Faced with new concepts in everyday life, many try to find answers to their questions. It is for this that it is necessary to describe any phenomena. One of them is such a thing as modulation. It will be discussed further.
general description
Modulation is the process of changing one or a whole set of parameters of a high-frequency oscillation in accordance with the law of an informational low-frequency message. The result of this is the transfer of the spectrum of the control signal to the high frequency region, since effective broadcasting into space requires that all transceiver devices operate at different frequencies without interrupting each other. Thanks to this process, information fluctuations are placed on the carrier, a priori known. The control signal contains the transmitted information. High-frequency oscillation assumes the role of a carrier of information, thereby acquiring the status of a carrier. The control signal contains the transmitted data. There are different types of modulation, which depend on what form of oscillation they use: rectangular, triangular or some other. With a discrete signal, it is customary to talk about manipulation. So, modulation is a process involving oscillations, so it can be frequency, amplitude, phase, etc.
Varieties
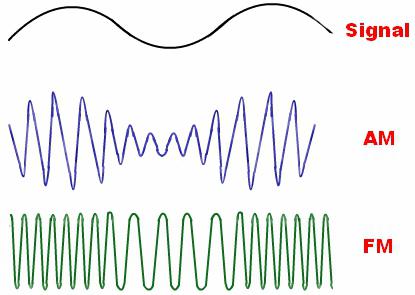
Now we can consider what types of this phenomenon exist. In fact, modulation is a process in which a low-frequency wave is carried by a high-frequency one. Most often, the following types are used: frequency, amplitude and phase. With frequency modulation , a change in frequency occurs, with amplitude modulation , amplitude, and with phase - phase. There are mixed species. Pulse modulation and modification are separate species. In this case, the parameters of the high-frequency oscillation change discretely.
Amplitude modulation
In systems with this type of change, the amplitude of the carrier wave changes at a high frequency with the help of a modulating wave. When analyzing the frequencies at the output, not only the input frequencies are detected, but also their sum and difference. In this case, if the modulation is a complex wave, such as, for example, speech signals consisting of a plurality of frequencies, then for the sum and difference of frequencies, two bands will be required, one below the carrier and the second above. They are called lateral: upper and lower. The first is a copy of the original sound signal shifted to a specific frequency. The lower band is a copy of the original signal that has been inverted, that is, the original high frequencies are the lower frequencies in the lower side.
The lower side is a mirror image of the upper side relative to the carrier frequency. A system using amplitude modulation, transmitting the carrier and both side, is called two-way. The carrier does not contain useful information, so it can be removed, but in any case, the signal band will be twice as large as the original. The narrowing of the strip is achieved by displacing not only the carrier, but also one of the side, as they contain one information. This view is known as single-band suppressed carrier modulation.
Demodulation
This process requires mixing the modulated signal with a carrier of the same frequency as that emitted by the modulator. After that, the initial signal is obtained in the form of a separate frequency or frequency band, and then it is filtered from other signals. Sometimes carrier generation for demodulation occurs on the spot, and it does not always coincide with the carrier frequency on the modulator itself. Due to the small difference between the frequencies, mismatches appear, which is typical for telephone circuits.
Pulse modulation
In this case, a digital modulating signal is used, that is, it allows you to encode more than one bit per baud by encoding a binary data signal into a signal with several levels. Bits of binary signals are sometimes paired. Four pairs of combinations can be used for a pair of bits, with each pair being represented by one of four amplitude levels. Such an encoded signal is characterized by the fact that the modulation rate in bauds is half that of the original data signal, so it can be used for amplitude modulation in the usual way. She found her application in radio communications.
Frequency modulation
Systems with this modulation suggest that the carrier frequency will vary accordingly with the shape of the modulating signal. This type exceeds the amplitude in terms of resistance to certain influences available on the telephone network, so it should be used at low speeds, where there is no need to attract a large frequency band.
Phase amplitude modulation
To increase the number of bits per baud, phase and amplitude modulations can be combined.
One of the modern methods of amplitude-phase modulation can be called one that is based on the transmission of several carriers. For example, in some application, 48 carriers are used, separated by a band of 45 Hz. By combining amplitude and phase modulation for each carrier, up to 32 discrete states are allocated for each individual baud period, so that 5 bits per baud can be transferred. It turns out that all this combination allows you to transfer 240 bits per baud. When operating at 9600 bps, the modulation rate requires only 40 baud. Such a low rate is quite tolerant of the amplitude and phase jumps inherent in the telephone network.
Pulse Code Modulation
This type is usually considered as a system for broadcasting analog signals, for example, voice in digital form. This modulation technique is not used in modems. Here the analog signal is gated at a speed twice as high as the highest frequency of the signal component in analog form. When using such systems on telephone networks, gating occurs 8,000 times per second. Each sample is a voltage level encoded by a seven-bit code. To best represent spoken language, coding is used according to the logarithmic law. Seven bits, together with the eighth, indicating the presence of a signal, form an octet.
To recover the message signal, modulation and detection is required, that is, the reverse process. In this case, the signal is converted nonlinearly. Nonlinear elements enrich the output signal spectrum with new spectrum components, and filters are used to isolate low-frequency components. Modulation and detection can be carried out using vacuum diodes, transistors, semiconductor diodes as non-linear elements. Traditionally, point semiconductor diodes are used, since planar input capacitance is much larger.
Modern views
Digital modulation provides much greater information capacity and provides compatibility with a variety of digital data services. In addition, with its help, information security is improved, the quality of communication systems is improved, and access to them is accelerated.
There are a number of restrictions that developers of any systems face: permissible power and frequency bandwidth, given noise level of communication systems. Every day the number of users of communication systems increases, as well as the demand for them, which requires an increase in radio resource. Digital modulation differs markedly from analog in that the carrier in it transmits large amounts of information.
Use difficulties
The developers of digital radio communication systems have such a main task - to find a compromise between the bandwidth of data transmission and the complexity of the system in technical terms. To do this, it is appropriate to use different modulation methods to get the desired result. Radio communication can also be organized using the simplest transmitter and receiver circuits, but a frequency spectrum proportional to the number of users will be used for such communication. For more complex receivers and transmitters, a smaller frequency band is required to transmit information in the same volume. To switch to spectrally efficient transmission methods, it is necessary to complicate the equipment accordingly. This problem does not depend on the type of connection.
Alternatives
Pulse width modulation is characterized in that its carrier signal is a sequence of pulses, while the pulse frequency is constant. The changes concern only the duration of each pulse according to the modulating signal.
Pulse-width modulation is different from frequency-phase. The latter involves modulating the signal in the form of a sine wave. It is characterized by a constant amplitude and a variable frequency or phase. Pulse signals can also be modulated in frequency. Maybe the pulse duration is fixed, and their frequency is in some average value, but their instantaneous value will vary depending on the modulating signals.
conclusions
Simple modulation types can be used, with only one parameter changing accordingly with modulating information. The combined modulation scheme, which is used in modern equipment for communication, is when there is a simultaneous change in both the amplitude and phase of the carrier. In modern systems, several subcarriers can be used, for each of which modulation of a certain type is used. In this case, we are talking about signal modulation schemes. This term is also used for complex multilevel species, when an exhaustive description of the characteristics is required for comprehensive information .
In modern communication systems, the most effective types of modulation are used, which minimizes the bandwidth in order to free up frequency space for other types of signals. The quality of communication only benefits from this, but the complexity of the equipment in this case is very high. Ultimately, the modulation frequency gives a result that is visible to the end user only in terms of ease of use of technical means.