The program Microsoft Word has a huge number of tools to change the text beyond recognition. Any of them can be found in the standard menus (version 2003 and earlier) or on the toolbar (versions 2007 and later). But if you need a quick conversion of the document, then using the graphical interface of the program makes you take unnecessary actions and waste time. Therefore, the developers came up with a combination of hot keys or hotkeys to access the main functions using the keyboard.
Function keys
They are in the front row of the keyboard. They have inscriptions in the range F1-F12. The functions they perform are shown in the table below.
Key | Action description |
F1 | Calls up reference information to the program. |
F2 | Allows you to move the selected picture or text once |
F4 | Re-executes the last command |
F6 | Enables access to all elements of the graphical interface. A single click allows you to use the elements of the status bar. Double - a toolbar (Word 2010 and newer). Triple - disable access |
F7 | Checks spelling. If there are errors, opens a dialog box to correct them. |
F8 | Selects text. Double-clicking selects a word around the cursor. Triple - the entire string. 4 clicks - all text |
F9 | Updates selected fields inserted using Insert> Express Blocks> Field |
F10 | Enables keyboard usage |
F11 | Goes to the next field (see key F9) |
F12 | One of the Save As ... Hotkeys in Word |
Window control
The first part of Microsoft Word, which can be controlled by hot keys, is the window and the interface. The button combinations that allow you to do this are summarized in the table below.
Hotkey | Description of the action |
Ctrl + F6 Ctrl + Shift + F6 | Switch open editor windows among themselves. The second combination goes to the previously displayed window. |
Alt + F5 | Reduces the size of all open Word windows to the default. Pressing again does not expand them. |
Ctrl + F10 | Reduces or enlarges the active window in full screen |
Ctrl + W Alt + F4 | Closes the editor window, offering to save the changes. The second combination is systemic |
Ctrl + F1 | Collapses and expands the toolbar in Word 2010, 2013, 2007, 2016 |
Win + M | Minimizes the active window. System |
Ctrl + Alt + Escape | Makes the window inactive. System |
Win + d | Minimizes all windows in Windows. System |
Alt + Tab | Toggles windows all windows open in the system, among themselves. System |
Printscreen | Takes a screenshot and puts it on the clipboard. To extract it, you can paste it into any raster graphics editor. System |
Alt + PrintScreen | Puts the image of the active window on the clipboard. System |
Ctrl + Alt + S | Divides the document sheet in half, allowing you to view each part independently of the other |
Tab Shift + tab | Helps you navigate the toolbar by slipping through the drop-down lists and moving the selection to the button in the lower right corner of the block |
Ctrl + mouse wheel rotation | Zooms in or out on a document |
Note: "system" means that the hotkey from Word can also be used on Windows.
File operations
The second function of hotkeys in the Microsoft Word editor is to operate with commands located in the File menu (all versions except 2007) and Office (Word 2007). These include:
Primary key | Additional key | Action description |
Ctrl | N | Creates a new document with the "Normal" style. |
O or F12 | Open a dialog box to select the file to open. |
S | Saves changes to the document. If this is your first time saving, this hotkey will bring up the Save As ... dialog box. |
P or Shift + F12 | Open the Print window to configure and launch it. |
F4 | Allows you to close the document, but does not close the editor |
F2 | Activates the Preview function |
Shortcuts in Word "Create Document", "Open", "Print" are universal for software packages of other developers.
Work sheet navigation
Word shortcuts are also assigned to this task. They are used in conjunction with special keys located in the navigation block in the right half of the keyboard. The table shows their capabilities.
Primary key | Additional key | Description |
Home | - | Puts the cursor at the beginning of a line |
End | - | Move cursor to end of line |
Page Up (PgUp) | - | Moves the cursor 1 sheet up, keeping the position |
Page Down (PgDn) | - | Moves the cursor down 1 sheet, retaining its original position |
Left Arrows \ Right Arrows | - | Move the pointer along the line in increments of 1 character |
Up / down arrows | - | Move the cursor up and down the lines. |
Ctrl | Home | Positions the cursor before the first character in the document |
End | Sets the cursor after the last paragraph in the document. |
right arrow \ left arrow | Allows you to move in a line left and right in increments of one “word” or punctuation mark along with a space after it. The word is understood as a continuous set of letters and numbers. For example, "Yl65465vaprflyopr" |
up / down arrows | Moves through the document, placing the cursor at the beginning of each paragraph |
Page up or Page down | Set the cursor to the beginning of the previous (1 command) or next (2 command) sheet |
G or F5 | Calls up the Find and Replace window with the Go tab active |
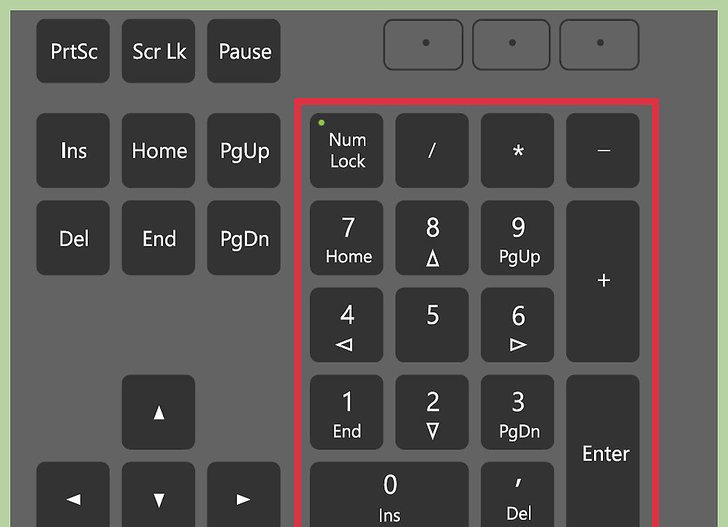
All these special keys are duplicated in the numeric keypad. To use, you need to disable the entry of numbers by pressing the NumLock button 1 or 2 times. A confirmation of the shutdown is the first non-burning light above the digital unit.
Text selection
A third application for hotkeys is the operation of selecting text. The most famous command for her in Word is "Select All" (hot key Ctrl + A). She selects all the text in the document. But more often, the selection of small fragments is required. Therefore, there are other combinations. Their list is given in the table below.
Primary key | Additional key | Description |
| Shift | Home | Selects all text from the beginning of the line to the pointer |
End | The same, but from the cursor to the end of the line |
Page Up or Page Down | Selects text from the top of the sheet to the bottom. The volume is adjusted by scaling the document using the slider in the lower right corner of the editor |
left / right arrows | Selects text in 1-character increments. |
up / down arrows | Selects text in 1-line increments. The end of the selection is usually located under the place of its beginning. |
Ctrl + Shift | Home | Selects all text from the beginning of the document to the cursor |
End | Selects text from cursor to last unprintable character (¶) |
left / right arrows | Highlight text in increments per word. |
up / down arrows | Selects whole paragraphs before or after the cursor |
Text editing
The fourth group of keyboard shortcuts in Word is for editing text. There are not many combinations, and they can also be used to work with uneditable fragments. Here is a list of them:
Primary key | Additional key | Description |
Ctrl | FROM | Copy selected text to clipboard |
V | Paste text behind clipboard cursor |
X | Cuts the selected text (deletes it, but stores the fragment on the clipboard) |
| Z | Cancels 1 any committed action |
Y | Returns the action canceled by the previous hotkey |
H or F | Opens the Find and Replace window with the active Replace and Find tabs respectively |
Delete | not | Deletes the text behind the cursor. |
Backspace | Deletes text before cursor |
Insert | Switches the insert and replace text mode. When this button is turned on, all text behind the cursor will be replaced by newly entered text. |
Formatting
The fifth option for using keyboard shortcuts in Word is formatting. A list of documented commands is shown in the table below.
Primary key | Additional key | Description |
Ctrl | D | Calling the Font Dialog Box |
B | Makes the text bold |
I | Adds an italic effect to the selected and subsequent text |
U | Emphasizes text |
= | Allows you to enter subscript (subscript) indices |
L | Puts the cursor or line on the left side of the sheet |
E | The same, but in the center of the sheet |
R | The same, but to the right of the sheet |
J | Stretches the contents of the string to the width of the sheet |
Enter | Insert page break (with transition to a new one) |
| Ctrl + Shift | + | Allows you to enter superscript (superscript) indices |
C | Copy Ready Formatting |
V | Formatting insert |
| Enter | - | Insert line break (transition to a new one) |
Unfortunately, other formatting tools are not connected to the keyboard shortcuts in Word. To continue using the keyboard for formatting, you can add your own combinations or use the alternative controls, which are included with the Alt or F10 keys.
Characters
Their library in the editor is quite large. In it you can find many of the symbols used in documents. For example, the sign of the diameter. In Word, the hotkey for it and other notations looks like Alt + X, where X is the number of the desired character, which can be found at the bottom of the list window.
The table below shows 10 characters with their codes for insertion.
No. | The code | Insert character | No. | The code | Insert character |
1. | 0216 | Ø | 6. | 0167 | § |
2. | 0215 | × | 7. | 0128 | € |
3. | 0169 | © | 8. | 0176 | ° |
4. | 0174 | ® | 9. | 0181 | µ |
5. | 0153 | ™ | 10. | 0223 | ß |
Assigning individual hotkeys
As an example of using this feature, we will add the Word "Insert lines below" hotkey in Word, since it is not assigned by default. To do this, you need:
- Click the "Office" or "File" button in versions 2007 and 2010, respectively.
- Go to the "Word Options" sub-item "Settings" and click on the button with the same name at the bottom of the window.
- In the new settings window, in the first list, select "Work with Tables | Layout".
- In the second list, find the TableIncertRowBelow item.
- Position the cursor in the line below it and press the desired combination. For example, Ctrl + Num4.
- Click "Assign" and "Close".
In this way, you can attach any tool present in Microsoft Word to keyboard shortcuts.
There are many hot keys in this editor , and in the article only those necessary for daily use are mentioned. More information about the combinations can be found in the help for the program called by the F1 key, or on the developer's website.