Currently, there are three types of cameras: compact, SLR and mirrorless. The first of them are the simplest, and mirror ones, on the contrary, are considered the most advanced. If you decide to seriously engage in photography, then you should stop your choice on the options of "mirrorless" or "DSLRs".
In this article, we’ll talk about the principles of operation and the design of a SLR camera. Knowing these parameters thoroughly makes no sense, but you need to have a general idea of the methods of its operation. This will allow you to look at the device from the other side, in order to thoroughly understand how to properly make high-quality and original photographs.
A bit of history
The invention of the camera was carried out in 1861. The aim was to obtain and store still images. Initially, in devices, these images were recorded on special plates, and later on on film for the camera. Around the 70s of the 20th century, digital technology appeared. Classic film cameras are a thing of the past. Today they are rarely seen by anyone. They are almost completely superseded by digital technology, which allows you to get very high-quality images. The most widespread are SLR cameras, which are recommended for professional photographs.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of a SLR camera, as well as the disadvantages, are reflected in the following table.
Benefits | disadvantages |
Shooting dynamic processes, i.e. in motion | Cameras are technically difficult |
Long battery life | The case is quite large |
The impressive appearance is more ergonomic | Component mobility reduces reliability |
The optics park is huge | Slow shutter speed is not possible |
Phase camera sensors provide high-quality and fast operation | Manual mode is difficult to operate. |
Principle of operation
A very simplified scheme of the professional SLR camera can be represented as follows:
- The shutter opens after we press the button. In this process, the light that is reflected from the object penetrates through the lens into the apparatus;
- in this way a picture is formed on a photosensitive element (matrix), photographing takes place;
- the shutter closes, then you can take new pictures.
Such a process takes place in a split second. However, different models have different process characteristics.
The image is available for viewing on the screen immediately, which is very convenient for the photographer. Then it is saved on a computer for further storage and viewing, or printing on photo paper.
Main elements
The SLR camera belongs to one of the more advanced designs. It has a number of features. The main elements of the device SLR camera can be called:
- lens;
- matrix;
- diaphragm;
- gate;
- pentaprism;
- viewfinder;
- rotary and auxiliary mirrors;
- lightproof housing.
An illustrative diagram is presented in the figure below.
Lens
Consider what the camera lens consists of.
Under the lens understand a special system of optics, which consists of lenses located inside the frame. They can be made both of glass (in the case of expensive models), and of plastic (with cheap models). A stream of light passes through the lenses. He is refracted. Thus, an image is formed on the matrix of the apparatus itself. In the case when we are dealing with an expensive and good lens, you can get high-quality photos with increased sharpness and clarity in the absence of various distortions.
The main characteristics of the lens:
- aperture shows how the brightness of the photographed object and the brightness of the image are related to each other;
- the focal length is reflected in millimeters from the optical center to the very focus where the matrix is located. The viewing angle depends on this parameter;
- zoom - the ability to zoom in on a distant object;
- a kind of bayonet mount.
Sometimes SLR cameras use a wide-angle lens. Such wide-angle cameras can be used to obtain images of nature, landscapes. Images are voluminous and colorful. Such lenses have a focal length of 24 to 40 mm.
Aperture Functions
The aperture of the camera lens is a mechanism that is designed to control the flow of light projected onto the matrix. Its location: between the lenses in the device itself. Structurally, it consists of a set of overlapping petals (from 2 to 20 pieces), which can have different shapes. The magnitude of their mutual shift determines the size of the hole formed. In this way, it is possible to change the amount of light that enters.
Depth of field of the image space depends on the size of the aperture: the smaller the size of the circle, the greater the depth of field.
Currently, SLR cameras are equipped with jumping type iris diaphragms. They are ways to close to the set value only at the very moment of shooting.
Mirrors
The light that has passed through the aperture opens onto the mirror. Next, the flow is divided into two parts. One of them is fed to phase sensors (reflected from the auxiliary mirror), which are created to determine whether the image is in focus. Next, the focusing system instructs the lens to move. In this case, they become such that the object falls into focus. This setting is called phase detection autofocus. In order to make out a mirror in the body of the device, you just need to remove the optics. This is one of the main advantages of SLR cameras over mirrorless digital ones.
The second stream falls onto the focusing screen. With this, the photographer is able to assess the depth of field of the future picture, as well as the focusing accuracy. The convex lens, which is located above the focusing screen, increases the size of the resulting image. The mirror disappears after pressing the shutter button, allowing light to flow into the matrix without obstacles.
Pentaprism and viewfinder
The stream of light that passes through the focusing screen enters the pentaprism. The latter has two mirrors in its composition. First, the image from the swivel mirror is upside down. Pentaprism mirrors overturn it, passing the final image in the usual form to the viewfinder.
The viewfinder is a device that allows the photographer to evaluate frames in advance. Its main features include:
- luminosity (formed depending on the quality and light transmission parameters of the glass from which it is made);
- size (area);
- coverage (this figure is 96-100% today).
SLR cameras can be equipped with the following types of viewfinders:
Optical options are more common. Similar devices are located near the lens system of the lens. Their advantage is the lack of energy consumption, and the disadvantage is some distortion of the image that falls into the frame.
Electronic devices are a small liquid crystal screen (LCD). The picture is transmitted from the matrix of the camera itself to it. This view can be used even in strong sunlight, as it is located inside the case. However, it consumes electrical energy during operation.
Mirror viewfinders are considered the best, as they are able to provide the highest contrast, the quality of the outlines of objects. Similar devices are transferred to digital photographic devices from analog films. The image seen by the photographer is created by a rotary mirror.
Matrix: the basics of work
The matrix of a professional SLR camera is an analog or digital-to-analog system with photosensors. The latter are photosensitive elements that convert light energy into an electric charge (proportional to the brightness of the light). As a result, the matrix converts the optical image into an analog signal (or digital). Then they pass through the converter - microprocessor or memory card.
The main features of the matrix are:
- resolution;
- the size;
- light sensitivity (ISO);
- ratio between signal and noise.
Two types of matrices have gained popularity in mirror photographic equipment:
- full-frame (the same size as a 35-mm film for the camera);
- truncated (diagonal reduced).
Matrices differ in the following formats:
- Full Frame - full-frame (35 × 24 mm);
- APS-H - matrices of professional cameras (29 × 19-24 × 16 mm);
- APS-C - used in models of consumer products (23 × 15-18 × 12 mm).
Basics of a DSLR device
In general, the device itself consists of two parts: the camera (sometimes called the carcass or the body of the camera) and the lens. The carcass together with the lens looks like this.
Next, we present a schematic representation of the device. It reflects the structure "in the context." In the figure below, the main nodes of the camera are indicated below the numbers.
Description of the main designations in the photo:
- An object is a set of lenses that can transmit light, thereby forming an image.
- Inside the object itself is a diaphragm, which is a set of petals superimposed on each other so that a round hole is formed.
- The area of this circle will depend on how far the petals are shifted from the starting position. It turns out that the diaphragm serves to control the amount of light that is transmitted. She has the ability to open and close. If it is completely closed, then the area of the hole is minimal and light penetration is also at a minimum. If it is open, then the picture is reversed.
- Further, the light that passed through the diaphragm hits the translucent mirror at number 3. If you remove the lens, the very first thing we see inside will be just a mirror. It is a division of the light stream into two parts.
- The first half of the light stream then falls into the focusing system at number 4. This system is nothing more than a few phase sensors that determine whether the image is in focus. These elements create the task of moving the lenses so that in the end the desired object is in focus.
- The next part of the light stream moves to the focusing screen 5. It allows you to evaluate the accuracy of the focus and determine what will be the depth of field in the final version of the picture.
- Next, after the focusing screen, the light enters the pentaprism in the camera. The image that goes from lens 1 to mirror 3 is inverted. The pentaprism in the camera consists of two special mirrors that turn the image so that it takes its normal position in the viewfinder.
- Further, from the pentaprism, the light moves into the viewfinder, where the final image (not inverted) is visible. The main characteristics of the viewfinder: coverage, size, lightness. Currently, in advanced cameras, its coverage is about 96-100%. If it is less than 100%, then in such a situation the photo is obtained a little more than the photographer himself can see. However, such a deviation is negligible. If the resolution of the matrix is high, then all the excess can be removed. The viewfinder size is determined by its area. His lordship is determined by his quality and light transmission of glasses. By increasing the viewfinder size and increasing the brightness of the glasses, it becomes easier for the photographer to focus and determine if the subject is in focus. It is a great pleasure for any photographer to work with such devices. However, their installation is possible, as a rule, only in high-end cameras, as well as in those that are above the average price level. After fully setting up the camera and all its parameters, the photographer presses the shutter button. At the moment, the mirror rises and the luminous flux falls on the most important element of the device - the matrix.
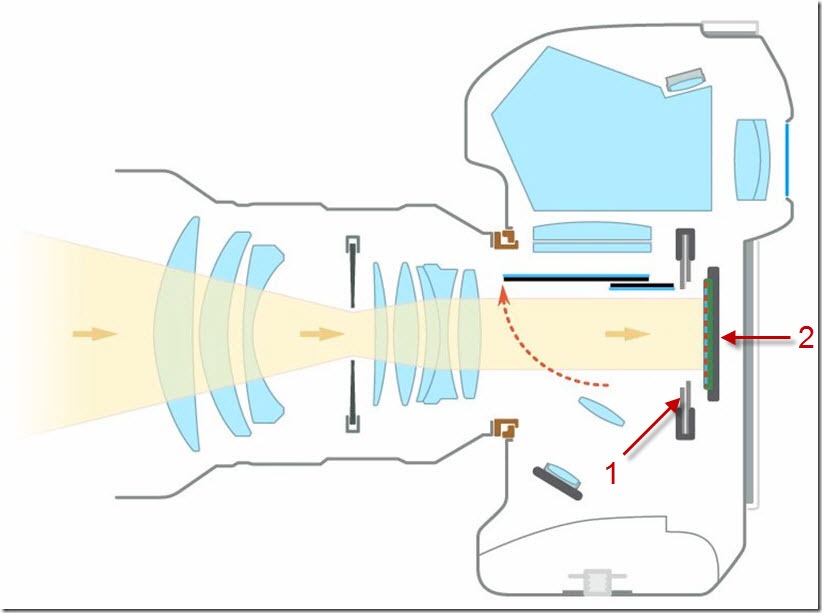
- In the figure, the mirror rises, opens the shutter 1. In mirrored apparatuses, the shutter is mechanical and determines the time of arrival to the matrix 2. This period of time is called the shutter speed (or exposure time of the matrix). The main characteristics of the shutter are as follows: lag and speed. Using the lag, you can determine how quickly the shutter curtains open after you press the shutter release. The smaller this lag, the higher the likelihood that a passing car will be captured in a high quality photo. As a rule, SLR cameras have a small shutter lag. It is measured in milliseconds. Shutter speed characterizes the minimum opening time, which means the minimum shutter speed. If you take a budget camera, then this value is 1/4000 s. If you take the expensive one, then the time will be 1/8000 s. When the mirror is raised, the light does not get anywhere, but moves directly to the matrix. For example, in a situation where we use a SLR camera, when photographing, we always look into the viewfinder, then after pressing the shutter release, the first thing we will see is a black spot. This time is determined by exposure. If you set the shutter speed to 5 seconds after you press the shutter release, a black spot will be observed at the same time. After the matrix of the SLR camera is exposed, the mirror will return to its original position, and the light will again enter the viewfinder. Thus, there are two main elements that regulate the flow of light entering the sensor. The first of these is aperture 2. It determines the amount of light. which is skipped. The second is the shutter, which controls the shutter speed, or the period of time during which the light is able to get on the matrix. It is these two mechanisms that underlie the functioning of the SLR camera. The effect of the photographing process depends on how they are combined. It is important for the photographer to understand their meaning.
- Matrix 2 can be represented as a microcircuit with photosensitive elements (photodiodes), which have the ability to respond to light. A filter is installed in front of the matrix in the camera, which is responsible for obtaining a color picture. Important characteristics of the matrix: size and signal-to-noise ratio. The higher these settings, the better for the quality of the photos.
After the matrix, the image goes to the ADC converter, from where it moves to the processor. Then it is processed, and there is a saving to the memory card.
Another essential part of an SLR camera is the diaphragm repeater. Focusing is performed with a completely open aperture. When a closed aperture is set in the camera settings, the photographer will not see any changes in the viewfinder. In order to see how the frame comes out, you can click the button. In this case, the aperture opens to the set value, the changes can be seen.
Basic Modes
The camera modes are usually grouped in the following four directions:
- automatic, in which the camera itself determines all the settings;
- portrait is used for shooting people and allows you to maximize the volume due to blurring the background;
- landscape mode gives maximum depth of field, due to which you can get excellent clarity;
- macro mode allows you to perform maximum approximation with focus on the object;
- sports mode is suitable for shooting sports competitions and moving objects;
- night portrait for shooting in poorly lit places using the flash;
- software automatic P makes it possible to set white balance, matrix sensitivity, jpeg settings. It is used when there is no time for manual settings;
- shutter priority mode S, in which the photographer sets the shutter speed and the camera sets the aperture. It is used when it is necessary to emphasize movement in the frame;
- Aperture A priority mode allows you to set the aperture value, and the camera selects shutter speed. It is used when shooting a portrait;
- Manual mode M: all parameters are set by the photographer on their own. Ideal for night photography and studio photography.

Canon SLR Camera
Canon SLR cameras are manufactured by the world market leader in video and photo equipment. The logo of this company is used on all amateur and professional devices. For almost a century of its history, the company has established professionalism in work, releasing one of the best models of cameras. Among the widest range, each user can find a camera in accordance with their preferences.
Canon in the market of modern electronics is one of the flagships in terms of the production of cameras. . . "". Electronic Optical System (EOS) - .
Conclusion
. , . .