There are three main types of worms: Flat, Round and Ringed. Each of them is divided into classes, which combine the types of worms by the similarity of certain signs. In this article, we describe types and classes. We will also touch upon their individual species. You will learn basic information about worms: their structure, characteristics, role in nature.
Type Flatworms
Its representatives live in marine and fresh water bodies, in tropical forests (their wet litter). These are various types of parasitic worms. They differ in body shape. The flat leaf-shaped bilateral symmetrical or ribbon-shaped body has a flat worm. Species belonging to this type possess muscular, integumentary, excretory, digestive, reproductive, genital, nervous systems, which develop from 3 germ layers (inner, outer and middle layers of cells). In total, more than 12 thousand of their species are known. Main classes: Flukes, Planaria, Tapeworms.
Planaria Class
Black, brown and white planarians live in silty places of ponds, lakes and streams. At the front end of the body, 2 eyes are visible, with which they distinguish darkness from light. The pharynx is on the ventral side. Planaria are predators. They prey on small aquatic animals, which they tear to pieces or swallow as a whole. They move thanks to the work of cilia. From 1 to 3 cm is the body length of freshwater planaria.
Their body is covered with elongated cells with special cilia (therefore they are also called ciliary worms). 3 layers of muscle fibers are located deeper - diagonal, annular and longitudinal. The worm (species related to planaria), due to their relaxation and contraction, shortens or lengthens, can raise parts of the body. A mass of small cells is located under the muscles. This is the main tissue in which the internal organs are located. A mouth with a muscular pharynx, as well as a three-branched intestine, make up the digestive system. The walls of the intestine are formed by a layer of bulbous cells. They capture food particles and then digest them. Digestive enzymes secrete glandular cells of its wall into the intestinal cavity. The nutrients resulting from the breakdown of food penetrate immediately into the tissues of the body. Undigested residues are removed through the mouth.
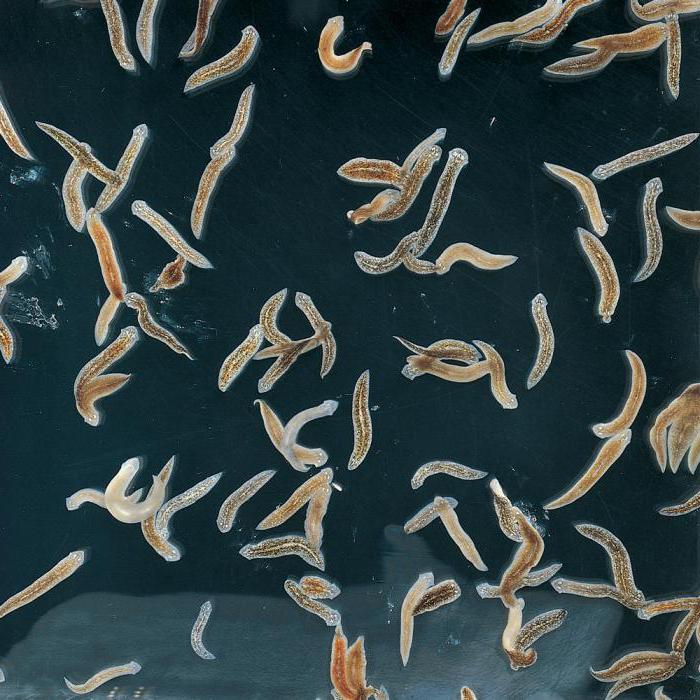
Ciliary worms breathe oxygen dissolved in water. This process is carried out by the entire surface of the body. Their nervous system consists of clusters of cells - head paired nodes, nerve trunks departing from them, as well as nerve branches. Most planaria have eyes (from 1 to several tens of pairs). They have tactile cells in the skin, and some members of this class have small pair of tentacles on the front end of the body.
Class flukes
It includes species of parasitic worms that have a leaf-like body without cilia. The most famous representative of this class is the hepatic trematode. About 3 cm is the length of his body. This worm settles in the ducts of the liver of sheep, cows and goats, holding in place with the help of the near-mouth and abdominal suction cups. It feeds on blood, as well as the destructible cells of the body of its owner. The hepatic trematode has a pharynx, mouth, bifurcated intestine, and other organ systems. Of these, the nervous and muscle are not developed as much as in free-living flatworms.
Class of tapeworms
It includes parasitic worms having a ribbon-like body, which consists of an undifferentiated short neck, a small head and many segments. The most famous types of tapeworms are pork and bovine tapeworms, echinococcus, and wide ribbon. Where do these organisms live? Bovine and pork chains live in the intestines of humans, echinococcus - in wolves and dogs, and a wide ribbon parasitizes in the body of carnivorous mammals and humans. Chains can reach a length of ten meters and even more (for example, bullish). These types of tapeworms on the head have hooks and suckers (echinococcus, pork tapeworm), or only suckers (like a bull’s tapeworm), or 2 deep suction grooves (for example, a wide ribbon).
The nervous and muscular systems in this class are poorly developed. Skin cells represent their sensory organs. Their digestive system has disappeared: tapeworms absorb nutrients from the intestines of the host with the entire surface of their body.
Echinococcus
Echinococcus is a small worm, the length of which is up to 6 mm. Its peculiarity is that the segments do not separate from its body, unlike lentets and tapeworms. The main owners of this worm are a wolf, a dog, a cat, a fox; intermediate - a cow, a sheep, a pig, a deer, a goat (maybe also a man). Large blisters develop in the lungs, liver, bones, muscles of the latter. In each of them grandchildren and daughter branches are formed. Inside them are the heads of parasites. The main hosts can become infected by eating meat with these blisters, and the intermediate hosts after eating food that is contaminated with the stool of sick wolves, dogs, and other main hosts of this worm.
Type Roundworms (or Cavitary)
They have a non-articulated body, usually long, rounded in cross section. This is the main similarity of roundworms of different species. On the surface of their skin there is a dense non-cellular formation called a cuticle. They have a cavity in the body that exists due to the destruction of the cells that make up the main tissue between the internal organs and the body wall. Their muscles are represented by a layer of longitudinal fibers. That is why roundworms can only bend. Their intestines look like a tube. It begins with a mouth opening and ends with anal (anal). Representatives of this type live in the seas, soil, fresh water. The difference between roundworms of different species is that some of them are pests of plants, while others are parasitic on humans and animals. More than 400 thousand species are in this type. The largest class is the class of Nematodes.
Nematodes Class
Nematodes are herbivorous worms that live on the roots of beans, garlic, onions and other garden plants, in underground shoots of potatoes (a species of Stem potato nematode), in the organs of strawberries (Strawberry nematode). About 1.5 mm is the length of their almost transparent body. With the oral apparatus of the piercing type, nematodes pierce plant tissues, after which substances are dissolved that dissolve the contents and walls of the cells. Then they absorb the formed substances, using the expanded part of the esophagus for this. How the pump acts its muscular walls. Food is digested in the intestines. Many nematodes live in the ground and use plant debris as food. They play an important role in soil formation.
Some members of this class are parasites. They live in the host (humans and animals). This, for example, roundworms (pork, horse, human, etc.), trichinella, pinworms, whipworms, rishts.
Roundworm
Roundworms live in the small intestine of the host. Up to 40 cm is the body length of the female (males are slightly smaller). They eat semi-digested food. Females lay eggs (approximately 200 pieces per day), which are excreted with human feces. In them, in the external environment, mobile larvae develop. When poorly washed vegetables are consumed, as well as food that is popular with flies, a person becomes infected with roundworms. Larvae in the gut of the host emerge from the eggs. After that, they invade the blood vessels and migrate through them into the lungs, heart and liver. The grown larvae enter the mouth, after which they enter the intestines, in which they become adults. They feed on the food of the host, whose body is poisoned by its secretions. As a result of their activity, ulcers form on the intestinal walls, and with a large number of parasites, obstruction and rupture of the walls can occur.
Type Annelids
Its representatives live in fresh water, seas, soil. Their body is long, divided into annular segments (segments) by transverse constrictions. We are all well aware of the appearance of earthworms. Their length ranges from 2 to 30 cm. The body is divided into segments, which can be from 80 to 300.
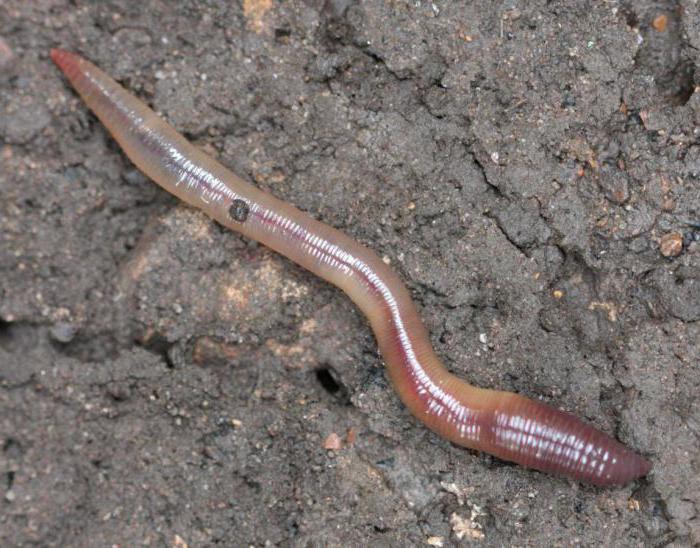

Internal segmentation corresponds to external dismemberment. The body cavity of representatives of this type is lined with a layer of integumentary cells. The delimited area of this cavity is located in each segment. Ringworms have a circulatory system, and many of them have a respiratory system. Their digestive, muscular, nervous, excretory systems, as well as the sensory organs, are more advanced than round and flat worms. Their “skin” consists of a layer of integumentary cells. Under it are the longitudinal and ring muscles. In annelids, the digestive system is divided into the pharynx, oral cavity, esophagus, stomach (in some groups), as well as the intestines. Undigested food residues are removed through the anus.
Ringworm circulatory system
All types of annelids have a circulatory system formed by the abdominal and dorsal blood vessels, which are interconnected by annular ones. Small vessels depart from the latter, which branch and form a network of capillaries in the internal organs and skin. Blood moves mainly due to the relaxation and contraction of the walls of the annular vessels surrounding the esophagus. It carries oxygen and nutrients entering it to all organs, and also frees the body from metabolic products. Types of annelids are characterized by a closed circulatory system (this biological fluid in them is located within the vessels and does not flow into the body cavity). Through the skin, breathing occurs. Some species of worms (marine) have gills.
Ringworm Nervous System
The nervous system in representatives of this type consists of paired sub-pharyngeal and supratharyngeal nerve nodes, which are connected into a ring by nerve cords, as well as nodes of the chain (abdominal). A paired node is located in each segment of annelids. To all organs nerves depart. Various stimuli (e.g. light) act on sensitive cells. The excitation that arose in them is transmitted to the nearest nerve node through the nerve fibers, and then to the muscles (along other fibers) and causes them to contract. In this way reflexes are carried out. Most representatives of this type have no sense organs.
The main classes of annelids
Ring-shaped can be both hermaphrodites and dioecious. How many worms (species) does this type include? Today, there are about 9 thousand, among which the main classes stand out: Multi-bristle and Small-bristle. The first live mainly in the soil (for example, this type of earthworms as burrows), as well as in fresh water bodies (in particular, tubuloids). Polychaete worms are a class that includes sandworms, Nereids, and sickles. The sand dwellers live in the minks dug by them, the Nereids live mainly in silty soil, in the coastal parts of the seas, and the sickles live in “houses” that they build from various materials.
Nereids
Nereids are the species of worms that are most diverse in the seas. Their color is green or reddish. The head is formed by the anterior segments of the body. She has palps, mouth, tentacles (organs of touch), as well as 2 pairs of eyes and 2 pits located behind them (these are the organs of smell). On the joints on the sides of the body are paired muscular short lobate outgrowths with tufts of bristles. These are limbs. In addition, nereids develop gills - special skin outgrowths. Often these are dioecious animals. Fertilization of eggs occurs in water, from which free-floating larvae appear, having a ciliated girdle. They eventually turn into adult worms.
The value of annelids
They are the food of many species of crabs, fish (Nereids and other marine worms). Earthworms are the main food of hedgehogs, moles, starlings, toads and other animals. Ring-shaped, feeding on silt, as well as various suspensions, free water from excess organic matter. In addition, earthworms and some other soil worm species eat plant debris and also pass soil through their intestines. By this they contribute to the formation of humus.
So, you got acquainted with the above classification, learned about what types, classes and types of worms exist. The photos from this article give a visual representation of some of their representatives. Worms are quite peculiar living organisms. Some of them are parasites, while others are of great benefit to our planet.