Glucose translated from Greek means "sweet." In nature, in large quantities it is found in the juices of berries and fruits, including grape juice, which is why the people have the name "wine sugar".
Discovery story
Glucose was discovered at the beginning of the 19th century by an English physician, chemist, and philosopher William Praout. This substance was widely known after Henri Braccono extracted it from sawdust in 1819.
Physical properties
Glucose is a colorless crystalline powder of a sweet taste. It is highly soluble in water, concentrated sulfuric acid, zinc chloride and Schweizer's reagent.
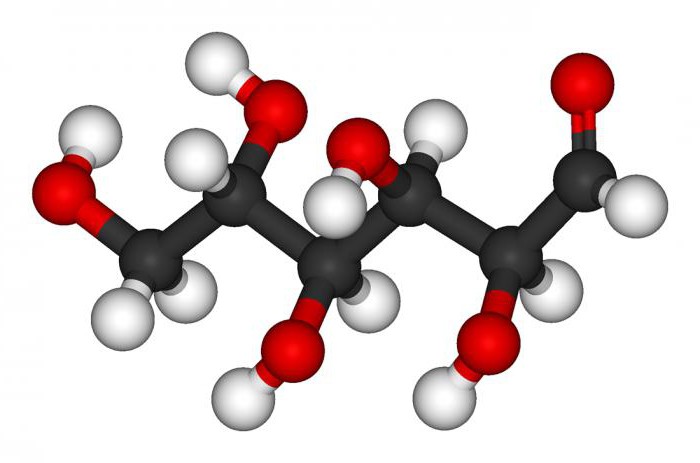
Molecule structure
Like all monosaccharides, glucose is a heterofunctional compound (the molecule contains several hydroxyl and one carboxyl groups). In the case of glucose, the carboxyl group is the aldehyde group.
The general formula for glucose is C6H12O6. The molecules of this substance have a cyclic structure and two spatial isomers of the alpha and beta forms. In the solid state, the alpha form predominates by almost 100%. In solution, the beta form is more stable (it takes approximately 60%). Glucose is the end product of the hydrolysis of all poly- and disaccharides, that is, glucose is produced in the vast majority of cases by this particular route.
Receiving a substance
In nature, glucose is produced in plants through photosynthesis. Consider industrial and laboratory methods for producing glucose. In the laboratory, this substance is the result of aldol condensation. In industry, the most common way is to obtain glucose from starch.
Starch is a polysaccharide whose monoparticles are glucose molecules. That is, to obtain it, you need to decompose the polysaccharide into monoparticles. How is this process carried out?
Obtaining glucose from starch begins with the fact that the starch is placed in a container with water and mixed (starch milk). The other water tank is brought to a boil. It should be noted that boiling water should be twice as much as starch milk. In order for the glucose production reaction to go through, a catalyst is needed. In this case, it is hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. The calculated amount is added to the boiling water tank. Then starch milk is slowly poured. In this process, it is very important not to get a paste, if nevertheless it has formed, you should continue boiling until it disappears completely. On average, boiling takes an hour and a half. In order to be sure that the starch is completely hydrolyzed, a qualitative reaction must be carried out. Iodine is added to the selected sample. If the liquid turns blue, then the hydrolysis is not finished, if it becomes brown or red-brown, then there is no more starch in the solution. But in this solution there is not only glucose, it was obtained using a catalyst, which means that acid also has a place. How to remove acid? The answer is simple: by neutralizing with pure chalk and finely chopped porcelain.
Neutralization is checked by litmus test. Next, the resulting solution is filtered. The point is small: the resulting colorless liquid should be evaporated. Formed crystals are our final result. Now consider the production of glucose from starch (reaction).
The chemical essence of the process
This equation for the production of glucose is presented before the intermediate product - maltose. Maltose is a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules. It is clearly seen that the methods for producing glucose from starch and maltose are the same. That is, in continuation of the reaction, we can put the following equation.
In conclusion, it is worth summarizing the necessary conditions in order for the production of glucose from starch to be successful.
The necessary conditions
- a catalyst (hydrochloric or sulfuric acid);
- temperature (not less than 100 degrees);
- pressure (atmospheric enough, but increasing pressure speeds up the process).
This method is the simplest, with a large yield of the final product and minimal energy costs. But he is not the only one. Obtaining glucose is also carried out from cellulose.
Pulp production
The essence of the process is almost completely consistent with the previous reaction.
The production of glucose (formula) from cellulose is given. In fact, this process is much more complicated and energy-consuming. So, the product that enters the reaction is waste from the wood processing industry, crushed to a fraction, the particle size of which is 1.1 - 1.6 mm. This product is treated first with acetic acid, then hydrogen peroxide, then sulfuric acid at a temperature of at least 110 degrees and a water module 5. The duration of this process is 3-5 hours. Then, hydrolysis of sulfuric acid at room temperature and a hydromodule 4-5 takes place over two hours. Then there is dilution with water and inversion for about one and a half hours.
Quantification Methods
Having considered all methods for producing glucose, methods for its quantitative determination should be studied. There are situations when only a solution containing glucose should be involved in the technological process, that is, the process of evaporating the liquid to obtain crystals is superfluous. Then the question arises, how to determine what concentration of a given substance in solution. The resulting amount of glucose in the solution is determined by spectrophotometric, polarimetric and chromatographic methods. There is a more specific method of determination - enzymatic (using the enzyme glucosidase). In this case, the counting is already the products of the action of this enzyme.
Glucose
In medicine, glucose is used for intoxication (this can be both food poisoning and the activity of infection). In this case, the glucose solution is administered intravenously using a dropper. This means that in pharmacy glucose is a universal antioxidant. Also, this substance plays a small role in the detection and diagnosis of diabetes. Here, glucose acts as a stress test.
In the food industry and cooking, glucose occupies a very important place. Separately, the role of glucose in winemaking, brewing, and home brewing should be identified. This is a method such as obtaining ethanol by fermentation of glucose. Let us consider this process in detail.
Alcohol production
The technology for producing alcohol has two stages: fermentation and distillation. Fermentation, in turn, is carried out using bacteria. In biotechnology, cultures of microorganisms have long been developed that allow you to get the maximum yield of alcohol with the minimum amount of time. In everyday life, ordinary table yeast can be used as reaction assistants.
First of all, glucose is diluted in water. In another tank, the used microorganisms are bred. Next, the resulting liquids are mixed, shaken and placed in a container with a vent pipe. This tube is connected to another (U-shaped). In the middle of the second tube, lime water is poured. The end of the tube is closed with a rubber stopper with a hollow glass rod having a drawn end.
This tank is placed in a thermostat at a temperature of 25-27 degrees for four days. Turbidity will be observed in the tube with lime water, which indicates the introduction of carbon dioxide into the reaction with it. As soon as carbon dioxide ceases to be released, fermentation can be considered complete. The following is a distillation step. In the laboratory, distillation refrigerators are used for distillation of alcohol - devices in which cold water passes along the outer wall, thereby cooling the formed gas and converting it back into liquid.
At this stage, the liquid that is in our tank should be heated to 85-90 degrees. Thus, the alcohol will evaporate, but the water will not be brought to a boil.
The mechanism for producing alcohol
Consider the production of alcohol from glucose in the reaction equation: 6126 = 225 + 22.
So, it can be noted that the mechanism for producing ethanol from glucose is very simple. Moreover, it has been known to mankind for many centuries, and brought almost to perfection.
The importance of glucose in human life
So, having a certain idea of this substance, its physical and chemical properties, use in various industries, we can conclude what glucose is. Getting it from polysaccharides already gives an understanding of the fact that, being the main component of all sugars, glucose is an indispensable source of energy for humans. As a result of metabolism, adenosine triphosphoric acid is formed from this substance, which is converted into a unit of energy.
But not all glucose that enters the human body goes to replenish energy. In the waking state, a person converts only 50 percent of the glucose received into ATP. The rest is converted to glycogen and accumulates in the liver. Glycogen breaks down over time, thereby regulating blood sugar. Quantitatively, the content of this substance in the body is a direct indicator of its health. The hormonal functioning of all systems depends on the amount of sugar in the blood. Therefore, it is worth remembering that excessive use of this substance can lead to serious consequences.
Glucose at first glance is a simple and understandable substance. Even from the point of view of chemistry, its molecules have a fairly simple structure, and the chemical properties are clear and familiar in everyday life. But, despite this, glucose is of great importance both for the person himself and for all spheres of his life.