Binocular (stereoscopic) vision allows us to see the surrounding objects in volume. Thanks to this function, a person is able to correctly assess the distance between objects. With various pathologies of the eyes and the central nervous system, binocular vision disorders can occur. How are such diseases manifested? And can binocular disorders be cured? We will answer these questions in the article.
general characteristics
What is binocular vision? Normally, a person perceives all surrounding objects and objects with two eyes. But at the same time he sees not two visual pictures, but one. Information entering the brain from two organs of vision is merged into a single volumetric (stereoscopic) image. Ophthalmologists call this ability of the human eye binocular vision.
First, each eye individually recognizes the objects of the surrounding world using retinal photoreceptors (cones and rods). Then the signals are transmitted to the visual center of the brain, where they are processed. Information received from the retinas of one and the other eye is merged into a single image. This is the process of combining two visual images, doctors call fusion.
For normal binocular vision, the following conditions are necessary:
- visual acuity with each eye of at least 0.3 diopters;
- the ability of the visual analyzer to fusion;
- coordinated work of the muscular and ligamentous apparatus of the eyeballs;
- lack of deviation of the visual axes from the point of fixation of the gaze;
- lack of retinal pathologies.
Violation of any of these conditions leads to binocular vision disorders. With such pathologies, the perception of the world becomes monocular. The coordinated work of two organs of vision is disrupted. A person perceives all objects alternately: with one or the other eye. Such a patient can correctly perceive the shape and size of objects, but it is very difficult for him to determine their location in space. There are great difficulties in estimating the distances between objects.
Etiology
Consider the most common causes of binocular vision impairment. The following eye and central nervous system pathologies can lead to such a disorder:
- diseases and injuries of the retina;
- cataract;
- corneal burns;
- structural defects in the ocular musculature;
- intoxication of the body with various poisons;
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- neurological diseases.
Binocular disorders are very rarely a separate pathology. Most often, this is only one of the symptoms of ophthalmic and neurological diseases.
The following forms of binocular vision impairment are most common:
- strabismus;
- amblyopia;
- anisometropia.
Next, we will consider the above types of disorders in more detail.
Strabismus: a general description
With strabismus (strabismus), the visual axis of one or two eyes deviates from the object in question. It occurs due to inconsistent work of the muscles of the organ of vision. At the same time, one human eye captures the eye on a specific object, and the other deviates in one direction and perceives completely different objects. As a result, a single visual image does not add up.
The following types of strabismus are distinguished:
These types of strabismus have different etiologies and symptoms.
Friendly form of strabismus
Friendly strabismus is the most common type of binocular vision disorder in children. It arises due to the following reasons:
- neurological disorders;
- adverse effects on the fetus during the prenatal period;
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- acquired farsightedness or myopia;
- decrease in visual acuity of one eye;
- heterophory (different strength of the muscles of the left and right eyes);
- complications after infectious pathologies.
With a friendly form of strabismus, the patient has changes in only one of the organs of vision. In this case, the movements of the eye muscles are not disturbed, and the angles of deviation from the visual axis are the same. This means that if one eye mows at 5 degrees, then the other deviates by the same amount.
Friendly squint often looks like a purely external defect and does not cause special inconvenience to the patient. This form of strabismus is not accompanied by double vision. However, strabismus can lead to decreased visual acuity over time. To make out an object, a person has to squint and strain his eyes. This leads to fatigue of the organ of vision and headaches. Therefore, friendly strabismus must be treated in childhood. Binocular visual impairment in adults is much worse than correction.
Paralytic strabismus
A paralytic form of strabismus is quite rare. This pathology often occurs in adults. His cause is eye injury, ophthalmic surgery, intoxication. Strabismus develops due to paralysis of the muscles responsible for the movement of the eyeball.
This type of binocular vision disorder is characterized by the complete impossibility of the eyeball moving towards the paralyzed muscle. Patients often experience double vision. With a paralytic form of strabismus, visual acuity sharply decreases. Myopia or farsightedness quickly develops. It becomes very difficult for a person to fix his gaze on any subject. This form of strabismus is quite difficult to treat.
Amblyopia
With this disorder, the patient's binocular vision is sharply disturbed. What is amblyopia? Patients often confuse this disease with strabismus. However, these are different pathologies.
Amblyopia develops as a complication of strabismus. Over time, functional changes occur in the squinting eye. He ceases to fully participate in visual perception. This disease is also called "lazy eye syndrome."
Moreover, in the affected organ of vision there are no anatomical changes. All violations are functional in nature. However, the diseased eye is very little involved in the process of visual perception, which leads to a one-sided decrease in visual acuity.
With amblyopia, a person differently sees a healthy and sick eye. Therefore, a single visual image in the brain does not add up. The affected organ of vision distinguishes colors and volume of objects well, but very poorly recognizes details.
Anisometropia
The human eye works like a lens refracting light rays. Doctors call this function of the organ of vision refraction. Normally, the refractive power of the left and right eye is the same.
If the refractive power of one eye is reduced, then ophthalmologists call this pathology anisometropia. This disease is always accompanied by impaired binocular vision. If the difference in the refractive power between the two eyes is more than 2 diopters, then this is accompanied by severe discomfort.
Anisometropia is most often caused by changes in the shape of the lens or cornea (astigmatism). Pathology can also develop in patients with cataracts and after ophthalmic surgery.
With anisometropia, a person sees with a healthy eye a clear and vivid picture, and a sick person sees a blurry picture. Therefore, a single visual image is not formed in the brain. There is double vision, patients complain of blurred vision. If a person covers the sick eye with his palm, then all symptoms disappear.
Diagnostics
There are several home tests with which you can independently check binocular vision:
- Sokolov's method. You need to roll up a tube of paper (like binoculars) and attach to one of the eyes. Opposite the other eye, place your palm and hold it at the level of the end of the pipe. If binocular vision is normal, then a person will see a hole in the palm of his hand.
- Method with a book. At a distance of 2-3 cm from the tip of the nose, you need to place a pencil and try to read the text of the book. With normal binocular vision, a person can do this without difficulty.
- Kalf's method. You need to keep two pencils in front of you, one in a vertical position, and the other in a horizontal position. Then you need to try to connect their ends together. If a person has problems with binocularity, then it will be difficult for him to perform this test.
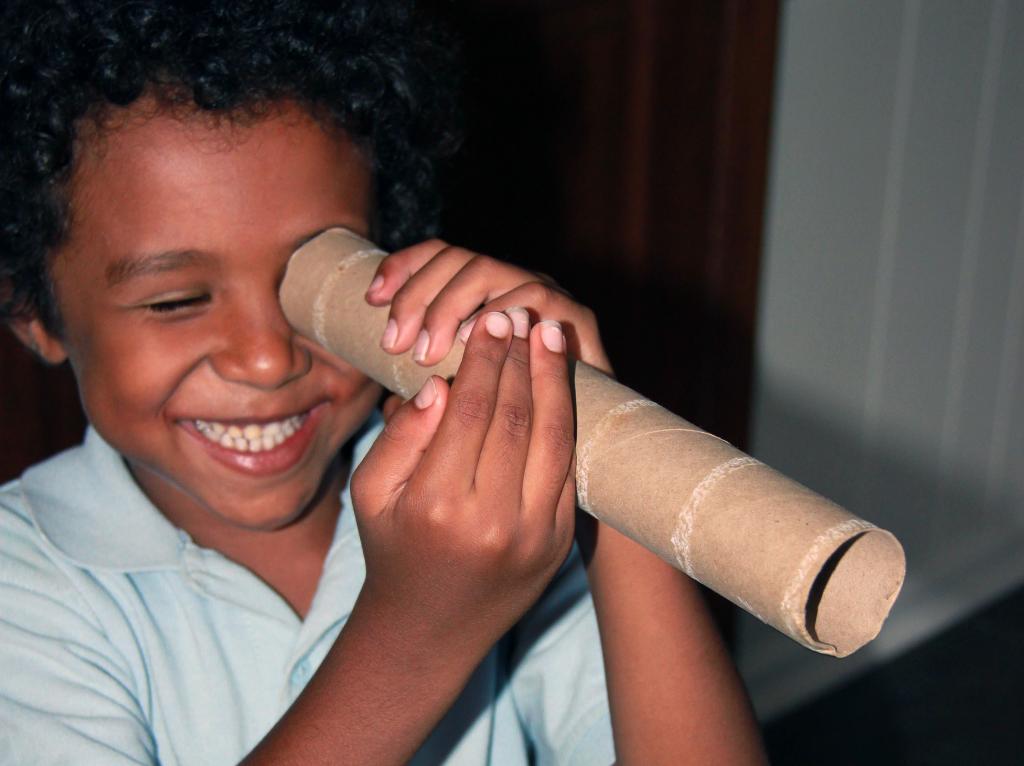
These tests will only help to preliminary assess the quality of stereoscopic vision. Only a specialist can accurately detect binocular disorders. If the patient has increased fatigue of the organ of vision, double vision or visible strabismus is noted, then it is urgent to visit an ophthalmologist.
Doctors prescribe the following diagnostic procedures for checking binocularity:
- Inspection on the Monobinoscope and Sinoptofor devices. These devices not only help to diagnose strabismus and amblyopia with high accuracy, but are also often used for medicinal purposes.
- Refractometry Using a special device, the refractive power of both eyes is evaluated and compared.
In addition, ophthalmoscopy and biomicroscopy are performed. This allows you to assess the condition of the tissues of the cornea, lens and fundus.
Therapies
The treatment of binocular vision disorders at an early stage is carried out by conservative methods. The following methods of therapy are used:
- Occlusion. The patient wears special glasses in which one of the glasses is sealed with a band-aid. The sticker is applied to the healthy side. This causes the patient to strain the squinting eye. This treatment method prevents the development of amblyopia against the background of strabismus.
- Hardware techniques. For treatment using devices "Monobinoscope" or "Sinoptofor". With their help, exercises are carried out for the eyes to combine several pictures into one whole. Also, these devices allow you to stimulate the eye muscles with light signals.
Drug treatment for binocular disorders is auxiliary in nature. Assign complexes with beta-carotene, vitamins A and C. This helps maintain visual acuity. With a paralytic form of strabismus, the use of nootropics, antioxidants and neuroprotectors is indicated.
If for 1.5-2 years the effect of conservative therapy is absent, then this is considered an indication for surgery. During surgery, the doctor weakens the eye muscle. This leads to the normalization of eye movements and the elimination of external signs of strabismus. However, binocular disorders can persist. Therefore, after the operation, a second course of hardware treatment is carried out using the Synoptofor device.
It is important to remember that treatment for strabismus and amblyopia is best done in childhood. In adults, such visual disturbances require prolonged and persistent therapy, and sometimes surgical intervention.