What types of astigmatism exist? How can this ailment be identified? You will find answers to these and other questions in the article. Astigmatism is called a refraction disorder (refraction of light), in which the picture is focused not at one, but at once at several points of the retina. This is due to the irregular shape of the cornea.
Together with farsightedness and myopia, astigmatism refers to ametropia. These are conditions caused by improper refraction. It should be noted that astigmatism is a very common pathology, which, according to various sources, is found in 25% of the total population. Consider the types, stages, symptoms and correction of astigmatism below.
What it is?
What is astigmatism? It is one of the underlying causes of decreased vision. In fact, astigmatism is a transformation of the standard refractive power of the transparent spheres of the eye, in which it may be weakened (astigmatism hyperopic) or increased (astigmatism myopic), as well as a pronounced disorder of sphericity. Moreover, as a rule, the refractive power in some meridians is greater, and in others less.
With such a violation, a person cannot choose the optimal distance to the object in order to clearly see it. The distance in one meridian for the refraction of light rays may be adequate, and in another - inadequately.
Causes of astigmatism
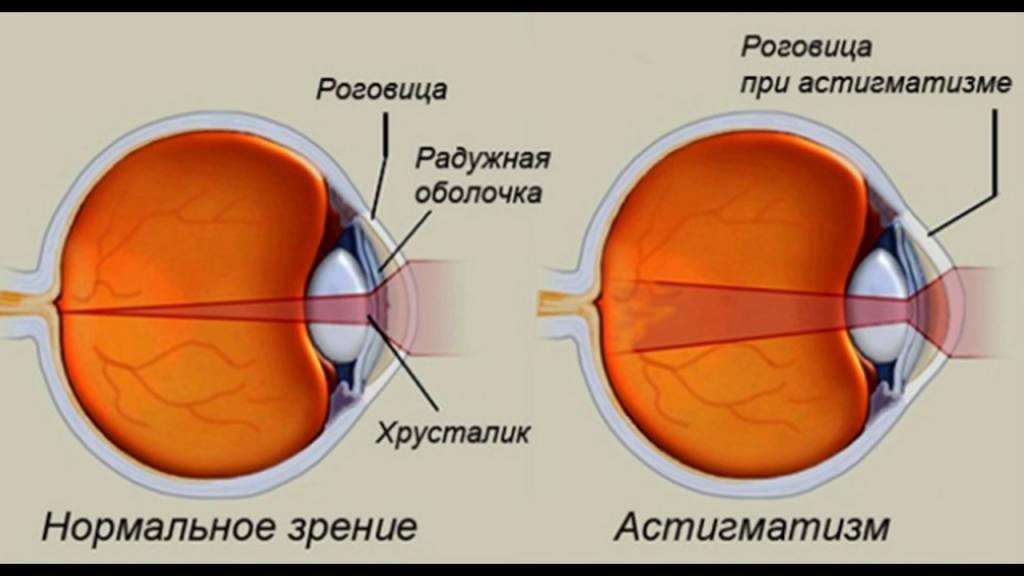
Symptoms, causes, signs and types of astigmatism are not well known. This ailment develops due to an irregular shape of the cornea (sometimes the lens). The word "astigmatism" is translated from Latin as "lack of a focal point."
It is known that the lens and cornea of the unscathed eye possess a spherical flat surface. With astigmatism, a disorder of this sphericity occurs, and as a result, different curvatures form in different directions. Different meridians of the surface of the cornea in this state possess unequal refractive power, so the picture of an object during the passage of light rays through such a cornea is distorted.
Some areas of the image are projected onto the retina, while others are projected behind or in front of it. But there are situations that are more complicated. As a result, a person sees not an ordinary picture, but a transformed one, in which some lines are clearly visible, while others are blurred. How do people with astigmatism see surrounding objects? Take a teaspoon oval and look into it. You will see your distorted reflection in it, and this is how people with astigmatism see everything around.
Symptoms
Types of astigmatism, we will consider further, and now we list the symptoms of this ailment. These include:
- Headache.
- Blurry vision that does not depend on distance.
- Straight line deformation.
- Constant eye strain.
- Rapid fatigue of the organs of vision.
Kinds
The disease is classified on the basis of certain factors. According to them, the following types of astigmatism are distinguished:
- due to appearance - acquired, congenital;
- by pathology - lens, corneal;
- by type: with oblique axes - direct, reverse;
- by the source of refractive power - wrong, right;
- in appearance - complex, myopic, simple;
- hyperopic - mixed, simple, complex.
It is known that the human eye is a structure that perceives not the object itself, but the light reflected from its surface. The radiation falls on the retina, from which information on the optic nerve is sent to the brain, where the final picture is formed. But before that, light passes through a cunning refraction mode.
Each point of the object reflects rays of light, which are first refracted in the cornea and enter the lens through a watery substance. Then, through the lens, the rays are sent to the vitreous body, are refracted again, and after that they appear on the retina.
The order of refraction of light rays and the intricate structure of the eye determine a large number of variations of this ailment.
Acquired and congenital astigmatism
Agree, the types of astigmatism are not so simple to study. The congenital form of this ailment is the most common, which is determined by pathological processes at the time of laying the organs of vision of the fetus in early pregnancy. Congenital astigmatism is usually inherited from parents. That is why it begins to develop at an early age.
If mom or dad suffers from this ailment, the baby should be checked for the disease as early as possible, because it can progress.
Those children who have impaired focusing often squint, bend their heads to one side, put their eyes together, and so on. If treatment is not scheduled in time, such correction methods can lead to the formation of persistent strabismus. It will persist even when you eliminate the root cause.
Everyone should know the classification of astigmatism. Congenital astigmatism is pathological and physiological. In the second case, the refractive differential in the main meridians is minimal. The imperceptible astigmatism of 0.5 diopters is associated with the progressive growth of the eyeball in babies, which causes negligible deformation. And even astigmatism of 0.75-1 diopters does not affect the visual function of the eye.
If the abnormal refraction exceeds one diopter, the condition is pathological in nature, accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity and needs special treatment.
Congenital astigmatism harms a person much more than acquired with age. Indeed, from the first days of life, a child perceives a picture incorrectly, which leads to a halt in the development of the visual apparatus as a whole.
Acquired astigmatism is not associated with physiological processes in the body and congenital pathology, therefore, it can manifest itself at any age. The disease evolves under the influence of external causes that lead to defects in the lens or cornea. It may appear due to the presence of such factors:
- Acute keratoconus is an ailment of the cornea, as a result of which it becomes thin and takes on a conical shape.
- Injuries - injuries of the eye with sharp or cutting objects, subluxations of the lens, tears of its ligaments.
- Keratitis - inflammatory processes in the cornea that are the result of infection, physical exposure or penetration of chemical substances that entail a violation of the integrity of the cornea and its bending.
- Complicated childbirth - imposing forceps on the head of the fetus, squeezing, causing deformation of the eyes and orbits.
- Pathology of the dentition - such ailments of the upper jaw and teeth, leading to deformation of the orbits, such as the protrusion of the upper jaw forward, an open bite, and so on.
- Surgical eye treatment can trigger the development of induced astigmatism. So, if the doctor too tightly sutured the sutures on the corneal wound, its shape can change significantly. The early removal of sutures is also identical, when, against the background of increased pressure, the intraocular edges of the incision diverge.
Lens and cornea
Types of astigmatism continue to be studied further. Corneal astigmatism (corneal) appears due to tuberosity on the surface of the cornea, its uneven curvature. Moreover, the bend of the aspherical cornea in the vertical direction, as a rule, is stronger, and as a result, the rays of light are refracted more than in the horizontal. This species can either be acquired (after suffering ailments and injuries), or be inherited (be congenital).
Lens astigmatism is much less common. The cause of this ailment is mainly a hereditary factor. It is characterized by the asymmetry of the lens or its placement relative to the anteroposterior center of the eye. Sources of acquired astigmatism are:
- senile cataract, in which the layers of the lens swell;
- trauma (displacement of the lens, eye contusion, which is accompanied by clouding);
- diabetes mellitus (an increase in blood sugar provokes organic changes in the lens).
Reverse and direct
We will analyze the following types of astigmatism of the eyes. The types of this ailment are determined by the power of light refraction (refraction) in the base meridians. If a more significant refractive reserve has a vertical meridian, this is direct astigmatism. With this type, vertical lines are captured more clearly. With age, direct astigmatism transforms into the opposite.
Inverse astigmatism refers to a violation in which the horizontal meridian has the ultimate refractive power. From here came a different name - horizontal astigmatism. This disease rarely develops. Since the external world is vertical, astigmatism of the opposite type causes discomfort and inconvenience.
There is another variation - astigmatism with oblique axes, when the meridians with the maximum and least refractive power pass not along the vertical or horizontal axis, but along the oblique, away from them.
Wrong and right
Any type of ophthalmologist can tell you about the types, types and correction of astigmatism. But it is better if you study these nuances yourself. Correct astigmatism is characterized by an elliptical outline of the eyeball. It occurs more often than other variations, as it is a congenital threshold of the cornea. The light passing through the oblong axis of the oval will be less refracted, and the light passing through the short meridian will be as strong as possible.
Over time, in 50% of cases, the ailment either increases or decreases. Moreover, the possibility of one or another development is almost identical. In other cases, the ailment does not change its form. Such modifications are associated with the natural development of the organs of vision, their activities during the growth of the baby.
In meridians, directed in different directions, with this type of ailment, the refraction of rays occurs either strongly or weakly. But the refractive power in each of them is identical along the entire length.
Simultaneously with the different curvature of the major meridians, irregular astigmatism is determined by the fact that the same meridian is refracted differently in different areas.
This type of ailment affects those who have undergone surgery, injuries or eye diseases. In these people, visual acuity decreases, severe headaches appear during visual stress, the objects in question are transformed, bifurcated.
Unfortunately, irregular astigmatism, as it is also called, is not amenable to therapy. In this case, the optical correction does not bring the desired result . This is the same precedent when an illness is easier to prevent than to cure.
Hypermetropic and myopic
Carefully study the types and treatment of astigmatism of the eyes, and then you can always prevent this ailment. What is myopic simple astigmatism (nearsighted)? This is a condition when some rays after passing through the refractive structure of the eye gather on the retina, and others in front of the retina (myopic focus). The greater the distance between the tricks, the greater the degree of violation, the more vague the picture will be.
It is known that astigmatism of 1 diopter with a vertical enhanced meridian does not cause any complaints of decreased vision. That is why it refers to the physical type.
Myopic complex astigmatism is a condition when the refracted light is collected in front of the retina at many points at a different distance from it, that is, myopic disorders are detected immediately in two meridians. This deterioration may appear due to the following reasons:
- Acquired (education on the corneal scar due to ailments, trauma, surgery, less often - the pathological form of the lens).
- Congenital (hereditary corneal distortion).
Hypermetropic astigmatism by the mechanism of appearance is identical to myopic. The difference here is that farsightedness (hyperopia) is a form of refraction when the focus is behind the retina and not in front. The violation is complex and simple, acquired and congenital.
Mixed astigmatism
Now consider mixed astigmatism. What is he like? Mixed astigmatism is a condition when two types of this distortion of vision are combined: the rays of one meridian form a focus behind the retina (hyperopic type), and the other in front of the retina (myopic type). With this pathology, any picture is perceived to be deformed, it is almost impossible to visually identify the size of the object, the distance from it.
The most severe form of visual impairment is mixed bilateral astigmatism, which is usually accompanied by late development of the visual organs and strabismus.
The higher the degree of the disease, the more difficult it is to heal. Therefore, it is important to detect the pathology of vision on time, since the sooner the correction and treatment measures are prescribed, the more likely they are to succeed.
How to treat?
Astigmatism can be cured. There are temporary methods for correcting vision, allowing the patient to lead a typical lifestyle until complete cure:
- Contact lenses. To correct astigmatism, special toric contact lenses are used, which, when worn, do not cause inconvenience, unlike glasses.
- Spectacle correction. With astigmatism, the patient must wear specific glasses with lenses in the form of a cylinder. Before their selection, a person undergoes a special diagnosis. Experts say that wearing glasses in people with a high degree of astigmatism can cause dizziness, pain in the eyes, and visual discomfort.
However, wearing contact lenses or glasses can only correct vision temporarily. Forever you can get rid of the disease with the help of laser vision correction (Lasik), which has recently been used more often for healing astigmatism.
Prevention
What is astigmatism prevention? It consists of the following nuances:
- Compliance with the regime of visual, physical exertion. Eyestrain must be alternated with outdoor activities.
- Compliance with the correct lighting regime. The workplace should be well lit.
- Applications of vitamins with lutein.
- Performing gymnastics for the eyes. Every 20 minutes during eye strain, gymnastics for the organs of vision should be performed.
- The treatment of eye ailments that affect the development of astigmatism.
- Relieve eye strain and improve blood circulation in the eyeball and surrounding tissues. This can be done using physiotherapy massage - color therapy, pneumatic massage, and so on. All these features are implemented in the Sidorenko Glasses apparatus.
It is important to remember that prevention of astigmatism is very important. Strictly speaking, astigmatism is not an ailment, but a “mistake” of the eye. However, this does not mean that it is safe. Comprehensive diagnosis and treatment can be done in many ophthalmological clinics. When choosing a medical institution, consider not only the cost of treatment, but also the reputation and level of the clinic's specialists.
Astigmatism in babies
Various types of astigmatism in children appear much more often than is commonly believed. Thus, a weak degree of astigmatism is detected in 40% of schoolchildren, and a strong degree in 6%. This pathology is not only inconvenient for the baby, it is also fraught with the development of myopia and a decrease in school performance. Therefore, it is very important to detect this problem in time and begin treatment.
A child suffering from any type of astigmatism (simple, complex, mixed, and so on), as a rule, does not complain about vision because he always saw it and does not know that this is wrong. This fact complicates the actual diagnosis. Astigmatism in babies is usually detected at an appointment with an ophthalmologist. Therefore, show your child to the doctor from 2 months of age and, if this ailment is discovered, visit this specialist every six months. And be healthy!