In the modern world, a huge number of ailments of various organs are known. Eyes are no exception. With the manifestations of the first symptoms, you should consult a professional doctor. Chorioretinitis of the eye is an inflammatory process affecting the posterior portions of the choroid of the eyeball. Pathology can also spread to the retina. This disease greatly reduces the speed of blood circulation processes. This fact is explained quite simply: the largest number of infectious agents lingers on the back of the eyeball. In this review, we will examine in more detail what eye chorioretinitis is, how to treat this disease, as well as preventive measures.
Disease development
So what do you need to know about this? Chorioretinitis of the eye spreads gradually. Initially, the disease affects the network of capillaries, which provide blood to the retina. After that, it switches to a network of large vessels. Inflammation can occur both in acute and in chronic form. The disease can be classified according to a number of symptoms. Each type of ailment has its own characteristics.
Chorioretinitis of the eye can manifest itself at any age. In a child, it can be a complication of infectious diseases, and in adults, it can develop as a result of improper use of optical correctors or due to contact with chemical reagents.
Classification
Let's dwell on this in more detail. Chorioritis of the eye can be classified depending on a number of signs that determine the form and type of development of the disease. These include:
- number of foci;
- distribution area;
- pathogens;
- duration of manifestation.
Depending on the area of distribution, they share:
- Central serous chorioretinitis of the eye (appears in the macular region).
- Peripapillary (appears near the optic disc).
- Equatorial (inflammation of the choroid near the equatorial part of the organ of vision).
- Peripheral chorioretinitis of the eye (occurs at the border of the dentate line).
The disease can manifest itself in one or more parts of the eye. According to this symptom, the disease can conditionally be divided into:
- focal chorioretinitis of the eye: when inflammation is concentrated in only one area;
- multifocal: an inflammatory process localized in several areas at once;
- diffuse chorioretinitis: characterized by a large number of inflammations with possible fusion.
Pathology can also vary in duration of manifestation. The acute form is said when the disease manifests up to one trimester. A chronic illness bothers for longer, at least three months.
Chorioretinitis of the eye can also be classified depending on what became the causative agent of the pathology. According to this symptom, the disease is divided into:
- infectious chorioretinitis;
- post-traumatic;
- non-infectious-allergic;
- infectious and allergic.
Most often we are talking about an infectious type of disease. There is also a congenital pathology - toxoplasmosis chorioretinitis. In this case, infection occurs in the womb with toxoplasmosis. Not only the eyes are affected, but also other organs. The foci of the disease are represented by pronounced contours with strong pigmentation.
By the nature of the occurrence, the disease under discussion is divided into the following types:
- Tuberculosis: A secondary disease that develops only when infected with tuberculosis. It manifests itself in the occurrence of disseminated tuberculosis. After treatment, chorioretinal scars may remain.
- Syphilitic: appears on the fundus, characterized by the alternation of fibrous foci of atrophy and pigmentation foci.
- Purulent: occurs due to immunodeficiency. The main danger of this form is the spread of exudate to other sectors of the eye. An immunodeficiency variety is distinguished, which is characterized by a large lesion area, necrotic and hemorrhagic character. This form of the disease is quite difficult and can even end in complete blindness.
The remaining varieties of the disease have practically no distinguishing features. Especially, myopic chorioretinitis can be distinguished. It usually develops in the region of the macula, located on the surface of the retina. The cause of the disease is recurring retinal hemorrhage.
Stages
How is chorioretinitis of the eye manifested? Symptoms depend on the stage of the disease. The initial stage is characterized by:
- the appearance of grayish-yellow foci with weak contours;
- the formation of exudate along the network of vessels;
- the appearance of small hemorrhages.
In the progressive stage of the disease, foci appear with pronounced outlines, strong pigmentation, as well as retinal atrophy.
Causes
Let's look at them in more detail. What causes chorioretinitis of the eye? Usually this pathology is a consequence of the following diseases:
- autoimmune pathologies such as arthritis and diabetes;
- infectious diseases: syphilis, toxoplasmosis, herpes virus;
- immunodeficiency diseases;
- exposure to toxins;
- viral diseases;
- damage and injury;
- allergic reactions;
- prolonged exposure to radiation;
- the development of complications.
Symptoms
So what should you pay attention to first? As a rule, the signs of the disease are most pronounced at the site of the focus of occurrence. Diagnose the disease by the following signs:
- blurred field of view;
- deterioration in visual acuity;
- the appearance of dark areas;
- the presence of outbreaks;
- flickering sparks during visual review;
- distortion of the shape and size of the objects under consideration;
- difficulty orienting in the dark;
- retinal clouding;
- hypersensitivity to bright light sources;
- the appearance of pain in the eye area;
- change in color perception.
These signs indicate the development of eye pathology, therefore, if one of the manifestations is detected, it is necessary to seek help from a qualified doctor and conduct a diagnosis. It should also be borne in mind that some types of the disease are asymptomatic. These include peripheral species.
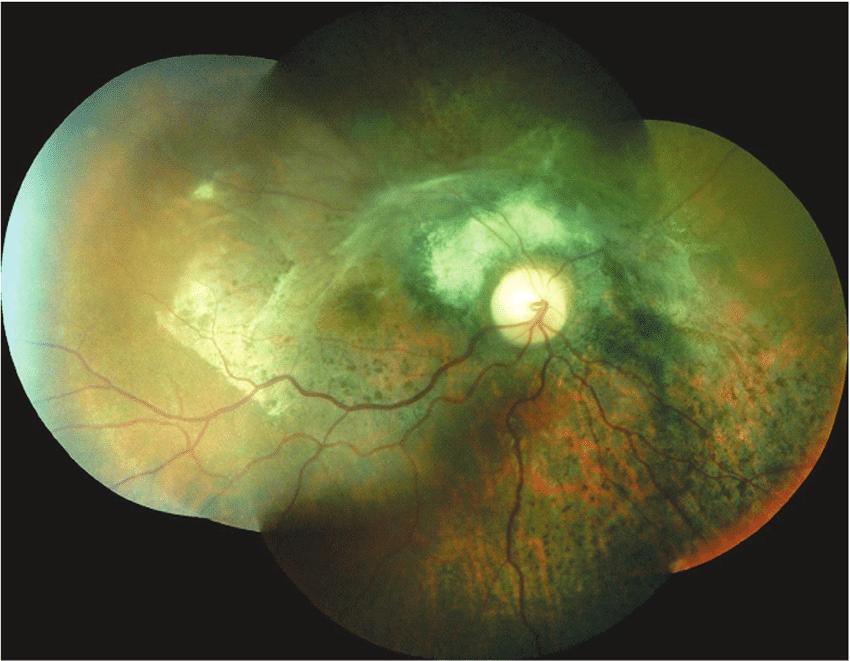
Diagnostics
How is chorioretinitis eye disease detected? What is it and what is its feature? To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is offered to undergo the following examinations:
- visual acuity checking: central chorioretinitis of the eyes is characterized by a deterioration in vision, while it will be impossible to correct it in the future;
- periometry;
- refractometry;
- biomicroscopy: this examination helps to identify the presence of deformities of the vitreous body;
- examination in transmitted light: may reveal clouding of the vitreous body;
- ophthalmoscopy: allows you to determine the degree of development of the disease;
- fluorescence angiography: reveals a change in the vessels of the fundus (the occurrence of shunts and microaneurysms);
- X-ray diffraction: allows you to determine the state of the retina and to determine whether it performs its functions;
- optical coherence tomography: shows the presence of morphological features of the focus of inflammation;
- Ultrasound: Detects the condition of optical media.
Specialists
Which doctor helps to eliminate chorioretinitis of the eye? The treatment of this disease should be under the control of several qualified specialists. If necessary, you can seek advice from a therapist, infectious disease specialist, immunologist, venereologist, allergist, TB specialist, ENT specialist, and dentist.
If central chorioretinitis of the right eye has been detected in a child, then you should consult a pediatrician.
Treatment
This aspect should be given special attention. How can this disease be cured? It should be understood that treatment for chorioretinitis is selected individually. Local therapy in this case can be extremely ineffective. The exception is parabulbar and retinobulbar injections.
Conservative drug treatment usually includes two groups of drugs:
- etiotropic: eliminate the provoking factor;
- antibiotics: used if the causative agent of the disease is bacteria.
If the cause of chorioretinitis of the eye is viruses, then interopherons, interferonogenesis inducers and antiviral drugs are usually prescribed for treatment.
The syphilitic variety of the disease under discussion is treated with penicillin antibiotics. If the patient has intolerance to this type of drug, he can be prescribed a course of doxycycline, macrolides and cephalosporins. The doctor should be responsible for determining the dosage of these medicines.
In inflammatory processes, "Pyrimethamine", "Sulfalimesin" can be prescribed. For the treatment of tuberculous chorioretinitis, the help of a TB specialist will be required. In the chronic form of the disease, a course of Isoniazid, Streptomycin, Kanamycin, and hormonal therapy can be prescribed.
A mandatory part of treatment is anti-inflammatory therapy. It may include taking drugs such as Indomethacin, Hydrocotisone, Diclofenac, Lexamethasone. They are usually taken orally, since their action is activated in the gastrointestinal tract. For intramuscular and intravenous administration, Didrospan may also be prescribed.
Detoxification treatments include Haemodesus and 5% glucose solution. These drugs are used intravenously.
Depending on the severity of the inflammation, immunotherapeutic agents may also be prescribed. For example, with the active form of the disease, immunosuppressants, such as Fluorouracil and Merkaltopurin, as well as immunostimulants, are used.
Hyposensitizing therapy may be possible with antihistamines. These include Erius, Suprastin, and Claritin. Also, to improve the body's resistance, the attending physician may prescribe the intake of B vitamins, ascorbic acid and multivitamin complexes.
If the pathology manifests itself over time, then extracorporeal detoxification methods can be used to treat it. These include plasmophoresis and hemosorption. Physiotherapy can also speed up the treatment process. Electrophoresis gives a wonderful effect with the use of Fibrinolysin and Lidase.
If the disease has caused serious complications, or if the inflammatory process has spread too much, surgical intervention may be required. To slow down this process, laser coagulation of the retina can be performed. This procedure is performed to limit chorioretinal foci from unaffected areas. When a chorioretinal membrane is formed or retinal detachment, vitrectomy is necessary.
Possible complications
This aspect is worth exploring first. Now that we know approximately what chorioretinitis of the eye is, how to treat this disease, possible complications should be analyzed. With inadequate therapy or an advanced stage of the disease, chorioretinitis can turn into serious problems. These include:
- formation of a neovascular membrane;
- retinal detachment;
- the appearance of retinal hemorrhages;
- venous retinal thrombosis leading to blindness.
Preventive measures
So what do you need to know about this? To prevent the development of a disease such as chorioretinitis in a child or adult, it is enough to adhere to the following recommendations:
- consult a specialist at the first symptoms of any disease;
- regularly visit the ophthalmologist’s office in order to check the state of eye health; visits to the doctor can be made already 3 months after birth;
- try not to injure your eyes;
- observe eye hygiene;
- timely reorganization of foci of inflammation in the sinuses and in the mouth.
It should be borne in mind that with the progression of the disease and untimely provision of medical care, the risk of developing various kinds of complications, up to subsequent disability, is very high.
Conclusion
Chorioretinitis is a rather complex and intractable disease. This term refers to inflammation of the posterior retina and choriodea. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of floating opacities and flies in the eyes. There may also be a decrease in visual acuity and a violation of dark adaptation, or so-called night blindness. There are many varieties of this pathology: tuberculous, post-traumatic, infectious, syphilitic, central chorioretinitis of the right eye. This disease can get sick at any age. It is worth noting that small children are at risk, as they are especially susceptible to infectious and viral diseases.
Drug therapy for the treatment of this disease usually includes taking antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. Also, the doctor may prescribe biogenic stimulants, reparants, mydriatics and glucocorticosteroids. Usually, the patient is recommended to take vitamin complexes for the overall strengthening of the body. Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment also give a good effect. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required.