This fairly common eye disease causes many problems and inconveniences to many patients who seek the help of ophthalmologists. What is iridocyclitis, symptoms and treatment of this disease - all this is described in detail in the article.
Iridocyclitis: what is it?
Under the terrifying term “iridocyclitis” is a disease of the choroid (ciliary body and iris). This is an inflammation of the anterior and partially middle section of the choroid, which can be both infectious and non-infectious in nature.
The nature of the course of the disease
By the nature of the course of the disease, several forms of iridocyclitis are distinguished:
- Acute (or subacute) - occurs suddenly, most often as complications of the flu or rheumatic disease.
- Chronic. This form of iridocyclitis is characterized by a sluggish course. It occurs, as a rule, with penetrating wounds of the eyes, as well as one of the symptoms of herpes (herpes iridocyclitis) and tuberculosis.
- Recurrent.
Types of inflammatory process
Depending on the form of the inflammatory process, the following types of iridocyclitis are distinguished:
- Fibrinous - occurs with an eye injury. In this case, fibrinous exudate is formed in the anterior ocular chamber. The formation of exudate is accompanied by no less dangerous symptoms: lacrimation, blepharospasm and photophobia. In addition, fibrinous iridocyclitis is characterized by severe pain in the injured eye, clouding of the vitreous body and the appearance of synechia. The disease can be diagnosed by reduced intraocular pressure and the deposition of fibrin on the inner surface of the cornea in the form of precipitate.
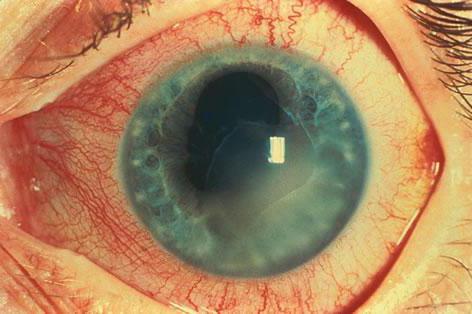
- Purulent iridocyclitis - also occurs when an eye is injured, usually two to three days after an unpleasant incident. It proceeds quite hard, with the formation of purulent exudate in the anterior chamber of the eye. In addition to trauma, purulent iridocyclitis often becomes a complication with protracted and at one time untreated sore throat, pyorrhea, furunculosis and other diseases caused by hematogenous entry into the body of the pathogen. In addition to white exudate in the eye, patients have pronounced eyeball irritation and pain. A neglected disease can go to the posterior ocular region and lead to endophthalmitis and panophthalmitis.
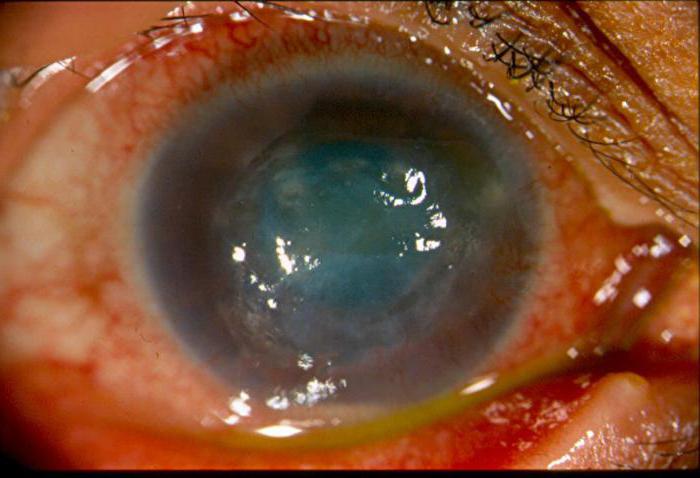
- Hemorrhagic iridocyclitis - occurs as a result of damage to the walls of the vessels of the eye by a viral infection. As a result of exposure to the virus in the moisture of the anterior ophthalmic chamber, as well as in the vitreous , hemorrhagic exudate with an admixture of blood is collected.
- Sympathetic iridocyclitis - the course of the disease occurs with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission, may last several months or years. The progression of the disease is slowed down, acute forms practically do not occur. First of all, the anterior part of the choroid of the eye is affected, combined with retinal detachment and the appearance of diffuse choriolites. Launched sympathetic iridocyclitis leads to inevitable infiltrative or exudative changes in the choroid. In addition, the occurrence of complications in the form of neuroretinitis is also possible.
- Serous iridocyclitis - in addition to the presence of serous exudate in the anterior ophthalmic chamber, this type of disease is characterized by the presence of a mild vascular injection. Gray precipitates appear on the back of the cornea. Serous iridocyclitis is dangerous primarily the development of secondary glaucoma, as well as clouding of moisture in the anterior chamber of the eye due to the characteristic constant fluctuations in intraocular pressure.
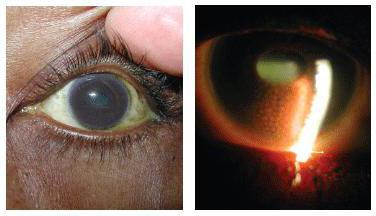
- Mixed iridocyclitis, or serous fibrinous. It is characterized by the simultaneous presence of whitish or pigmented precipitates on the cornea, as well as hyperemia and edema of the iris. In addition, it is possible clouding of the vitreous body and synechia.
In addition to the above symptoms inherent in a particular type of iridocyclitis, the disease occurs with the occurrence of local plethora in the optic nerve disc, as well as focal chorioretinitis.
Signs of the disease
In acute course of iridocyclitis, the following symptoms are observed in patients:
- Severe, night-time pain in the eyes.
- Unhealthy eye reaction to light. Under the influence of light, profuse lacrimation is observed.
- A sharp deterioration in vision.
- Turbid shade of the iris.
- The narrowed deformed pupil reacts poorly to light.
- Deposition of exudate on the vitreous, crystalline and posterior surface of the cornea. This deposition is called “precipitate”.
- The formation of adhesions between the lens and the pupil.
- Decrease in intraocular pressure.
- Enlarged perilimbal blood vessels.
In addition to the listed symptoms, the list may be supplemented further. It depends on the type of acute iridocyclitis. Namely, they distinguish between influenza and rheumatic acute iridocyclitis.
An acute inflammatory iridocyclitis is characterized by an extensive inflammatory process, eventually leading to fusion of the anterior lens shell and the edge of the iris. The rheumatic form is accompanied by sharp pain and hemorrhage in the anterior chamber of the eyeball.
Chronic iridocyclitis has the same symptoms as acute, with the only difference being that all signs of the disease are less pronounced. Despite this, the disease is not less dangerous, but on the contrary, it is less treatable.
Disease age
Most often, iridocyclitis overtakes people aged about 40 years, but cases of the disease of children, adolescents, as well as the elderly are not excluded.
Causes
If we consider the etiological aspect of the occurrence of the disease, then distinguish:
- Infectious iridocyclitis - occurs under the influence of parasites, fungi, bacteria and viruses.
- Allergic iridocyclitis.
- Iridocyclitis caused by systemic diseases (rheumatism, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis).
- Iridocyclitis caused by eye injury.
- Iridocyclitis, arising from metabolic disorders and endocrine diseases.
The causes of the development of the disease include:
- Infectious diseases (tuberculosis, herpes, syphilis, flu).
- Systemic diseases.
- Allergies.
- Eye injuries.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Inadequate nutrition.
- Low immunity.
- Diseases of the oral cavity.
- ENT diseases.
Diagnosis of the disease
How to recognize iridocyclitis? A number of additional studies will help clarify the diagnosis to the doctor:
- Determination of visual acuity. One of the signs of the disease is visual impairment caused by the presence of exudate or edema of the cornea in the eye.
- Determination of intraocular pressure. An increase in pressure inside the eyes is another wake-up call for suspecting iridocyclitis. Usually, an increase occurs due to the formation of adhesions in the iris-corneal corners of the eyes.
- Biomicroscopy
- Inspection in transmitted light - reveals the presence of exudate in the vitreous body.
- Ophthalmoscopy If the patient suffers from iridocyclitis, then one of the diagnostic methods is ophthalmoscopy. In this case, examination of the fundus will be difficult or almost impossible due to inflammation in the anterior part of the eye.
- Ultrasound examination of the eye.
- Laboratory research methods: general blood test, biochemical blood test, rheumatic test, coagulogram, allergy test.
- PCR
- IFA.
- X-ray of the lungs and sinuses.
With the results of the studies and tests taken, the patient is sent for a consultation with a therapist, infectious disease specialist, allergist, rheumatologist and dermatovenerologist to confirm the presence of the disease.
Treatment of iridocyclitis
The choice of treatment method depends primarily on the form of its course. The standard treatment for iridocyclitis includes both outpatient and inpatient methods. In addition, with an uncomplicated form, consultative treatment can be applied.
A successful outcome guarantees only an integrated approach, that is, a combination of all known methods. First of all, it is necessary to remove the inflammatory process, and then take measures to prevent scarring and the appearance of adhesions.
Drug therapy
Any disease requires a thorough approach, including iridocyclitis. Treatment, drugs can be either strictly individual (if the patient has an allergy), or general.
Drug treatment is prescribed depending on the form of the disease:
- A non-specific form of iridocyclitis is treated with hormonal therapy using drugs such as Prednisolone and Hydrocortisone. The drugs have anti-inflammatory effects, have a powerful effect not only for treatment, but also to prevent the overflow of the disease into a more complex form, as well as possible complications.
- The purulent form of iridocyclitis is cured by broad-spectrum antibiotics. At the same time, analgesics can be prescribed to relieve painful sensations of the eyes that accompany iridocyclitis. Antibiotic treatment coupled with painkillers gives a good effect. Discomfort is also easily removed by infraorbital novocaine pterygopalatine-orbital blockades. In addition to antibiotics, the purulent form of the disease also requires daily thorough treatment of the skin around the eyes with a chatter or special gel. In some cases, the doctor may decide to prescribe a subcutaneous injection with biostimulants.
Regardless of the form and stage of the disease, the formation of synechiae (i.e., adhesions), as well as the fusion of the lens of the eye with the iris, mydriatics are used, which include:
- Medriacil solution.
- A solution of adrenaline in a ratio of 1: 1000.
- Atropine sulfate solution (used in 1% concentration).
- Drops "Diclof" (non-steroidal, it is possible to replace them with "Na-clof" and "Indomethacin"), used to enhance the therapeutic effect of the above mydriatics.
These funds are aimed primarily at the expansion of the pupil. In the event that iridocyclitis is caused by any systemic disease, treatment of eye disease should take place in conjunction with getting rid of the cause. Isolated therapy is not able to give long-term desired result.
Adjunctive therapy
In addition to medical treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures will also be useful. An ophthalmologist can be prescribed magnetotherapy, electrophoresis using trypsin and lidase, as well as UV radiation. Additional treatment of iridocyclitis will prevent the occurrence of relapses, and can also overcome the residual symptoms of the disease.
Alternative treatment methods
Alternative therapy is suitable for those who are pursued by chronic iridocyclitis. Treatment in this case involves:
- Hirudotherapy, or treatment with leeches. Two leeches should be placed on the temple above the sore eye. The main condition for such therapy is the supervision of a qualified specialist.
- Dry heat treatment (applying to a sore eye).
Iridocyclitis: home treatment
As you might have guessed, the disease in question is very dangerous, jokes with him are bad. In any case, the patient needs specialist advice in order to avoid frightening consequences. If you are suddenly overtaken by acute iridocyclitis, treatment at home it is justified if used to alleviate one’s condition until an opportunity to visit a doctor appears. Therapy in this case is to remove the acute form of inflammation. Moreover, home treatment may involve not only the use of folk remedies, but also medicines.
Traditional medicine recipes
With iridocyclitis, it is recommended to take decoctions:
- A mixture of 1 liter of lemon juice with garlic chopped on a grater in an amount of 400 grams should be diluted with boiled water (1 teaspoon of the mixture in 1 glass of water). Take 2 times a day. Store the prepared mixture (previously closing the lid) in a dark, cool place.
- A decoction of aspen bark. Water with bark (in any proportions) should be boiled for 15 minutes, and then let it brew for 4 hours. Take every other day, 1 glass per day. The resulting infusion has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect that can muffle iridocyclitis.
Treatment with folk remedies is not complete. Remember: no matter how effective at first glance the result may seem, a thorough elimination of the cause of the disease will be required. And this is possible only with the use of medicines.
Disease prevention
As you know, the disease is better to prevent than to cure. Prevention of iridocyclitis involves:
- Strengthening immunity (hardening).
- Proper nutrition.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Timely fight against infectious and inflammatory diseases that can lead to iridocyclitis.
- Timely flu vaccination.
- Protection against hypothermia in the winter season.
Do not mess with iridocyclitis - the consequences can be terrible!