Most people know that muscle volume is not the only indicator of their strength. To make sure of this, it is enough to recall what physique the great Bruce Lee had and what he was capable of. Of course, in martial arts, in addition to strength, technique and dexterity play an important role. In reality, it happens that two people with different muscle volumes perform equally well in weightlifting disciplines. And sometimes even the one who is much smaller in volume, presses more weight. Probably for this reason, not all men are addicted to muscle pumping. Today we will learn on what, besides volume, muscle strength depends.
Volume
The larger the muscle, the stronger it is hypertrophied. There are two types of muscle hypertrophy: myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic. When muscle fiber increases in volume, there is mainly a second kind. The increase is due to saturation of the muscle with sarcoplasm. Such hypertrophy alone does not increase strength. But, fortunately for athletes, in its pure form it does not occur. Therefore, even with an increase in volume, myofibrillar hypertrophy is involved to some extent, which increases strength. So even for those who work exclusively for the mass, strength is also growing.
Innervation
The strength of the muscles to some extent also depends on the innervation. It is expressed by the provision of muscles with motor neurons. As you know, muscle tissue contracts under the influence of a brain signal. It goes to muscle fibers along motor neurons - motor nerves. The more neural connections a muscle has, the more it uses motor units and the more difficult work it can do. Novice athletes typically recruit no more than 80% of the muscle fibers. For professionals, this figure reaches 100%. To influence the innervation, you just need to exercise regularly. After some time, under the influence of constant loads, motor neurons will more tightly braid your muscles.
Tendon Thickness
Strength and endurance of muscles depends to a large extent on this factor. The human body is structured in such a way that if it comes across a weak spot during the development of any physical parameters, it stops this very development, regardless of our efforts. In this case, it is understood that the muscle cannot become more resistant to stress than the tendon. When the muscle contracts more than it can, the tendon just breaks away from the bone. Therefore, the body, being a perfect system, inhibits the growth of muscle strength if it approaches the tensile strength of the tendon. Unfortunately, this factor can only be partially affected. The thickness of the tendons is mainly laid in childhood, at the genetic level. An adult with regular training can slightly increase tendon endurance, but only slightly.
Fiber ratio
Many probably know that in the human body there are fast and slow muscle fibers. They are also called white and red, respectively. Of course, the difference between them is very arbitrary. Red fibers contain more mitochondria and are better supplied with blood, so they do not cause muscle strength, but their endurance.
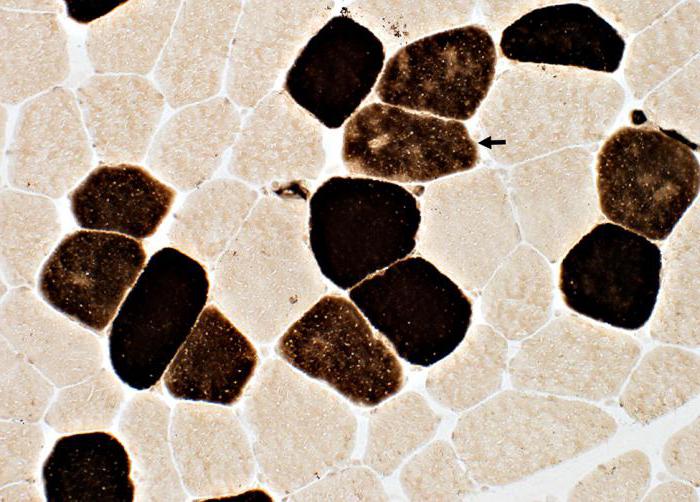
White fibers, in turn, are more suitable for short-term blasting, in which strength is needed. What muscles perform tasks - such are their fibers. For example, the shin is famous for its endurance, and the pectoral muscle - for strength. As the body ages, the percentage of slow fibers increases, while fast fibers decrease. This happens by transforming one species into another. This factor cannot be affected. The fiber ratio is laid genetically. Therefore, some people from birth are better given aerobic exercise, and others - power. All that a person can in this case is to choose exercises that better develop this or that type of muscle fiber. But the difference, as you know, is very arbitrary here.
Muscle elasticity
As you know, all the muscles in our body work due to contractions and sprains. The greater the difference between the two conditions, the greater the strength of the muscles. Roughly speaking, the same principle works here as in a rubber band. The more it is stretched, the greater will be the compression force. The ability to stretch, and therefore the contraction force, depends on the elasticity of the muscles. This is not even a physiological feature, but a biomechanical one. Fortunately for athletes, this factor can be affected. For muscles to be elastic, you just need to stretch yourself regularly and competently.
Tendon location
To make it clear how this factor affects muscle strength, we analyze it in detail using the example of biceps. Physiologically, the arm is designed in such a way that there is always a gap from the place of attachment of the biceps to the elbow joint. Its length is different for each person. How does this affect muscle strength? The law of leverage works here. The closer the point of application of force (the place of attachment of the tendon) to the axis of rotation (elbow joint), the more the arm needs to spend strength to bend. Roughly speaking, if you move the tendon a couple of centimeters towards the hand, then the strength of the arm muscles will increase significantly. Of course, this is possible only in theory. The same law of leverage applies to almost all muscle groups that a person has. Muscle strength in this case is given to us from birth. The location of the tendon cannot be affected in any way. For different people, it differs literally by a couple of millimeters. It seems that this is a slight difference, but it plays a rather significant role in the formation of strength.
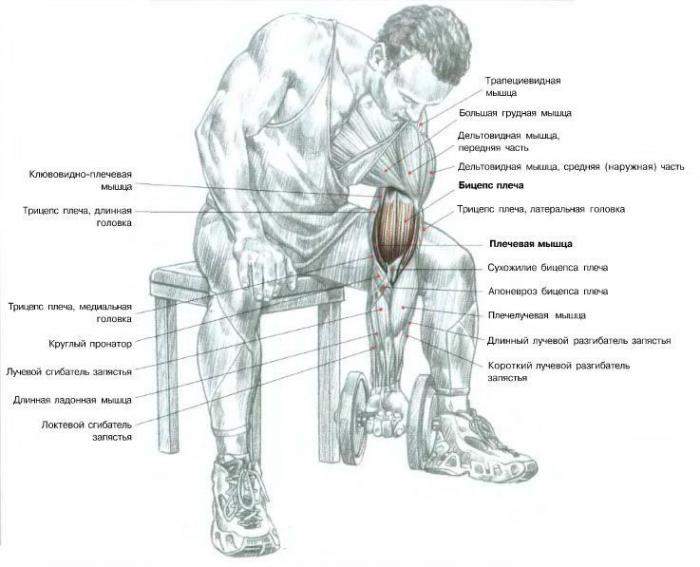
Muscle fiber count
What is the strength of the rope? Of course, in a huge number of thin threads. The same can be said about our muscle tissues. The muscles may be the same in volume, but may consist of different amounts of fibers. This characteristic is laid genetically and does not change throughout life. However, studies of scientists have shown that when exposed to the growth hormone, muscle fibers can divide. But this topic has not been thoroughly studied to date to give encouraging comments. And besides, we are interested in the natural strength of muscles, without the intervention of any drugs. A large number of fibers contributes to increased innervation, therefore, favorably affects the strength. The one whose muscles contain more fibers is able to show greater strength than the one whose muscles are voluminous.
Psycho-emotional factor
Sometimes our strength does not depend on the abilities of the body, but on the level of motivation. There have been many cases in history when a man showed phenomenal strength when threatened with life. For example, having fallen from the balcony, the man grabbed the pipe and sagged in his arms until the rescuers arrived. After he tried to repeat this achievement on the crossbar, but could not sag even 10% of that time.
Muscles contract with the force with which the nervous system sends signals from the brain. In an emergency, the signal is so large that the body uses all the energy resources to complete this task. Perhaps that is why the power athletes pound their chests and shout themselves before entering the arena.
An important role here is also played by the strong-willed qualities of the individual. Another example is a person who does not know how to swim, takes a drowning child from a raging sea, and a lifeguard with a perfect torso is at a loss on the shore. It may not be muscle strength here, but the principle is the same. Anyone who is set for salvation will do this even as a skinny, completely unsportsmanlike person.
Conclusion
Today we learned what the strength and work of muscles depend on, and partly dispelled the view that large muscles are stronger. Why partially? Because the volume to some extent still increases strength indicators. But if you compare the size of the muscles with the other seven factors, its place will be very small.
Surprisingly, these factors do play an important role. If we compare two men with the same physique, but different muscle characteristics (one has all of the above indicators), then we will see the difference in strength indicators. Moreover, it will be calculated not in tens, but in hundreds of percent.
Nevertheless, no self-respecting athlete in the event of failure will not refer to a physiological predisposition to light loads, and there are two reasons for this. Firstly, 5 out of 8 factors can be affected. That is, the development of muscle strength is really possible. Catching up with someone who is given nature to lift large weights is realistic, but a titanic work will have to be done. Secondly, the most important role is played by the psychoemotional factor. A properly motivated person is capable of anything.