In winter, stars in the sky light up much earlier than in summer, and therefore not only astronomers and lovers of late walks can enjoy them. And there is something to see! The majestic Orion rises high above the horizon, accompanied by Gemini and Taurus, and next to them the Charioteer lights up - a constellation with a long history and a large number of interesting objects. It is precisely today that is in the center of our attention.
Location
The charioteer is a constellation bright and clearly visible to the naked eye. In shape, it resembles an irregular pentagon. The best reference point for finding this celestial pattern is Ursa Major. A little to the right of it you can see a rather bright point. This is Alpha of the Ascendant, the Chapel is a star that can be seen even under not very favorable conditions. She marks one of the vertices of the pentagon. A little to the right (east) of the Chapel is a small elongated triangle formed by three luminaries. These stars in the sky, together with Alpha of the Ascendant, form the "Kids" asterism.
Landmarks can serve as other heavenly drawings. The charioteer is located north of the Gemini and east of Perseus. You can observe the constellation in our country almost the whole year. It rises above the horizon in December and January, and in June and July, on the contrary, Voznichny is poorly visible due to bright nights and low location.
Legend
The stars of the constellation Charioteer in ancient times were associated by scientists with several characters. In Mesopotamia, the heavenly drawing was called the “shepherd’s staff” or “scimitar”. It is not known, however, whether he included the Capella. In Babylon, almost all the bright stars of the Ascendant were also correlated with a shepherd watching goats or sheep. Among the Bedouins, they were considered a group of animals. The charioteer was a herd of goats.
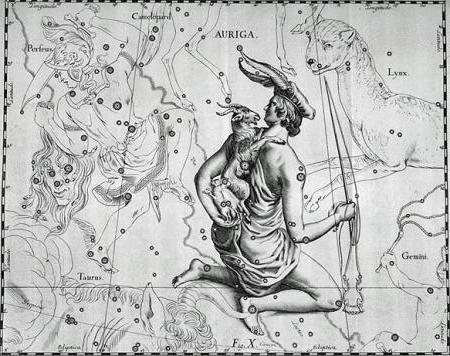
In ancient astronomy, this celestial pattern was also originally considered to be associated with grazing goats. Later, the main part of the constellation became associated with the figure of a person driving a chariot. In ancient Greece, several characters of myths associated with the charioteer. Most often it was Erichtonius, son of Hephaestus and a pupil of Athena. He is credited with the invention of a chariot with two wheels and four horses (quadriga). In reward for this, as well as for devotional service to Athena, Erichtonius was placed in heaven by Zeus. So the constellation Charioteer appeared.
Traces of the past
The mythology of ancient Greece and its preceding representations have left their mark on the traditional image of the constellation. On the maps of the night sky you can see the charioteer in the image of a man with a goat on his back and two kids on his arm. In antiquity, even a separate constellation of the Goat was distinguished, which correlated with the mythical Amalfeus, who nourished Zeus. It was composed of Capella, ε, ζ and η of the Ascendant. The latter form the same small triangle, which is located to the right of the brightest star of the picture.
Interesting objects
The constellation of the northern hemisphere of the sky, the charioteer, includes approximately 150 “points”. On its territory there are many interesting objects. First of all, these are the stars: Capella (alpha), Menkalinan (beta), Al Anz and Hedus (epsilon and zeta). In addition, the planetary nebula IC 2149 and a large cluster of galaxies MACS 0717 are located here. With binoculars or a small telescope in the region of the sky occupied by Voznich, one can see the open star clusters M36, M37 and M38. They are 4-4.5 thousand light-years distant from our planet.
Alpha constellations
If at least once to see this heavenly drawing, then the question of which star is the brightest in the constellation Charioteer will resolve by itself. The chapel stands out well among other "points" above the head. It is considered the sixth brightest in the sky and is clearly visible even under not very favorable conditions for observation.
The chapel is a star with an apparent magnitude of 0.08. It is 40 light-years distant from the Sun. For the earth observer, it looks yellow-orange, which is why it is often confused with Mars. The chapel is a system of two pairs of stars. The first and brightest combines similar cosmic bodies. They belong to the yellow stars and exceed our star in diameter by 10 times. The distance between the components of the pair is only two-thirds of the length of the segment "Sun - Earth".
The second part of the system consists of red dwarfs. They are removed from a pair of yellow stars for one light year. Red dwarfs are much smaller and emit a relatively small amount of light.
Beta Charioteer
Menkalinan is a star, the second brightest in this heavenly figure. Its name in Arabic means "the shoulder of the one who holds the reins." Beta Auriga - a triple star system. Its two components are almost identical to each other. Each star that makes up a couple shines 48 times more powerful than the Sun and belongs to the class of subgiants. The distance between the elements of the pair is very small - only 0.08 astronomical units, which is equivalent to the fifth part of the segment "Earth - Sun". In the nuclei of both components of the pair ended hydrogen. Stars are experiencing the stage of evolution when their size and brightness begin to increase due to new processes that occur in the bowels. A small distance separating the components leads to their deformation under the action of tidal forces. Another consequence of this interaction is the synchronization of the period of revolution and rotation around the axis. Its result is expressed in the fact that two stars are always turned to each other on the same side.
The third component of the system is a red dwarf, distant from the pair at a distance of 330 astronomical units. It is impossible to notice it with the naked eye from the Earth.
Epsilon
The charioteer is a constellation of at least one object which holds the eyes of many modern astronomers chained to itself. This is an epsilon of heavenly drawing, with the traditional names Almaaz ("kid") and Al Anz (the exact meaning is unknown). The eclipsing double star attracts the attention of many experts around the world because of the mystery of one of the components. A striking element of the epsilon system of Voznichy is the supergiant of spectral class F0. Its radius is 100-200 times larger than the sun. In brightness, the star "ahead" of our luminary in 40-60 thousand times.
The second component is supposed to belong to the spectral class B. In the literature it is referred to only as “invisible”. Every 27 years it overshadows a bright star for 630-740 days (approximately 2 years). It is called invisible because it emits extremely little light for such an object, that is, it is rather difficult to study it. It has been suggested that the dark component is a binary system surrounded by a dense dust disk, or is a translucent star or a black hole. Recent studies using the Spitzer telescope have shown that, most likely, the mysterious element is a Class B star. It is surrounded by a dust disk consisting of rather large particles resembling gravel in size. However, the point on this issue has not yet been set and the study of the system continues.
Zeta
Another eclipsing double in this celestial pattern is the Zeta of the Charioteer. The historical names of the star are Headus and Sadatoni. It shines 1700 times brighter than the Sun. The system consists of two components. The first is the orange giant of the spectral class K4. The second is a white-blue star located on the main sequence and belonging to class B5. Every 2.66 years, it "disappears" for a dimmer, but larger, component. Such an eclipse leads to a decrease in the total brightness of the star by about 15%.
The average distance between the components of the system is estimated at 4.2 astronomical units. They rotate in elongated orbits.
The charioteer is a constellation that is interesting both for observation without any adaptations and for thorough research using professional equipment. Its objects can tell a lot of interesting things, but because astronomers around the world send their telescopes to them.