A network topology is a physical and logical way of combining a group of computers into a single network. The most common network topology is “bus”, “star”, “ring”. Each of them has its advantages and disadvantages and is used depending on the situation. One way or another, they are used in the construction of modern local area networks. Let's look at their key features, find out the strengths and weaknesses of each of them.
"Tire"
This type of organization of a local network provides for the use of a single cable, with which all used workstations are interconnected. Each of them transmits a signal to all computers connected to the line, but only the one whose address is indicated in the packet receives data. The rest simply ignore the information received.
In the "common bus" topology, terminators are necessarily used that are located at the ends of the main cable and jam the signals that reach them in order to avoid their reflection. Without these devices, collisions would inevitably arise in such a network, due to which normal operation would be impossible. Of course, conflicts still arise, but thanks to the terminators their number is minimal. If this still happened, then the station simply sends the packet again after a random period of time determined by the algorithm.
Advantages of the bus topology
This networking has several advantages over other methods. Among them are the low cost of the structure and the simplicity of its creation. Organizing such a local network is quite simple, you just need to stretch the "common bus" and connect computers to it through special connectors. This topology assumes a low consumption of the network cable, since only its small segments are used, connecting the "bus" with the workstation.
It makes sense to use the "common bus" in small offices or, conversely, on highways connecting several networks together. One of the advantages of this topology is that if one of the workstations breaks down, the network is not broken. The rest of its participants can continue their work as if nothing had happened. When you connect a new computer, there is no need to stop the network, which is also an indisputable advantage of the "common bus".
The disadvantages of the "common bus"
The disadvantages of this topology are due to the same reasons as its advantages. For example, connecting all computers with a single cable significantly reduces network reliability. An open "bus" anywhere will put an end to the entire system. Moreover, in networks with such a topology it is very difficult to diagnose a malfunction. Another disadvantage of the "tire" is its low performance. All data of such a network passes through one cable. This makes it impossible to work at high speeds.
Another stone in the "common bus" garden is the dependence of the speed of work on the number of computers on the network. Since workstations have to communicate on the same communication channel, the more computers are connected to such a network, the lower will be the speed of its work. That is, the "common bus" is well suited for a small number of nodes that do not require a serious level of security. After all, this type of topology also has problems with security. The fact is that every client in such a network has access to the information of other computers.
Ring topology
This type of organization of the local network is arranged so that each computer in it is connected to the next one until the circuit is closed, forming a ring. A signal in such a network passes in one direction, from one computer to another, until it reaches the destination. A marker is used to identify the workstation that is currently transmitting information. Computers transmit it in turn until it reaches a node that wants to send data. Then he sends the information in batches, one by one, without waiting for confirmation of delivery. The workstation receiving the data, in turn, sends a report on the receipt of the packet. After receiving a delivery confirmation, the computer sends the marker further in a circle so that someone else can use it. The ring topology is organized in such a simple way. This design has both advantages and disadvantages.
Pros of the "ring"
The advantage of this topology is its simplicity. This network is very simple to implement, and it does not require significant cable costs. A power cord is needed only for laying from one computer to another, there are no additional costs. Also in the "ring" you can achieve high data transfer speeds, because you do not need to wait for a delivery report to send a packet.
Another plus of networks with a similar organization is that they can be very long. There is no need to amplify the signal with the help of additional equipment, since each workstation updates and restores the data itself. But behind the simplicity and cheapness of this topology, there are disadvantages that made its use very limited.
Ring Topology: Flaws
When organizing this type of network, you need to remember that its reliability is poor. The reason for this is that its performance depends on each computer that is included in it. That is, if one of the workstations breaks down, then the entire network ceases to function. The “ring” topology also assumes that to connect a new computer you need to completely stop the network, which is very inconvenient for both the administrator and users.
Another reason not to use this topology is low productivity with a large number of workstations. Since the data constantly goes in a circle, each new client on the network slows down its work. Moreover, one old computer can make a ring network incredibly slow, regardless of the speed of the other members of the ring. All this significantly limits the application of this topology in modern networks, but in some cases its use is justified.
"Star"
Probably the most common network topology is the star. The "ring" discussed above is used much less frequently, and the "common bus" too. On a star topology network, workstations are directly connected to the hub. This important network element can be either active, signal recovery, or passive, which simply provides a physical cable connection. The server is also connected to the hub, like other computers, which makes communication between them extremely simple.
Typically, the size of a network with a star topology is limited only by the number of ports on the hub, but theoretically there cannot be more than 1024, although it is difficult to imagine a hub with so many ports. Through the hub passes all the traffic in the star network, so the reliability and performance of the entire system depends entirely on this device.
Advantages of the Star Topology
If you need to build a fast and reliable network, then a star topology is a great choice. A “ring” or “common bus” can also be used in some parts of the network. The advantages of the "star" - in its reliability and simplicity. Each workstation has a separate network cable, which is very convenient and practical. Thanks to this, it is very easy to find and fix problems in such a network, and its maintenance takes much less time and nerves. When connecting new computers to a star network, it maintains its functionality unlike other construction options. For example, the ring topology cannot boast of such flexibility.
Network speed with a star topology is limited only by the bandwidth of the cable and hub ports. Also in such a network there are no collisions of transmitted information. Each computer transmits its data through a separate cable. If you need a large network, you can combine several networks with the star topology. Despite all its advantages, this type of networking has its drawbacks.
The disadvantages of the "star"
If a hub breaks in a network with a star topology, it will stop working. This dependence on one element of the system significantly reduces the reliability of the network. Another problem is the high cost of installation. Each workstation has its own cable, which must be routed and secured. So the cost of communications and boxes for it can be added to the price of the cable, and it turns out that the “star” will cost much more than, for example, the “ring” topology.
Another drawback of the star topology is the maximum cable length to the workstation. It should not exceed 100 m, otherwise the signal will weaken and distort. Therefore, the coverage radius of such a network does not exceed 200x200 meters. For further expansion, you will need to add additional hubs to the network.
Topology combination
So, you familiarized yourself with all the options, but didn’t decide which topology you need - a bus, a star, a ring? This is not surprising, since modern networks often require a combination of topologies. For example, several servers can be combined into a "common bus", but a network with a star topology will branch out from each of them. Depending on the task being solved, the device of the local network can be the most diverse. You can find such options in which each computer is connected to each, although this is very rare. Another interesting option is two “rings” having one common computer.
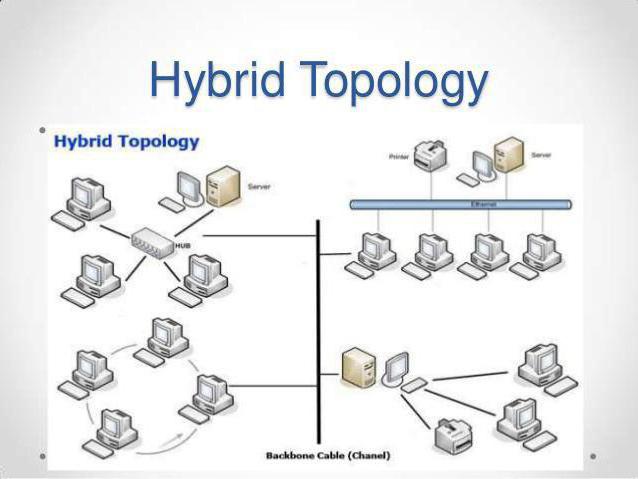
In enterprises, you can often find different topologies within the same building. The whole network can be built in the form of a "star", but in separate offices the topology is "ring" or "common bus". In large networks, combining different types of network organization is often the only solution to the problem. After all, in the end, it doesn’t matter that you have a “star,” “ring,” “tire.” Network topology is needed only for solving practical problems. Does your network work stably and solve all the tasks assigned to it? Then it doesn’t matter which topology was used to create it.