The branch of biology that studies the animal organisms that inhabit the globe is called zoology. One of its sections directly considers a group of multicellular animals - crustaceans. Their structure, features of life, as well as the importance of crustaceans in nature and human life will be considered in this article.
Crustacean taxonomy
Among the invertebrate organisms that inhabit our planet, animals stand out that unite in the Type Arthropods. Crustaceans are one of the superclasses of this taxon, whose representatives live mainly in fresh or sea water. Only some of them, such as wood lice and land crabs, live in humid land. The Crustaceans are included in the Overclass: the class of lower crayfish and the class of higher (decapod) crayfish.
In turn, each of these taxa consists of smaller systematic groups - orders. Lower crustaceans are the basis of zooplankton, therefore they are important in nature and human life. Essentially, being one of the first links in the food supply chain, lower cancers are a food supply for fish and aquatic mammals. Thanks to representatives of the isopods, copepods, and branched squads, marine inhabitants receive high-grade protein feed, since easily absorbable polypeptides are part of the body of lower cancers.
The class of higher crustaceans includes one detachment - decapod crayfish, which is represented by such animals as crabs, lobsters, spiny lobsters and shrimps.
Structural features of crustaceans
The division of animals into classes is based primarily on differences in the external structure of these organisms. In lower cancers, such as cyclops (order of copepods), daphnia (order of branched), woodlice (order of isopods), the body contains an unstable number of segments (segments), and there are no limbs on the abdomen. On its last segment there is a specific formation - a little fork. The body itself has a soft and thin chitinous shell through which the internal organs of animals are visible.
Higher crustaceans, whose representatives have a solid chitinous shell saturated with lime, are also distinguished by a strict division of the body into the cephalothorax and abdomen with a constant number of segments in them. So, in crayfish in the cephalothorax, 5 and 8 segments, respectively, and the abdomen has 6 segments. Also, higher crayfish, unlike lower ones, have swimming legs on their abdomen.
Metabolism and life
As mentioned earlier, the life of crustaceans takes place mainly in water. Therefore, they clearly manifest the so-called idioadaptations - adaptations to a specific habitat: breathing with the entire surface of the body or gills, streamlined body shape, carapace consisting of chitin and impregnated with a water-repellent substance - calcium carbonate.
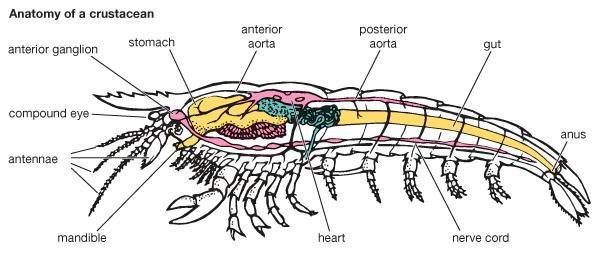
Crustacean systems, such as circulatory, respiratory and excretory, provide homeostasis - maintaining a normal metabolic rate. It should be noted that all crustaceans have an open circulatory system, and the heart has the appearance of a pentagonal sac-shaped organ with 3 pairs of valves. Arteries depart from it to the cephalothorax and abdomen, through which blood carries nutrients and oxygen to all organs of the animal, pouring into a mixed cavity of the body called myxocel. From it already venous blood enters the gills, where it is freed from carbon dioxide and saturated with oxygen, turning into arterial. Through the holes in the pericardial sac, it enters directly into the heart.
Scutelli - a peculiar group of crustaceans
These animals, which are a group of freshwater inhabitants, can live in drying ponds. When the water evaporates, the shield itself is buried in the soil and for a certain time does not lose its viability. Eggs laid by a female at the bottom of a reservoir can last up to 15 years. They are easily transported by the wind along with soil particles, so shields live almost everywhere except for Antarctica and African deserts.
Crustacean life cycle
Representatives of this superclass have both its simple forms, for example, direct development of crayfish, as well as more complex ones, including larval stages. In this case, development is called indirect. It is characteristic of orders of copepods and cladocera, and also occurs in higher crayfish, such as lobsters or lobsters. Crustaceans, whose representatives have pelagic or planktonic forms of larvae, the so-called nauplii and zoea, are widespread in nature: they are inhabitants of the coastal waters of Australia, North America, and Europe. All phases of the crustacean life cycle are controlled by their endocrine system, represented by androgenic, postcommissural, and sinus glands. They secrete hormones that regulate the processes of puberty, molting and the transformation of larvae into adults.
The value of crustaceans in nature and human life
Animals included in the order of decapod crayfish, such as lobsters (lobsters), lobsters, crabs, are valuable commercial species that provide humans with delicious and high-protein meat. Representatives of the lower crayfish are of great importance: cyclops, daphnia, water donkeys, which are food for fish, for example, such valuable as salmon and sturgeon.
Crayfish, often called orderlies, cleanse the bottom of dead organic matter. Although the importance of crustaceans in nature and human life is overwhelmingly positive, some animals are harmful, for example, carp lice cause mass death of commercial fish species. And cyclops are intermediate hosts of parasitic worms: rishta and broad tape.
We were convinced that these animals belonging to the Type Arthropods are an important link in the natural ecosystems of our planet and the importance of crustaceans in nature and human life should not be underestimated. Some species of these animals (for example, broad-toed crayfish, mantis shrimp) are listed in the Red Book, and their destruction is prosecuted.