Corneal dystrophy is a combination of hereditary diseases that cause clouding of the cornea and a decrease in visual acuity. In rare cases, acquired forms of corneal dystrophy are found. The cornea is a convex transparent part of the eyeball, which is located in the anterior region. It includes several layers: the protective layer of the epithelium, the second protective layer of the Bowman membrane, the thick layer of tissues and fluids - the stroma, the posterior boundary layer - the Descemet membrane, and the inner layer that removes excess water - the endothelium. Dystrophy of the retina of the eye affects one of these layers. To a slight degree, this is expressed in the accumulation of certain tissues in the middle layers.
Types of disease
The cornea is multilayered in composition, and the types of dystrophies are divided according to the principle of damage to the layers:
- Epithelial.
- Stromal.
- Endothelial.
- Membrane dystrophy.
Primary
In addition, dystrophy is divided into primary and secondary. It is believed that the primary form of dystrophy of the retina of the eye is congenital, that is, it is a genetic disease that spreads to both eyes. The congenital form of dystrophy is characterized by a slowed course, and the patient discovers the first symptoms in himself only by the age of 30. Diagnosis is complicated by the genetic condition of the disease, so the primary form of dystrophy is detected only after genetic analysis.
Secondary
Secondary, she also acquired retinal dystrophy, usually affects only one side. And it occurs due to various injuries, inflammations, surgical interventions and various disorders in the human immune system. Medicine has more than two dozen varieties of corneal dystrophies and combines them into three categories, due to which layers of the cornea are affected by the disease. Superficial dystrophy of the retina of the eye spreads only on the front layers - the epithelial and Bowmanov’s membrane. A disease concentrated in the stroma is included in the category of stromal dystrophy of the retina. In the third category are dystrophies of the deep layer, affecting the descemet membrane and endothelium.
Causes
There are a lot of reasons for dystrophy of the cornea of the eye, therefore, it is not always possible to establish what was its catalyst. The main causes are primarily the hereditary factor, followed by pathologies of the immune system, post-traumatic neurotrophic changes, consequences of corneal inflammation or operations performed. Secondary dystrophy of the cornea, appear as a result of existing pathological processes.
For example, after burns of sclera or conjunctiva, tear fluid deficiency, collagenosis, congenital glaucoma, eversion and inversion of the eyelids, with exacerbation of keratoconus due to vitamin deficiency. In a patient with diabetes mellitus, against the background of strong lasting changes in the body, diabetic retinopathy often occurs. Diabetes mellitus affects blood vessels, and small retinal vessels are no exception. The blood flow in the capillaries increases, after which it is completely blocked, neovascularization and hemorrhage occur. The vascular system of the retina is very fragile, any violation of its functions can become a catalyst for the development of corneal dystrophy. Immune system dysfunctions in many cases contribute to scarring of the corneal layers. An improper diet, diet, or eating poor quality foods causes dystrophy. Systematic smoking and the use of alcohol-containing drinks adversely affect the retina and can be one of the factors in the development of corneal dystrophy. If the patient suffered severe viral diseases, but did not completely cure them, then these diseases or their consequences will cause retinal degeneration. The same applies to chronic cardiovascular diseases and pathologies of the endocrine system. Progressive diabetes mellitus, circulatory system dysfunctions, metabolic disorders, especially in the presence of excess weight, form a serious risk factor for the patient.
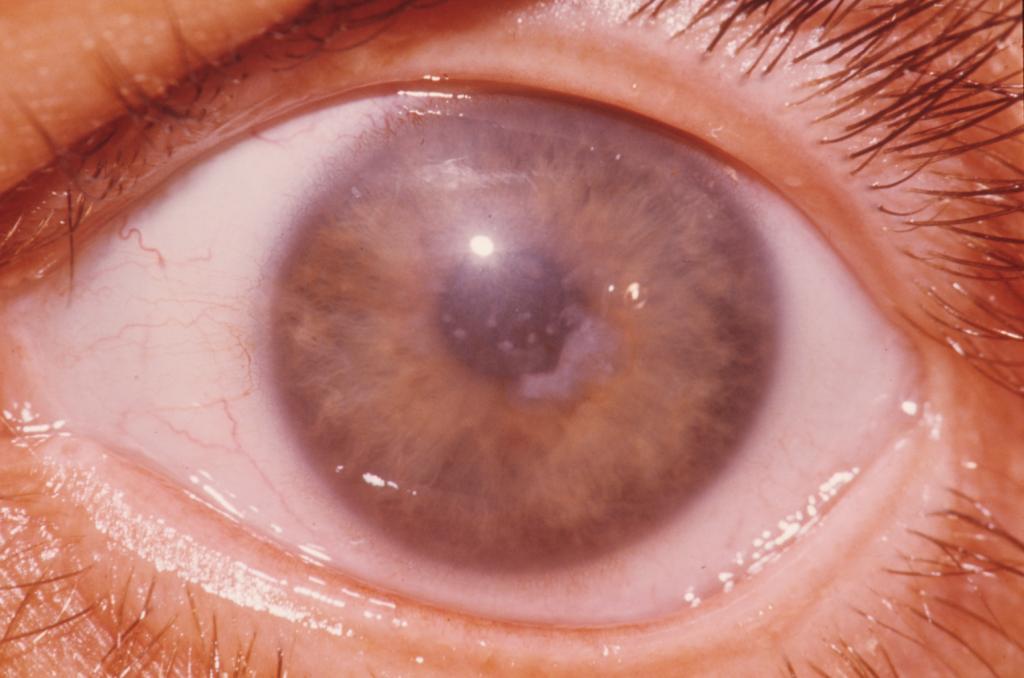
Symptoms
The first signs of corneal epithelial dystrophy can begin as early as 10 years old, as a rule, the disease does not occur later than forty-five years of age. Dystrophy of the retina of the eye is a group of diseases, but their symptoms are manifested in a single set of symptoms. The basic symptoms of corneal dystrophy include:
- methodical deterioration in visual acuity;
- clouding and swelling of the cornea;
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
- involuntary discharge of tear fluid;
- photophobia;
- soreness;
- foreign body sensation in the eye.
The main symptom
A pronounced sign of stromal dystrophy of the cornea of the eye is a significant visual impairment in the morning, with a gradual improvement towards the end of the day. During the night, moisture accumulates in the corneal tissues, it begins to dry slowly after a person gets up and vision returns to normal.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a dystrophy of the cornea of the eye, you should contact an ophthalmologist. The medical professional should examine the patient using an ophthalmic slit lamp. In addition to the study using a slit lamp, to make the correct diagnosis, the patient is invited to undergo a full examination. It necessarily includes: perimetry and visometry, measurement of fluid pressure inside the eye, assessment of the structure of the eye using ultrasound, examination of the nerve cells of the eye, fundus examination, biomicroscopy, laboratory analysis of corneal infiltrate, OCT.
How to treat corneal dystrophy?
The methods for treating all corneal dystrophies are the same, despite the different types of disease. Typically, treatment includes drugs to restore the epithelium, eye drops and ointments. Drops for eyes and ointments have a positive effect in tissue repair, create a protective barrier, relieve swelling and moisturize the surface of the cornea. Such drugs as Solcoseryl, VitA-Pos, Actovegin, Korneregel, vitamins and enzymes are suitable for treating retinal dystrophy.
With a confirmed diagnosis of dystrophy of the retina, it is important to strengthen and expand the small vessels inside the eye. This is helped by preparations of angioprotectors and relaxers of smooth muscles of blood vessels, this group includes Complamin, Papaverine, No-shpa. Medicines that prevent the occurrence of clogging blood clots in blood vessels - antiplatelet agents, are often prescribed for such eye pathologies. Your doctor may use Clopidogrel or Ticlopidine. The drug "Lucentis" inhibits the growth of newly formed vessels, and "Pentoxifylline" evens out the microcirculation of blood and lymph in the retina. For the treatment of dystrophy, Oftan-Katahrom, Taufon, Emoksipin, Balarpan drops are best suited. They actively favor the harmonization of metabolic processes and tissue repair. In case of inflammation of the cornea, antibacterial drugs Levomycetin, Tobrex, and Phloxal are additionally prescribed. If necessary, select contact lenses that help restore the epithelium. All of the above treatments are more suitable for the initial stage of the disease.

Physiotherapy
Methods of physiotherapy - electrophoresis and laser irradiation - are widely used in the treatment of corneal dystrophy. But physiotherapy is not able to prevent the destructive process of the disease. Physiotherapy is designed to suspend the pathological process and preserve the patient’s vision.
In the vast majority of cases of corneal dystrophy of the eye, one cannot do without an operation that is selected individually. Laser retinal coagulation, vasorestruction, revascularization, vitrectomy or keratoplasty are performed. The last operation is aimed at removing the affected area of the cornea. A donor transplant is installed at the site of the removed site. As a rule, after the operation, the patient's condition quickly improves and the disease almost never recurs. In rare cases, the patient has to repeat this operation.
Folk methods
In the initial stages of corneal dystrophy, in combination with the main treatment, traditional medicine is able to deal with the symptoms of the disease. Hirudotherapy helps many patients, which will improve the functioning of the immune system, reduce blood sugar, relieve inflammation and remove harmful substances from the blood. Alternative medicine offers a wide range of recipes for treating corneal dystrophy. The reviews are positive. For example, if there is a risk of retinal detachment, it is recommended to drip into the eyes a mixture of goat milk and boiled water in a one to one ratio. Good drops for the eyes are obtained from a decoction of celandine and a mixture of decoctions of caraway and cornflower. Herbs are not only used as useful drops, but are also often taken orally, for example, infusions from birch leaves and lingonberries. Treatment of corneal dystrophy of the eye with folk remedies is quite effective. But it should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
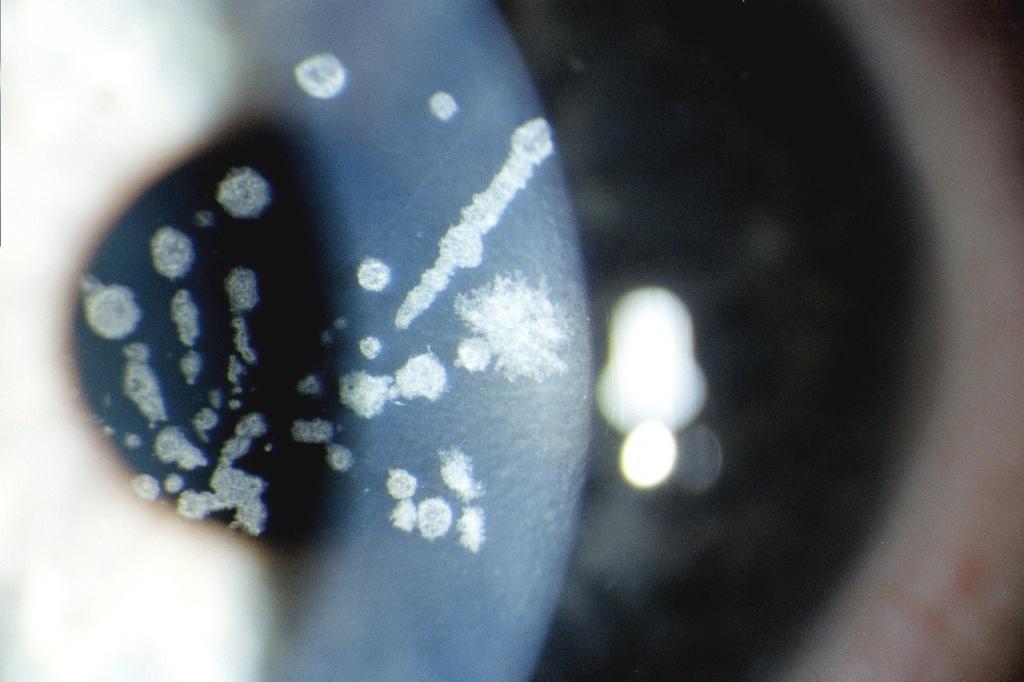
Preventative measures
There are no special procedures to prevent corneal dystrophy. If the patient has a genetic disposition for this disease or other eye pathologies, then even in the absence of problems, an ophthalmologist should be visited. People with a diagnosis of retinal dystrophy must undergo a routine examination twice a year to avoid relapse. It is also necessary to protect the eyes from contact with ultraviolet rays, that is, wear glasses with tinted glasses as often as possible. It is forbidden to expose the eyes to strain, while working at a computer or reading, it is imperative to take breaks. Corneal dystrophy of the eye, left without proper treatment, ultimately leads a person to complete blindness and subsequent disability. Dystrophy of the retinal membrane has a favorable prognosis if the patient promptly seeks help and performs all the procedures prescribed by the doctor. If such diseases were not observed, then preventive measures will be common. That is, compliance with the correct sleep and rest regimen, a balanced diet.