of taxation is the transaction by the taxpayer of the sale of excisable goods produced in Russia, the receipt and posting of these products, certain types of transfer of goods (tolling scheme), the operations of moving excisable goods outside of Russia.
Pp 1 p. 6 Article 182 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation records the occurrence of an excisable item during confiscation and posting of ownerless goods by this indirect tax. It is subject to taxation and the transfer of excisable property to the authorized capital of companies.
Excise taxation procedure
Excisable goods are not subject to excise duty, transfer between divisions of a manufacturing enterprise, initial transfer of confiscated goods for subsequent industrial processing, import of excisable goods into the customs territory, followed by refusal in favor of the state, import of excisable property to the port SEZ.
The current excise tax rates for the period up to 2015 are presented in Art. 193 of the Tax Code.
The tax authorities carry out documentary checks, take into account the tax payer’s contract with their counterparty, payment documents in conjunction with a bank statement on the transfer of funds, a cargo customs declaration, copies of supporting transport documents evidencing the export of excisable goods outside of Russia.
The tax period for the internal sale of excisable goods is one month, for those transported across the border - according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of determining the amount of excise duty
Initial conditions : distillery produces vodka with ethyl alcohol content of 40%. Its production is characterized by a monthly volume of 500 liters. The current tax rate is 210 rubles per liter of anhydrous ethyl alcohol. The amount of excise tax on ethyl alcohol purchased is 1650 rubles.
Solution : The tax base will be: 500 x 40% = 200 liters.
The amount of excise tax corresponding to the sold vodka: 200 l x 210 rubles = 42 000 rubles.
Amount of excise tax payable: 42,000 - 1,650 = 40,350 rubles.
Conclusion
Indirect taxes are an indispensable attribute of the modern tax system. Of particular importance in it is VAT, which provides the largest amount of tax budget revenues (for Russia 33–35%). It should be noted that the VAT tax rate is an important incentive for economic development. , , 1992 , 28% 18%.
, - , . , , .