The Great Patriotic and World War II - events that occurred at the same time, in a certain territory against one enemy, fascism. The Patriotic War, being part of the World War, was fought in its average time period.
The outbreak of hostilities was a clash of interests between the great powers. The world hegemony of Great Britain and France as a result of the conclusion of the Versailles peace in the First World War most infringed on the territorial interests of the USSR and Germany. The Soviet Union did not demonstrate its revenge-seeking ideas, while Adolf Hitler came to power, using the mood to return the former lands, power and power to the German people. Germany was preparing for war.
The objectives of the participating countries
The characterization of the pre-war situation of World War II and the Great Patriotic War is briefly reduced to the creation of political and economic conditions under which Germany was able to decisively demonstrate its expansionist aspirations, while the leading European countries preferred contemplative policies.
This war was the longest, bloody and destructive in the history of mankind. Germany, Italy and Japan, striving for the redivision of the world, having concluded an alliance among themselves, planned to create huge colonial territories and destroy the local population. This was the main reason for the Second World War and the Great Patriotic War. On the part of these countries, the war was aggressive, aggressive.
In order to counter occupation, the countries under attack united against a common enemy. At this time, all political and ideological differences between them were rejected.
The first stage of World War II
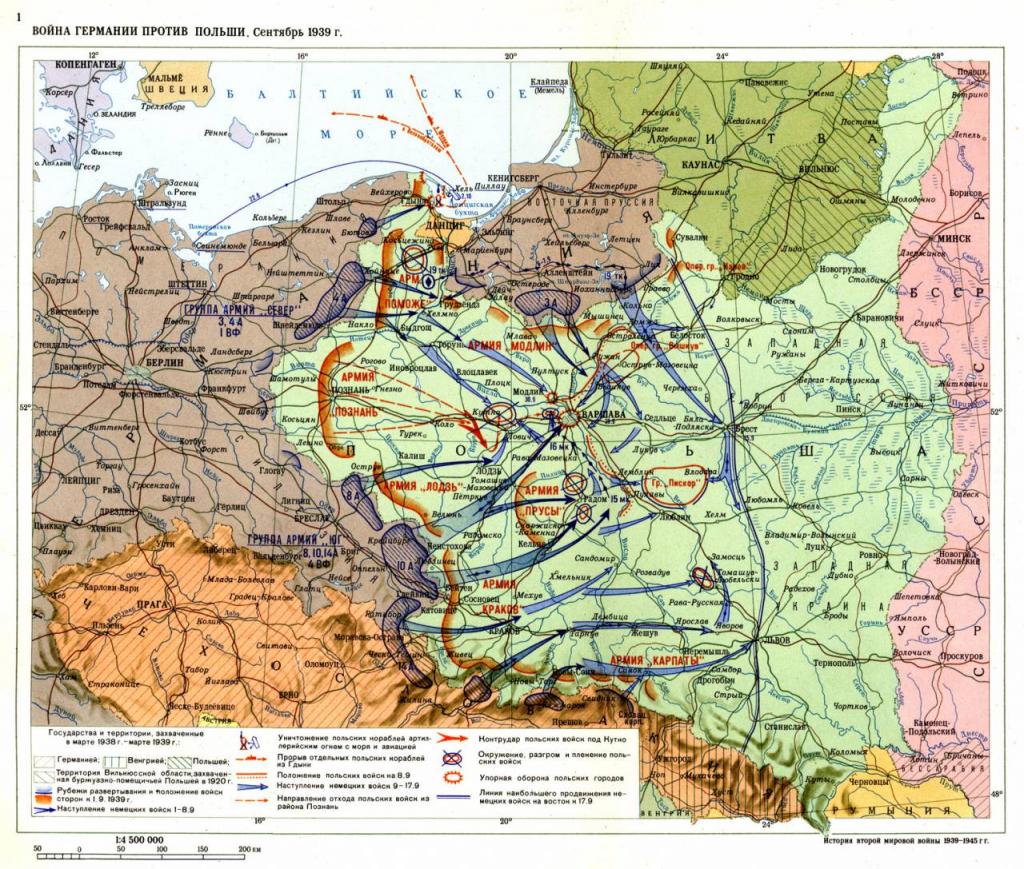
09/01/1939 German troops entered Poland. This day is considered the beginning of a bloody war. France and Great Britain, being its allies, immediately declared war on Hitler, but this ended the assistance to the Polish state. Neither the two great powers, nor fascist Germany, were fighting among themselves. Finding herself without support, Poland abandoned by the allies to their fate, resisted as much as they could, but, in the end, fell. Its allies counted on satisfying Hitler's appetite in Europe, and that his further blow would come in the USSR. But without receiving a proper rebuff, Germany in April of the forties captured the territories of Norway and Denmark. This period is called by historians a “strange war”.
Developing the offensive, Hitler occupied France, Holland, Belgium and Luxembourg. The victory of the German army, inspired by nationalist ideas, was given without much difficulty. A collaborative state was created on the occupied territory of France, that is, a new government led by Pétain, who voluntarily agreed to cooperate and submit to the occupation regime. Historians call it the Vichy regime.
The response of the Soviet Union
The threat of the beginning of World War II and World War II for the Soviet country was pushed aside for a while, and Stalin got the opportunity to prepare a little for it. The Polish state, abandoned by the runaway leaders, remained at the mercy of fate. Soviet troops entered the territory of Western Ukraine and Belarus to protect the local population, which led to the annexation of these territories to the USSR as union republics.
The next step of the Soviet government was the spread of influence and the subsequent annexation of the three Baltic republics: Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia. An attempt to include Finland in its membership was unsuccessful, but as a result some territorial concessions were achieved. And finally, Bessarabia, surrendered by the Romanian government, also became part of the USSR. Thus, by increasing its own territory, the Soviet state significantly strengthened the country's security and military power.
The modernization of the armament of the army and the training of command personnel were carried out at an accelerated pace.
The Triple Pact of the aggressors
Before Germany entered Soviet soil, the USSR had little to do with a world carnage erupting on the planet. In September 1940, the aggressor armies of Germany, Italy and Japan, united, concluded the Triple Pact. Later, Bulgaria, Hungary and other countries joined it.
By June 1941, only two independent states remained in Europe: the USSR and Great Britain, which was subjected to powerful air raids, but successfully defended.
Hitler's plan for the USSR
The periodization of World War II and the Great Patriotic War classifies the events of June 1941 - May 1945 as the second stage of hostilities. The main task that Hitler posed for Germany was the conquest of living space in the East. He planned to start a war with the USSR only after the final pacification of Europe. But the Barbarossa plan was signed even before the end of the war with England, since the Führer was very concerned about the intensified rearmament of the Soviet troops.
Hitler’s calculated blitzkrieg had to be completed before winter, the Soviet army should be driven back beyond the Urals, and the territory liberated from the Soviets would eventually be inhabited by the German colonists. The local population, reduced at times, was to be used for rough work. Of course, the Asian territory remaining in the USSR would also be under the control of the Reich, and numerous concentration camps were planned to be transferred here from Europe.
Such was the goal set before Germany by her Fuhrer, who wanted to destroy the incomprehensible Russian people and their savage culture. From the first day of the struggle for their life and future, this war became for the Soviet people domestic, popular, and liberating.
Three stages of World War II
Historians traditionally divide the events of military operations of that time into three periods of the Great Patriotic War. World War II main events merges with World War II in this time period.
Stages of events:
- From June 22, 1941 to November 1942. The beginning of hostilities on the territory of the USSR, the failure of Operation Barbarossa, the battles of 1942.
- From November 1942 to December 1943. Fracture during the war, the defeat of the Germans in Stalingrad and the Kursk.
- From January 1944 to May 9, 1945. The liberation of Soviet territory and European countries, the surrender of Germany.
The beginning of the war with the Soviet people
The outbreak of war amounts to huge losses. Five million fighters were disabled dead, wounded, or captured. The Germans destroyed many Soviet tanks and aircraft. In a short time, the enemy captured one and a half million square meters. kilometers of territory. It seemed that the Barbarossa plan was being implemented.
As always, danger united the Soviet people, gave them strength. Hitler hoped that in difficult conditions ethnic hatred would begin, but the opposite happened. The country has become a single family, protecting all its national values.
The largest and most significant event of that period was the battle for Moscow. From September 1941 to April 1942, on the outskirts of the capital, the confrontation of the two armies continued. Finally, Soviet soldiers managed to push the enemy 100-250 kilometers away. This was Hitler's first significant defeat in the entire history of World War II and the Great Patriotic War. The victory served as a signal to other countries to make decisions. England and the USSR entered into an agreement, and later signed an agreement with the United States on support and military supplies to the Soviet army. So the anti-Hitler coalition was born.
The victory raised the morale of the defenders of the motherland, the legends of the invincibility of the German army were dispelled. Japan, frightened by this turn of events, refused to enter the war with the USSR and attacked Asian countries, occupying Thailand, Singapore, Burma and others.
The second period of World War II
It is characterized by heavy battles and losses on both sides and is marked by a turning point in military events.
Germany, striking the south of Russia, went to Stalingrad and the Volga. The purpose of the offensive was to cut off the Soviet army from the Ural factories, depriving it of industrial and fuel support. The Soviet leadership, who learned to fight during the period of hostilities, strengthened the material base of the army, decided to give a decisive battle to the enemy near Stalingrad. Many-kilometer fortifications were created, the well-known order of the Generalissimo banning retreat was issued. Several months of confrontation ended in the defeat of the Nazis.
The battle of Kursk, which took place after some time, contributed to the beginning of the expulsion of the enemy by victory. From this turning point of World War II and World War II, the destruction of fascism on the planet began.
Anglo-American troops waged a liberation struggle in the Pacific Ocean. Egypt, Tunisia were freed from the German and Italian occupation. They spoke decisively about the opening of a second front in the north of France, which was discussed at a meeting of the top officials of the USSR, America and England in Tehran. Russia made a promise to fight against Japan at the end of the war in Europe.
Completion
The years of World War II and World War II are marked by complete liberation from the invaders of Soviet territory and the beginning of the campaign of Soviet troops in Europe. Germany’s allies: Romania and Bulgaria fell without resistance, heavy fighting broke out for Hungary, but the most desperate resistance was in Poland. At the same time, in the north of France, in Normandy, fighters of the second front landed. Anglo-American and Canadian forces were assisted by the local Resistance movement.
When the fighting went on in Germany, the second meeting of the "Big Three" took place in Yalta. The leaders of the three states decided to divide the defeated Germany into occupation zones. The storm of Berlin began on April 16, and on April 30, the victorious Banner rose above the Reichstag. On May 8, Germany surrendered.
The end of World War II and World War II
05/09/1945 is celebrated by the Soviet people as a victorious day in the war, which has changed a lot in the life of the country. But the Second World War continued, and Russia, fulfilling the promise given to the Allies, entered into it.
The main defeat of the Japanese troops was carried out by the Americans, having liberated by this time many captured Asian countries. Rejecting the ultimatum on surrender, Japan was subjected to an atomic bombardment from the air.
The Soviet Union liberated Manchuria, South Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands and North Korea within three weeks. Japan signed a surrender on 09/02/1945. The World War ended.
The results of World War II and World War II
To the positive results, experts include, first of all, the destruction of the fascist machine, the liberation of the world from aggressors. At the cost of terrible losses and incredible efforts, the Soviet people saved themselves and the planet from enslavement.
The achievements of this victory were:
- freedom and independence;
- expansion of state borders;
- the destruction of fascism;
- the liberation of the peoples of Europe;
- the emergence of a socialist camp.
The price of victory was very high. Six long years have passed since the moment when the Second World War and the Great Patriotic War ended. During this time, about 30 million Soviet people died, a third of national wealth was destroyed, more than 1,700 cities were ruined, 70,000 villages, many factories, factories, roads were wiped off the face of the earth. Only 3% of the conscripts born in 1923 returned home, which still makes itself felt by demographic failures.